41 draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge
Q. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be. Explain what kind of correcti... Solved • Jun 2, 2020
Find R from the diagram. R > H tan 1 = (72:0cm)tan48:75 = 82:1cm: Problem Giancoli 32-60 (II) A ray of light, after entering a light fiber, reflects at an angle of 14:5 with the long axis of the fiber, as in Fig. 32-56. Calculate the distance along the axis of the fiber that the light ray travels
Ques: (a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between infinity and the optical centre of a concave lens. (b) A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. Calculate (i) the distance of the object from the lens. (ii) the magnification for the image formed. (iii) the nature of the image ...

Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge
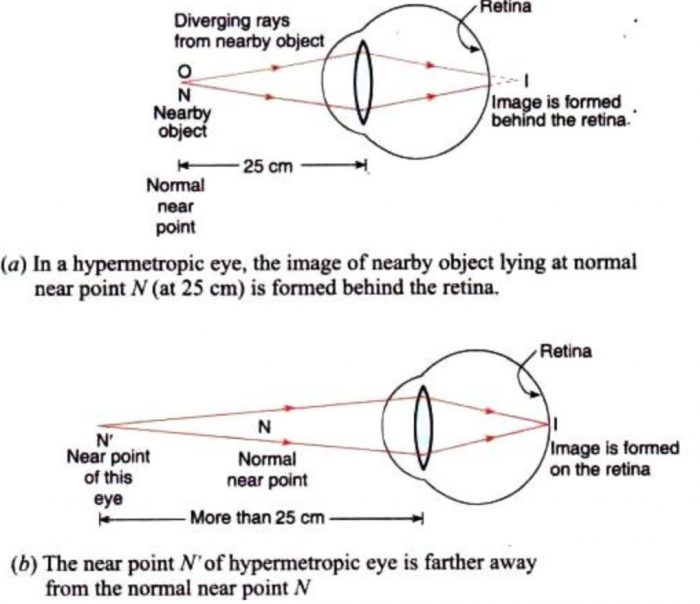
Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be. Nearsightedness and its correction. New Page 1 For all positions of the object the image is erect smaller in size than the object and formed within the focal length of the lens. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted. The physics ...
The ray diagram above shows how an image is formed in a convex mirror. Ray 1 approaches the mirror parallel to the principal axis. To draw the reflected ray, draw a dashed line from the focal point, F, to the point where ray 1 strikes the mirror. The reflected ray is in the same direction as the dashed line.
The convex lens is a lens that converges rays of light that convey parallel to its principal axis (i.e. converges the incident rays towards the principal axis) which is relatively thick across the middle and thin at the lower and upper edges. convex lens can converge a beam of parallel rays to a point on the other side of the lens.
Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge.
The method of drawing ray diagrams for a double concave lens is described below. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it travels towards the focal point on the opposite side of the lens; this ray will strike the lens before ...
Refraction and Lenses. Which must be included when drawing ray diagrams? Check all that apply. Cleo stated that light travels through air in straight paths, and when it moves from air to water, light changes direction, speeds up, and bends toward the normal. Which statement best describes Cleo's mistake?
Jimmy87. 660. 13. When you look up a ray diagram for a telescope you get the following: From reading my book it seems clear that the objective lens forms and image on the focal plane. This then serves as an image for the eyepiece. Since the focal length of the eyepiece at the focal length of the objective lens you get a virtual image at infinity.
draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be. Explain what kind of corrective lens you should use. Answer the same question for farsighted people; Question: draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be ...
In order to draw a ray diagram, take two rays of light from the object. Ray 1: A ray parallel to the principal axis . Ray 2: A ray passing through the pole . After reaching the lens, ray 1 will bend and pass through the focus. Ray 2 will pass without any deviation. The two rays will converge at a point and recreate an image.
