43 orbital diagram of elements
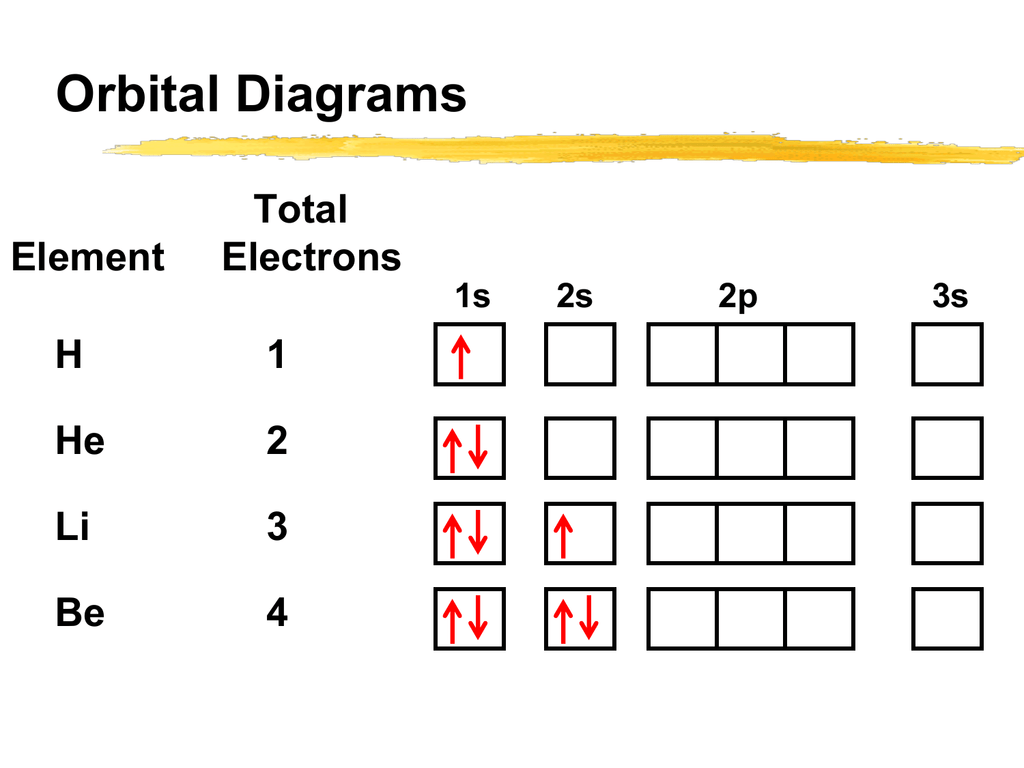
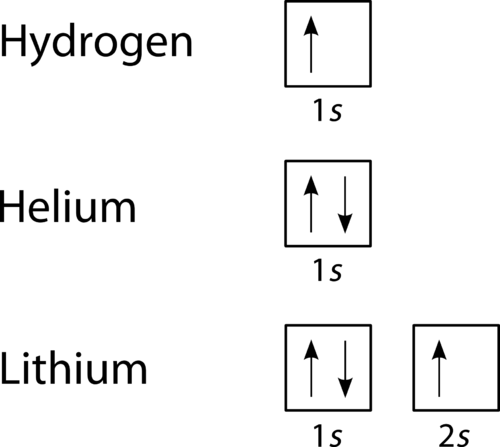
The orbital filling diagram for helium The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
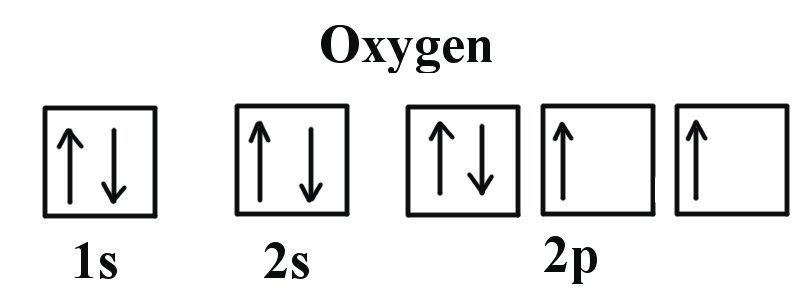
Electron configuration of fluorine (F) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
Orbital diagram of elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used (derived from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation). There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes, each consisting of a set of six parameters, are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics. A real orbit (and i... An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s → 2s → 2p x 2p y 2p z → 3s → 3p x 3p y 3p z → Two elements define the orientation of the orbital plane in which the ellipse is embedded: Inclination ( i) — vertical tilt of the ellipse with respect to the reference plane, measured at the ascending node (where the orbit passes upward through the reference plane, the green angle i in the diagram).
