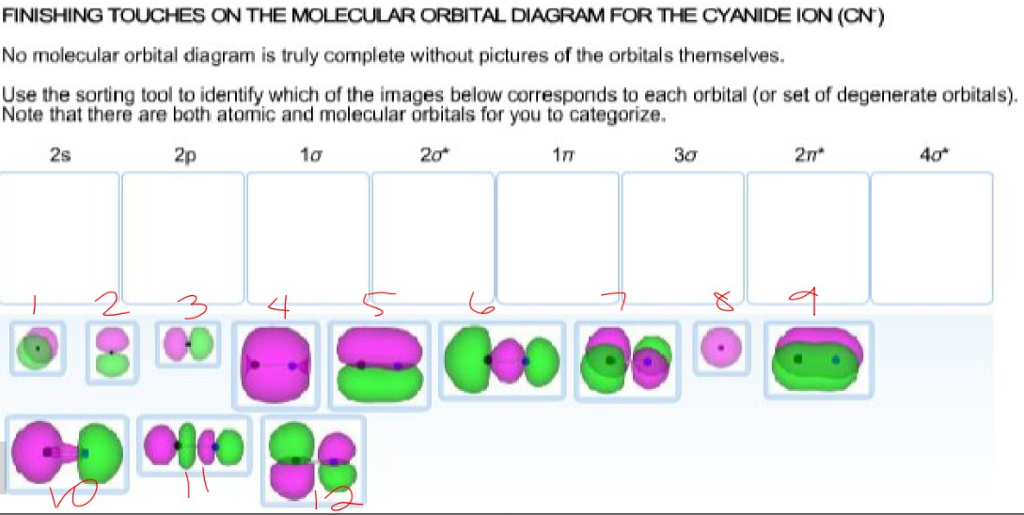
42 complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn
The molecular orbital energy diagram for N₂ is shown below. Based on this diagram, what is the bond order of N₂? D) 3-- BO=12 (number of bonding electrons − number of antibonding electrons) BO =12 (number of bonding electrons − number of antibonding electrons) BO = 12(10−4)=3. What is the mass percentage of O in CO₂? 72.71%. What is the mass percentage … Molecular orbital Diagram Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory heteronuclear ...
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn
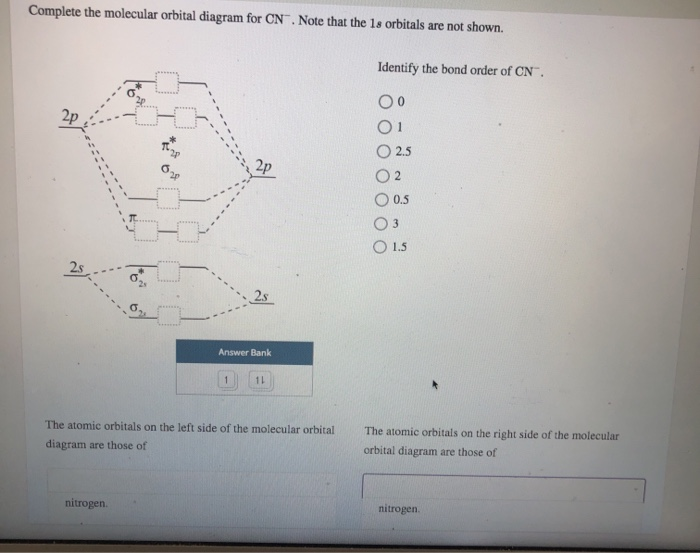
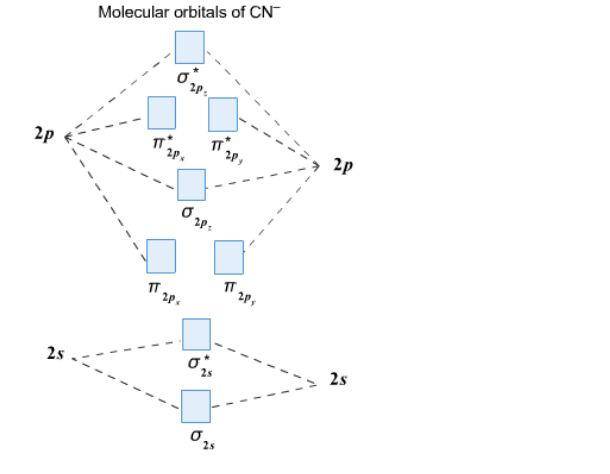
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN¯. О 1.5 2p ´2p 2p 2 1 0.5 2.5 3 2s 2s 2.s Answer Bank 11 1 The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of orbital diagram are those of 9. Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn. together to produce a sigma molecular orbital [σ = (1sa + 1sb)]. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms, this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This ... Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram to figure out the electronic configuration for CN.Which of the following statements is correct?a) CN is diamagnetic.b) CN− is paramagnetic.c) If an electron is removed to give CN+, the bond order increases.d) The π*2p orbital is the highest energy orbital containing an electron in CNe) If an electron is added to give CN−, the bond length decreases. Source 1: wikianswers.com Rating: General Information colorless gas WebMO Calculations: used to produce chemical compounds, especially polymers formerly used as a disinfectant for preserving biological specimens carcinogenic to humans Formaldehyde (H2CO) Molecular Orbitals Source We're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN-and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Step 2: Fill the molecular orbitals with electrons. Step 3: Determine the bond order. Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Group ...