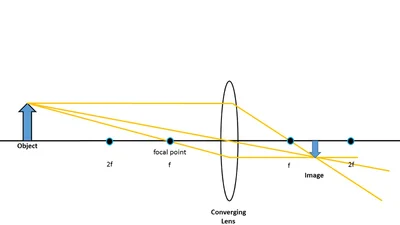
In Figure 1, the object distance is greater than the focal length of the lens. The ray diagram shows that the image is formed where the three principal rays converge on the far side of the lens. As is apparent from the diagram, the image is larger than the object. Since visible (real) light rays converge, the image is said to be real.
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
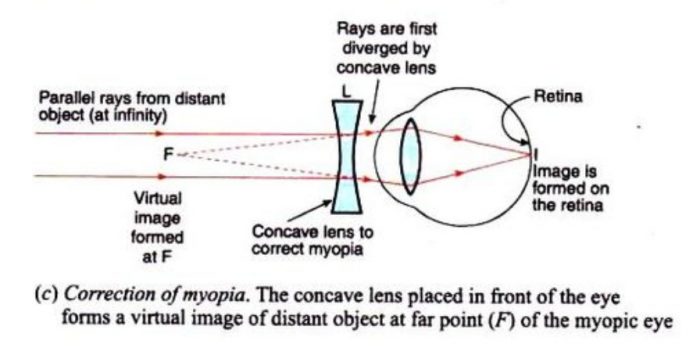
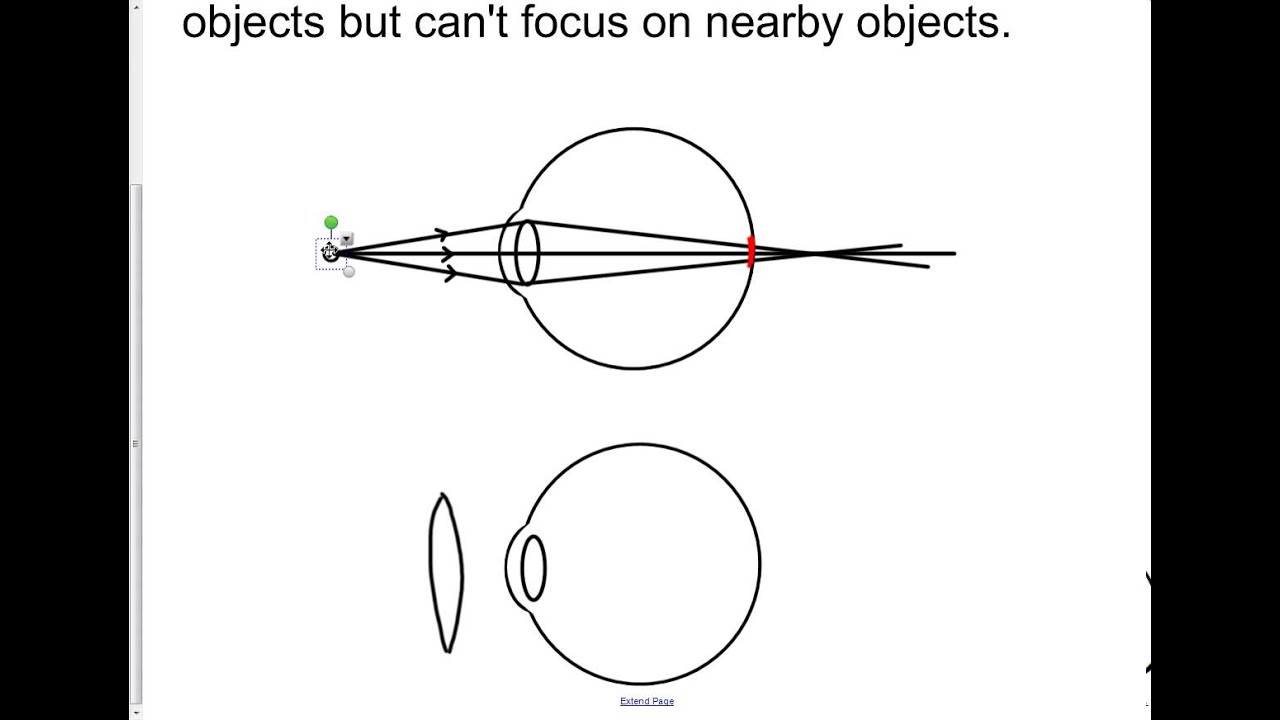
Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be. Once the ray hits the lens bend it so that it goes directly away from the focal point on the near side of the lens. Nearsightedness and its correction. Since the nature of the problem of nearsightedness is that the light is ...