Orbital diagram of elements. Orbital Diagrams. Another way to represent the order of fill for an atom is by using an orbital diagram often referred to as "the little boxes": The boxes are used to represent the orbitals and to show the electrons placed in them. The order of fill is the same but as you can see from above the electrons are placed singly into the boxes before ... Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom The number of orbitals depends on the value of 'l' and each orbital can accommodate a maximum of 2 electrons. Number of orbitals for a given subshell is equal to: 2l+1. So, in case of 1s (2*0+1=1, 1 orbital only) the subshell itself acts as orbital. Similarly, for 2s, there's just one orbital and the subshell itself acts as orbital. An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the ...
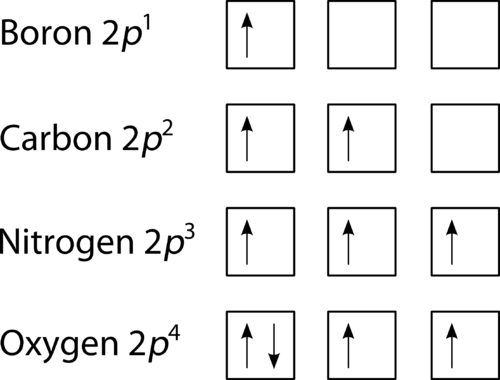
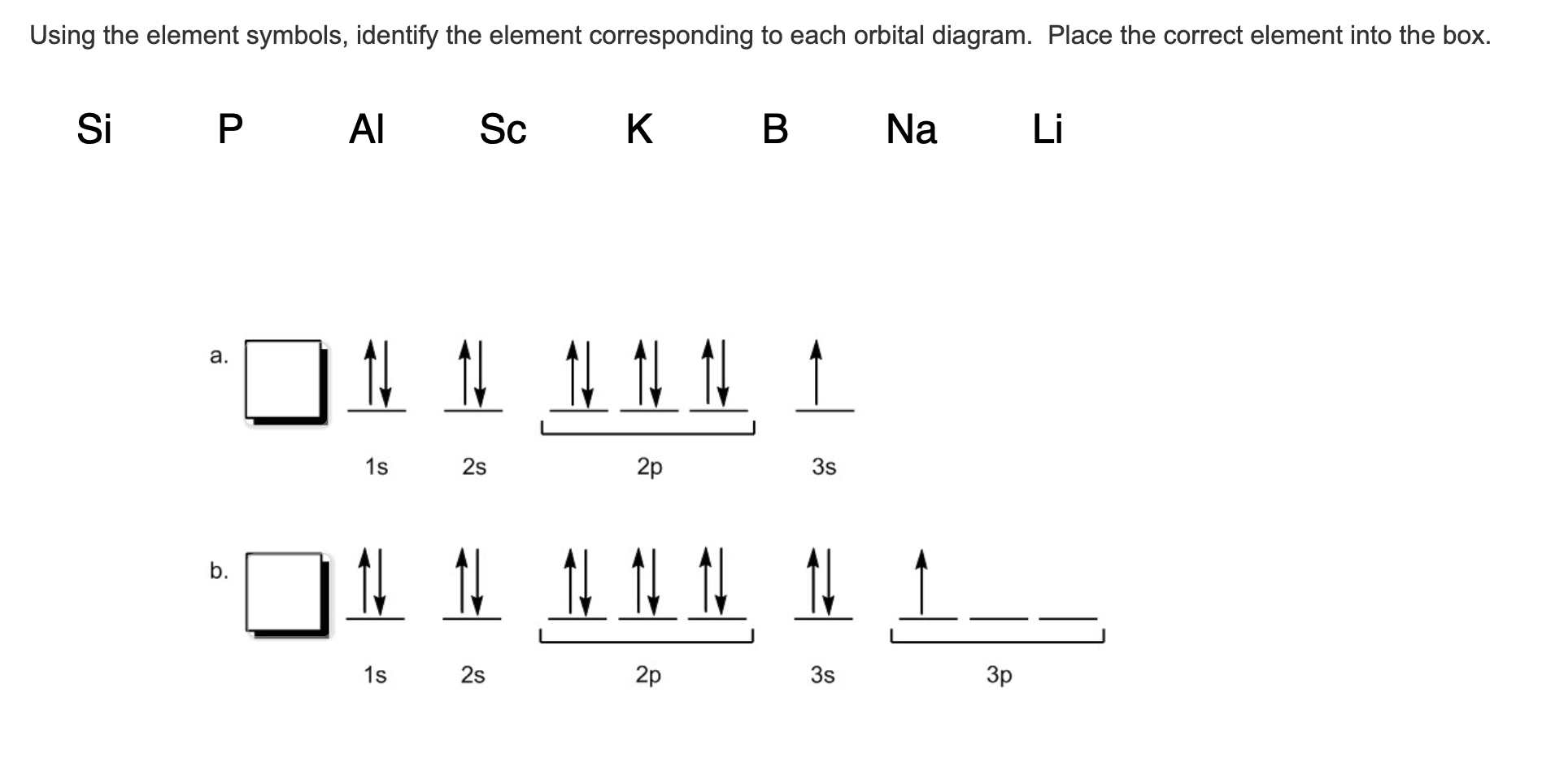
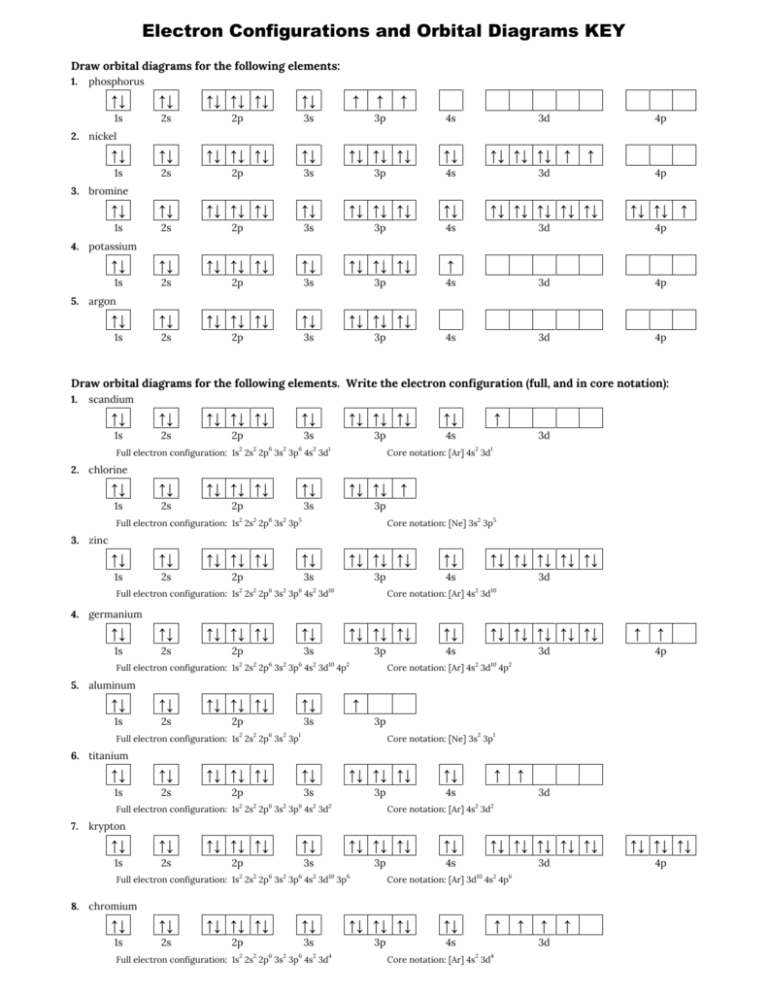
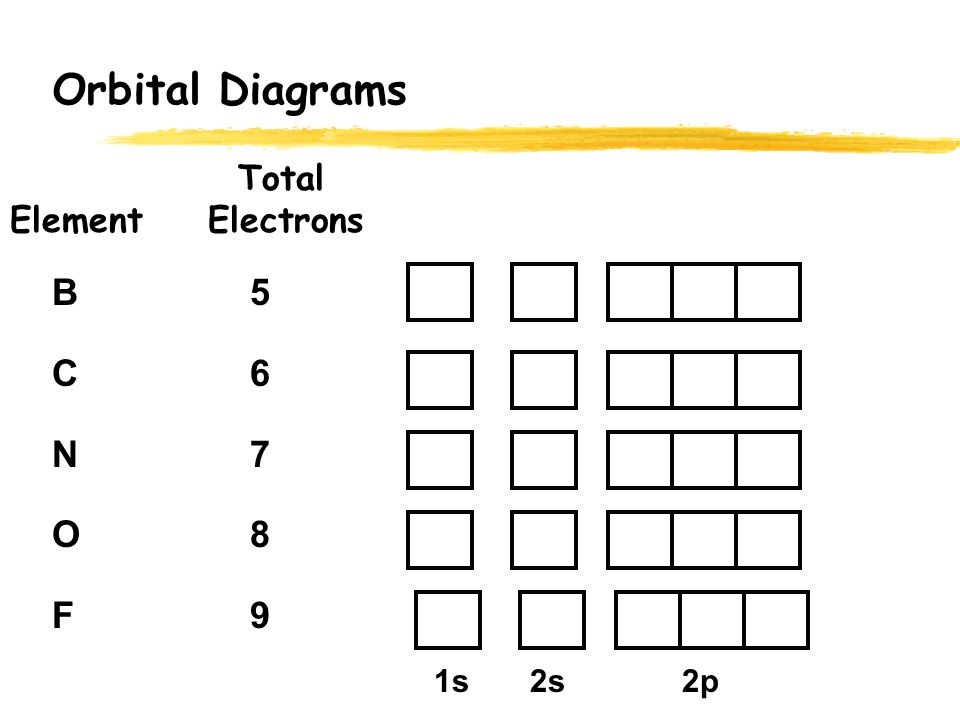
Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Below) January 1, 2022 April 10, 2021 by Admin Orbital diagrams (Orbital box diagrams) of all elements are mentioned in the chart given below. The four different orbital forms (s, p, d, and f) have different sizes and one orbital will accommodate up to two electrons at most. The orbitals p, d, and f have separate sub-levels and will thus accommodate more electrons. As shown, each element's electron configuration is unique to its position on the periodic table. Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams KEY Draw orbital diagrams for the following elements: 1. phosphorus ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p. orbital diagram represents an orbital. Orbitals have a capacity of two electrons. Arrows are drawn inside the boxes to represent electrons. On the periodic table, hydrogen and helium are the only two elements in the first row, or period, which reflects that they only have electrons in their first shell. Hydrogen and helium are the only two elements that have electrons exclusively in the orbital in their neutral, non-charged, state. The second electron shell, 2n, contains another ...
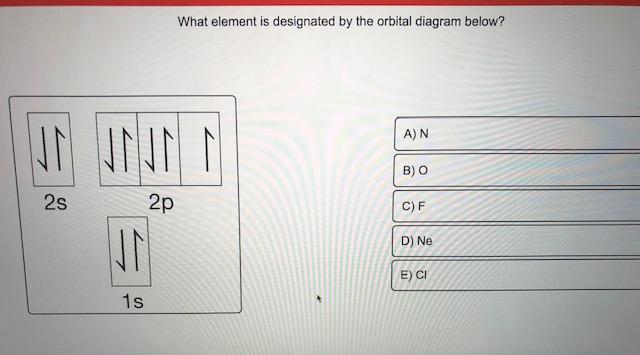
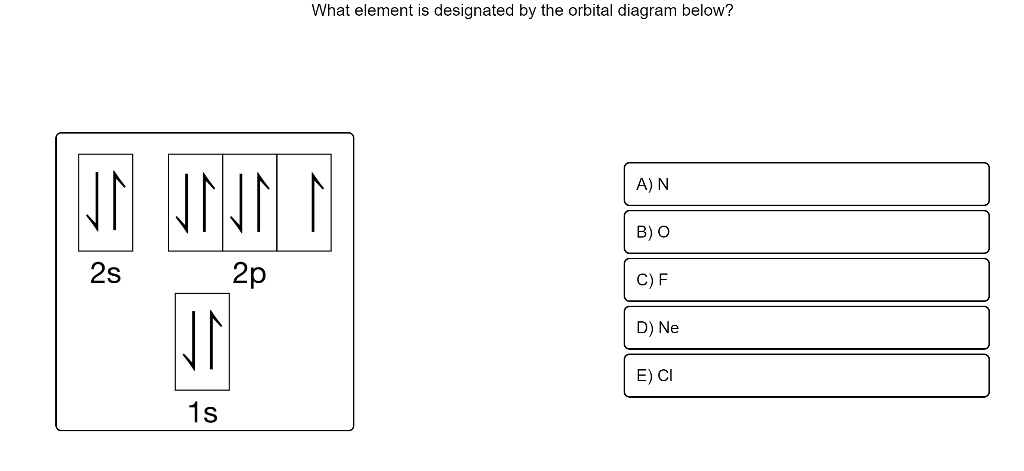
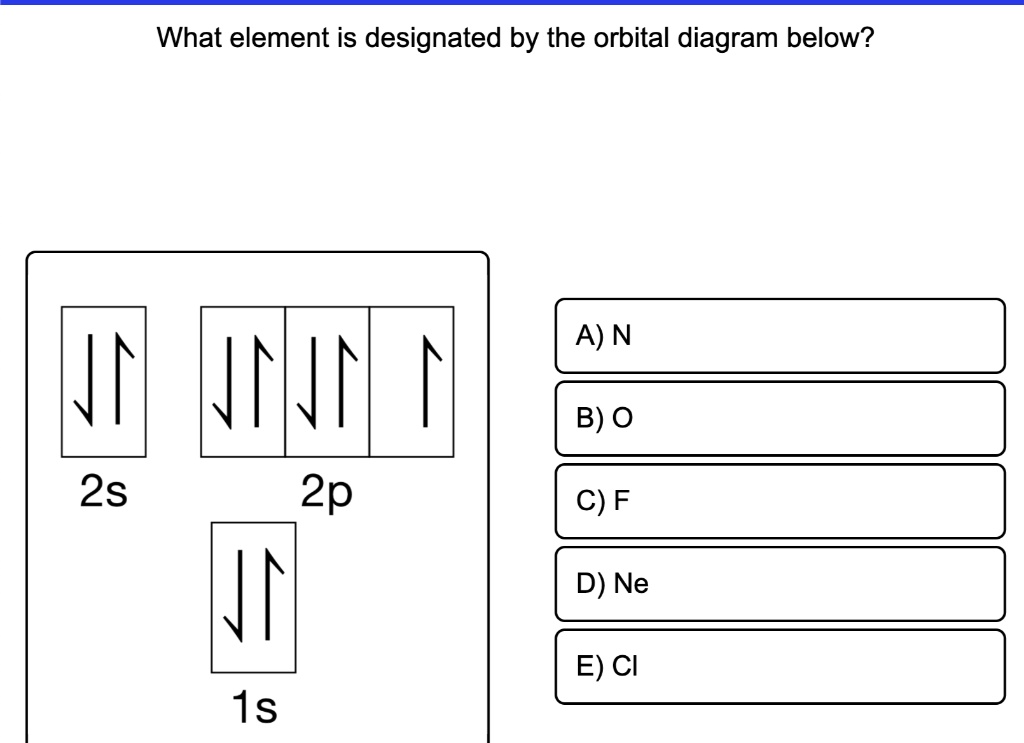
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau... Orbital Diagrams of First 36 elements. TestNew stuff! Provide the symbol for the element with the following orbital digram. Provide the symbol for the element with the following orbital digram. Nice work! You just studied 43 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode. The symbol of this element is Se, and the atomic number of the Selenium is 34. It has similar properties to Sulphur, tellurium, and arsenic. Are you searching Selenium Electron Configuration (Se) with Orbital Diagram? Then today, on-site, you will get an easy and quick learning diagram of Selenium. Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. We start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron. Referring to Figure 3 or Figure 4, we would expect to find the electron in the 1 s orbital.
For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron shells are shown, moving outward from the nucleus. The final ring or shell of electrons contains the typical number of valence electrons for an atom of that element. The element atomic number and name are listed in the upper left.
The 6 electrons will go to the 2p orbital, and the next 2 electrons will place with 3s orbital, and now we have only 8 electrons in which 6 electrons will go with 3p orbital, and the last 2 electrons will be with 4s orbital. So, we have Calcium Electron Configuration is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s²
Gallium (Ga) orbital diagram 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise direction and the next electron will enter the 1s orbital in the anti-clockwise direction.