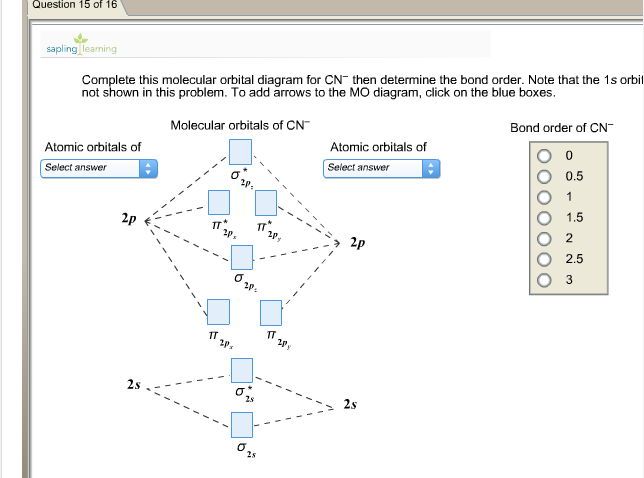
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. Bond order of CN O 0 O 0.5 Molecular orbitals of CN Atomic orbitals of Atomic orbitals of Select answer Select answer O 1.5 2 2Py oading image. The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. Of the bodies that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the four gas and ice giants and the four terrestrial planets, followed by an unknown number of dwarf planets and innumerable small Solar System bodies. 6. There is one p orbital on boron but there is no adjacent atom with another p orbital. Add it to the molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. 7. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2 1. Orbital diagram, after Barrett (2002), showing the participating atomic orbitals from each oxygen atom, the molecular orbitals that result from their overlap, and the aufbau filling of the orbitals with the 12 electrons, 6 from each O atom, beginning from the lowest-energy orbitals, and resulting in covalent double-bond character from filled orbitals (and cancellation of the …
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN−. Note that the 1𝑠 orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN−. The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in carbon is six. What do the molecular orbitals of cyanide look like, compared with those paired HOMO's and LUMO's in the molecular orbital energy diagram. May 21, 2021 · Hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2) is an important green oxidant 1 widely used in a variety of industries and a promising clean fuel for jet car and rockets 2,3,4,5,6,7 (60 wt% H 2 O 2 has an energy ... Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).
Jun 15, 2020 · Ir(acac) 3 @ZIF-8 was then pyrolysed at 900 °C to decompose Ir(acac) 3 (ref. 38) and carbonize the organic linkers 39,40, leading to iridium single atoms on nitrogen-doped carbon (Ir 1 /CN ...
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
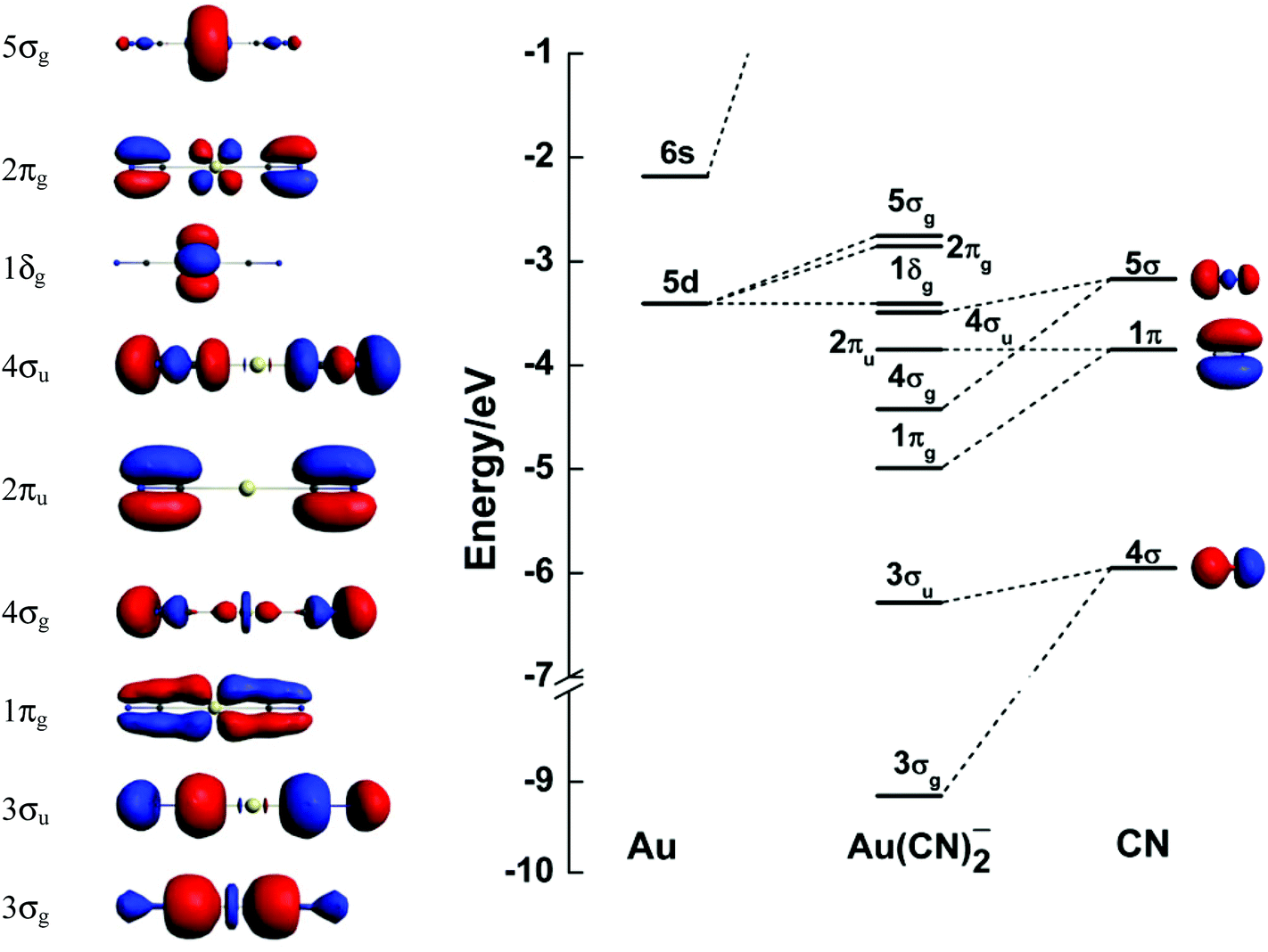
For the compounds that have square planar structure the molecular orbital is bit complicated. The compound Pt(CN) 4 2-has square planar structure. The molecular orbitals forms through the combination of central metal atom gaining a pair of electrons from each ligand. The platinum metal (Pt) is in '+2' oxidation state.