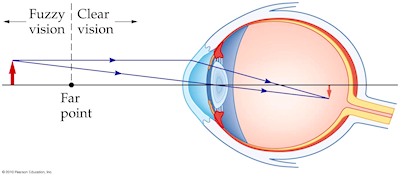
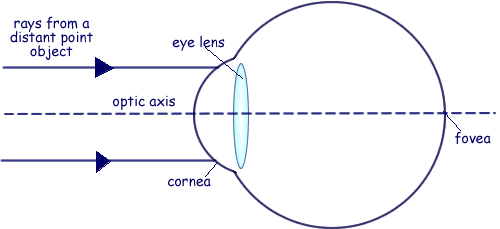
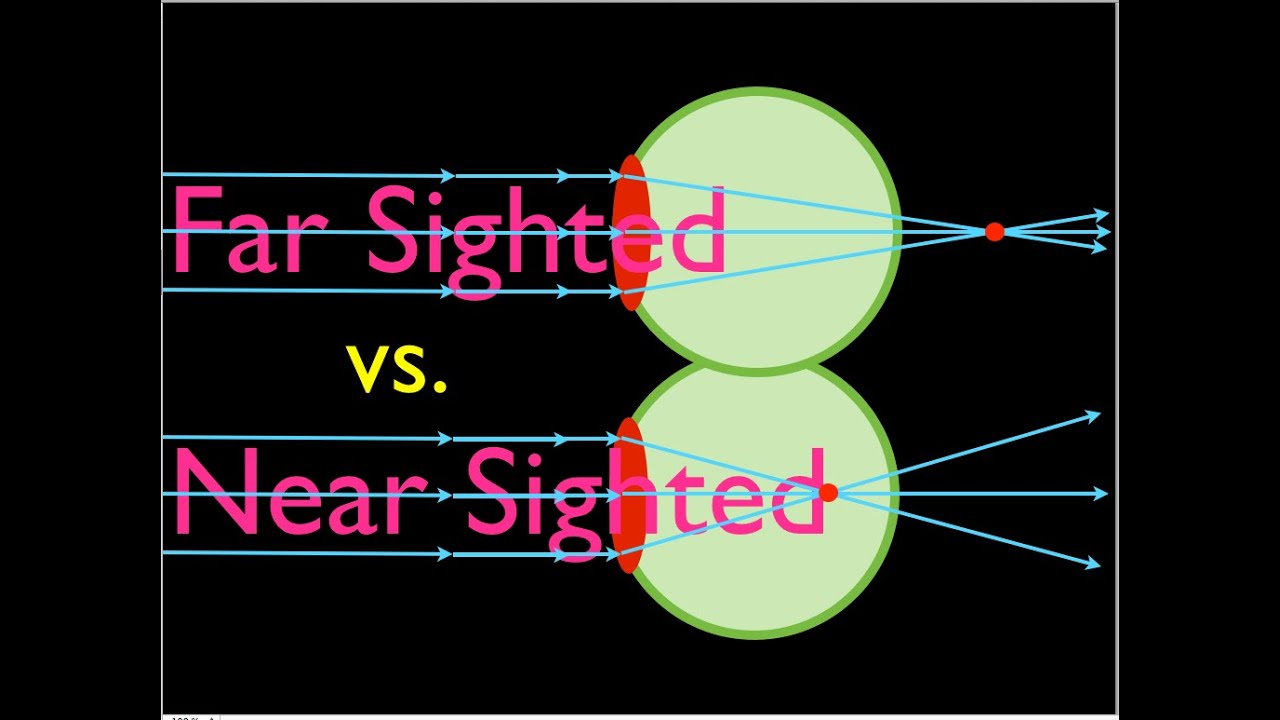
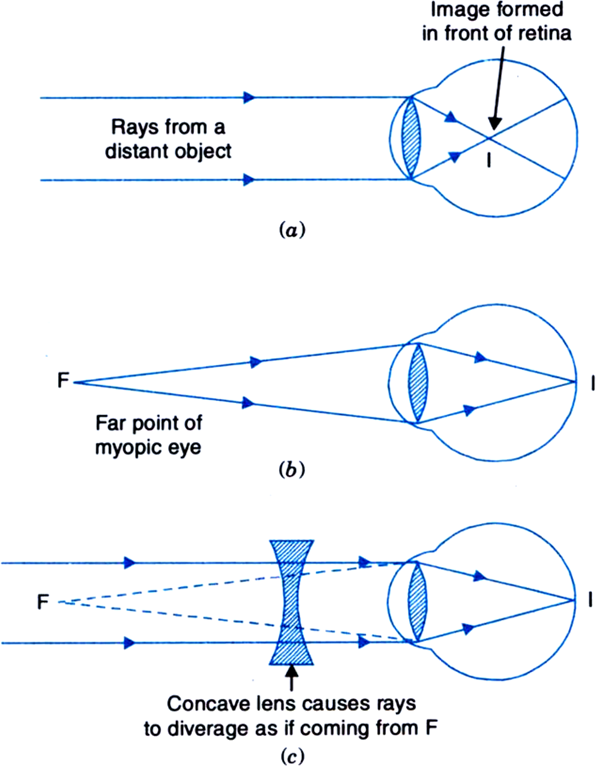
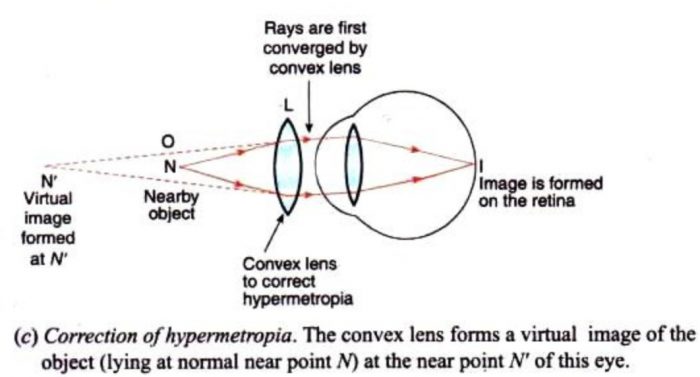
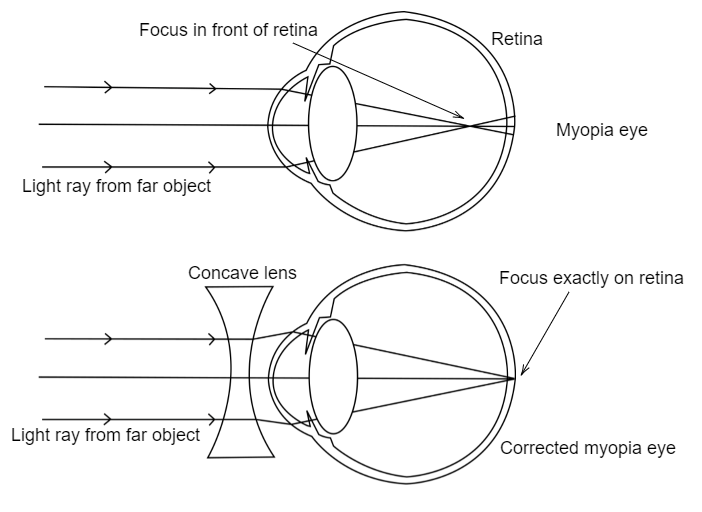
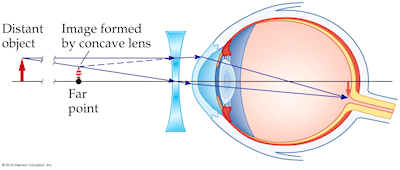
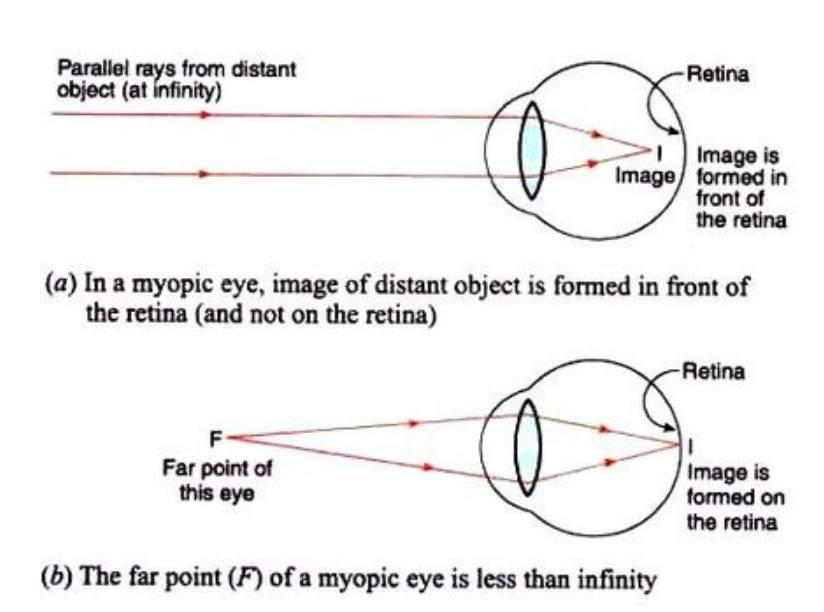
Nearsighted, short sighted or myopic people can see nearby objects clearly but have a problem in viewing distant objects as the image is formed before the retina causing it to be blurred. A concave lens can correct the vision by diverging the rays of light emanated from distant objects which are the converged by the eye lens to form a distinct ...
If the image is on the same side as your eye over here, then it should be a positive image distance. Now, for this diverging case, maybe the image ended up over here somewhere. I'm going to draw an image over here. Again, image distance from the lens, center of the lens, to where your image is, so I'm going to draw that line.
Question: Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people . Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be. Explain what kind of corrective lens you should use. Answer the same question for farsighted people. 2.99.
A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. Start studying chapter 30 and 31. Nearsightedness And Its Correction Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people. All of the above the wavy bright and dark lines ...
Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, the real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. The size of the image is the same as compared to that of the object.
Convex lenses. Convex lens examples. This is the currently selected item. Concave lenses. Object image and focal distance relationship (proof of formula) Object image height and distance relationship. Thin lens equation and problem solving. Multiple lens systems. Diopters, Aberration, and the Human Eye.
Draw The Ray Diagram For Nearsighted. View the step by step solution to. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label … Written By Romana Amelia Wulandari. 8:19 AM Add Comment Edit.
Ray diagrams are used to. figure out where an image will be located. In drawing a ray diagram rays can be drawn. From the tip of the object arrow Through the focal point in front of the lens ... Nearsighted people can clearly see objects that are close to them. true.
Description of how to draw ray diagram s for diverging lens es for grade 10 science. The students can use a convex lens diagram to understand the ray 's path after passing through a convex lens . The students may create a convex ray diagram by hand, but the process is lengthy, and at the same time, complicated.
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.









.png)







0 Response to "41 draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge"
Post a Comment