An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. Electrons are indicated by arrows inside the circles. An arrow pointing upwards indicates one spin direction, while a downward pointing arrow indicates the other direction.
Orbital diagram. Cerium electron configuration ← Electronic configurations of elements . Ce (Cerium) is an element with position number 58 in the periodic table. Located in the VI period. Melting point: 798 ℃. Density: 6.77 g/cm 3. The order of filling the orbitals with electrons in the Ce atom is an exception to the rule. ...
An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals.
Orbital diagrams give you all of the information you need about the electron configuration and occupied spin states for chemistry or physics, and are easy to both create and interpret. Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE Sciencing_Icons_Biology Biology Sciencing_Icons_Cells Cells Sciencing_Icons_Molecular Molecular Sciencing_Icons_Microorganisms
The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. This electron must go into the lowest-energy subshell available, the 3 s orbital, giving a 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 1 configuration.
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal –each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for “build up” •Electrons are notated with an arrow –Up arrow goes first then, down arrow –Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
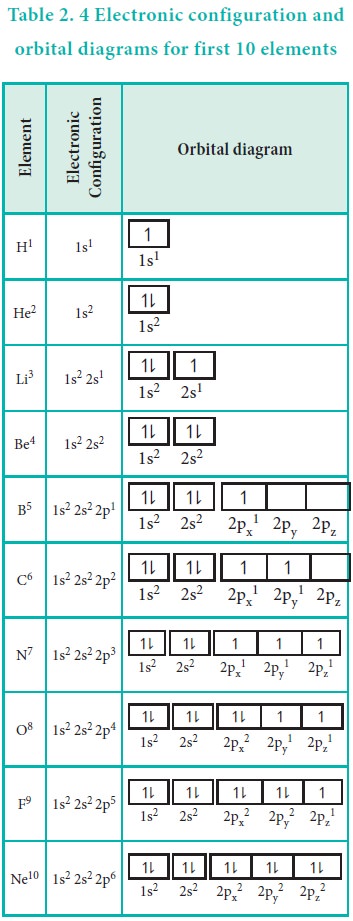
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin–one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below.
Orbital Diagram Lab Background. The electrons in an atom occupy distinct principal energy levels. To be located in ... whether the element is a metal or nonmetal. We'll deal with these elements in the next part of this unit on the Periodic Table.
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ...
Orbitals and Electron Configuration. The Periodic Table with Oxidation Numbers and Electron Configurations. S Block. P Block. D Block. F Block. 1. Hydrogen. 1.
diagrams. For C the gap between the 2s and 2p orbitals is small, this is why C forms sp hybrids. However for all the other elements to the right of C such as N, O, F the sp gap is larger and gets increases long the periodic table, thus for F the gap is very large. Put the 2s and 2p AOs on the diagram taking note of the
Two elements define the orientation of the orbital plane in which the ellipse is embedded: Inclination ( i) — vertical tilt of the ellipse with respect to the reference plane, measured at the ascending node (where the orbit passes upward through the reference plane, the green angle i in the diagram).
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s → 2s → 2p x 2p y 2p z → 3s → 3p x 3p y 3p z →
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used (derived from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation). There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes, each consisting of a set of six parameters, are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics. A real orbit (and i...
























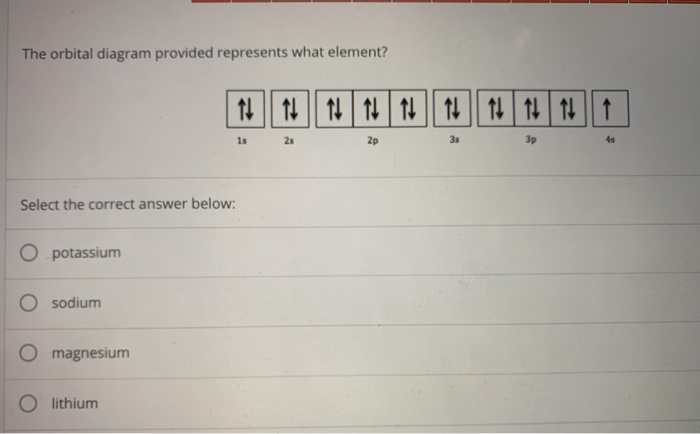

0 Response to "43 orbital diagram of elements"
Post a Comment