The molecular orbital diagram of NO shown in the figure below also applies to the following species. Write the molecular orbital electron configuration of each, indicating the bond order and the number of unpaired electrons. (a) CN (b) CO-(c) BeB-(d) BC +
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
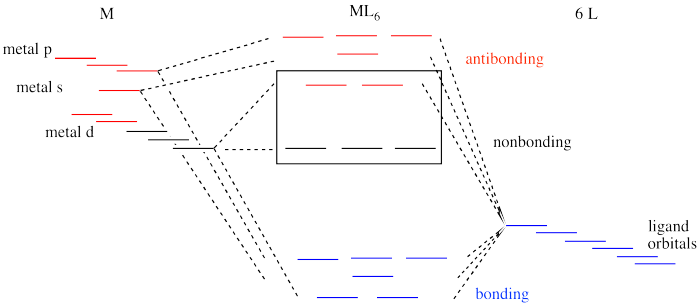
orbital from the σ-bonding. The molecular orbital of t2g* are greater in energy than nonbonding sets of t1g, t2u and t1u. On the other hand, the bonding molecular orbitals of t2g are lower in energy than that of nonbonding SALCs of the ligands. Therefore, when 36 electrons (12×2 from π-bonding and 6×2 from σ-bonding) from ligands are ...
Tania Havenga. University of South Africa. Here is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. http ...
Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN^- then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbit not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes.
the Hale-Bopp comet. The valence-shell molecular or-bital diagram for SO is shown on the right. Complete the molecular orbital diagram by (a) identifying which atom is on the left side and which is on the right side, (b) labeling the valence-shell atomic orbitals with their appropriate ns and np designations, (c) adding the ap-
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for NO by filling in the valence electrons in the occupied orbitals. Sketch the shape of the π and π* orbitals, clearly showing all nodes. Determine the bond order of NO and whether it is ... The extra electron in CN-occupies a σ-orbital. This is a bonding orbital and so
Homework Help Question & Answers Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN- then determine the bond order Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN - then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. Bond order of CN - 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure solved by expert teachers from latest edition books and as per NCERT (CBSE) guidelines.Class 11 Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NCERT Solutions and Extra Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks.
Helps students to turn their drafts into complete essays of Pro level. Proofreading. Giving you the feedback you need to break new grounds with your writing. Proceed To Order. Benefit From Success Essays Extras. Along with our writing, editing, and proofreading skills, we ensure you get real value for your money, hence the reason we add these extra features to our homework help …
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN-. a. Label the elements and add the electrons where appropriate. b. Determine the bond order of CN-. c. Will the bond between the C and the N be strengthened or weakened by the removal of 1 electron? 2s 2p 2s 2p AO's MO's AO's s s* s s* p p p* p*
Free PDF download of Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques prepared by expert Chemistry teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register online for Chemistry tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination.
Vollhardt Organic Chemistry Structure Function 6th txtbk.PDF. Download. Vollhardt Organic Chemistry Structure Function 6th txtbk.PDF
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B. O. = 8 − 2 2 = 3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, in case you need help. 57.6K views View upvotes View 1 share Kakali Ghosh , High School Teacher at Schools
Despite the extensive experimental studies, grasping the complete theoretical description of the “bonding model” has not yet been reached, due to the inability of experimental tools to fully describe the details of molecular orbital interactions and to make a profound population analysis, which is based on studying the electronic structures of the substrate and surface particles [88, …
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular…
🚀To book a personalized 1-on-1 tutoring session:👉Janine The Tutorhttps://janinethetutor.com🚀More proven OneClass Services you might be interested in:👉One...
Complete the MO diagram (below) to determine if OF⁻ is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. OF⁻ is diamagnetic. OF⁻ has 14 electrons in the valence shell. There are no unpaired electrons in this ion. Consider the fourth period elements Ca, Mn, Co, Se, and Kr. Which of these atoms are paramagnetic? A) Ca, Mn, Co B) Mn, Co, Kr C) Ca, Kr, Se D) Mn, Co, Se E) Ca, Kr. D) Mn, …
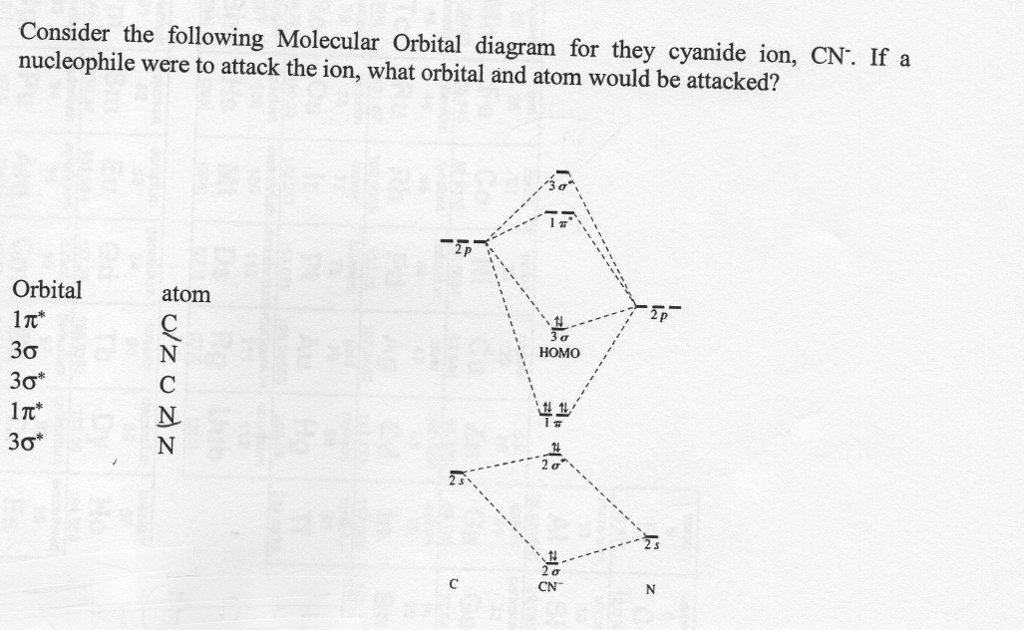
The molecular orbital model indicates that all three carbon-nitrogen species are stable, and that CN-, with a bond order of 3, is the most stable. Both the Lewis structure and the molecular orbital model show a bond order of 3 for the CN- ion.
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their lack of electrical charge.. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN¯. О 1.5 2p ´2p 2p 2 1 0.5 2.5 3 2s 2s 2.s Answer Bank 11 1 The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of orbital diagram are those of 9.




















0 Response to "42 complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn"
Post a Comment