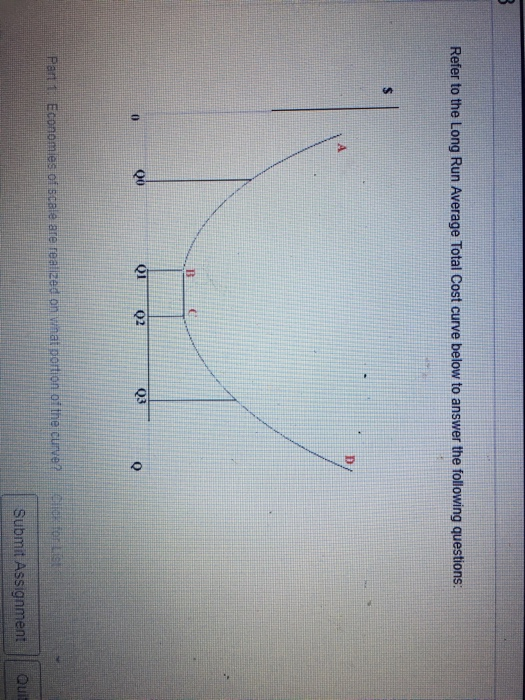
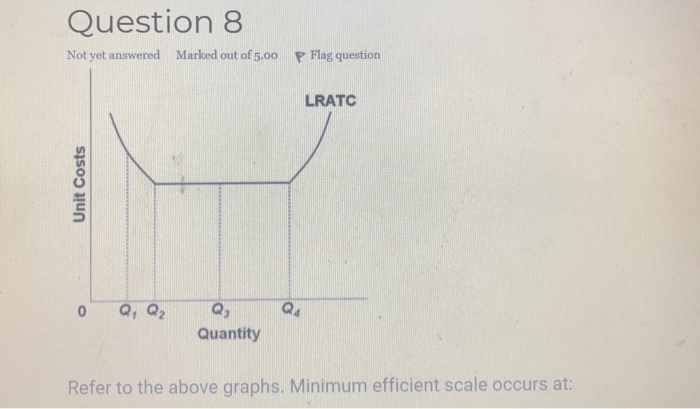
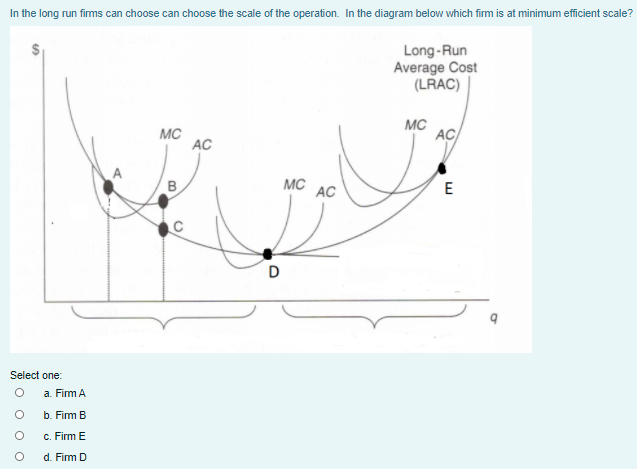
40 refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale
Refer to the diagram to the right. Identify the curves in the diagram. additional cost of producing an additional unit or output. Marginal cost is the. $340. Vipsana's Gyros House sells gyros. The cost of ingredients (pita, meat, spices, etc.) to make a gyro is $2.00. Vipsana pays her employees $60 per day. Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale: is achieved at Q1. In the short run: TVC will increase for a time at a diminishing rate, but then beyond some point will increase at an increasing rate. Which of the following represents a long-run adjustment?
Economics questions and answers. Long-Run ATC Unit Costs O, Q2 Q3 Output Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale Multiple Choice occurs at some output greater than Q3. is achieved at 24 O Is achleved at 23 cannot be identified in this diagram. Question: Long-Run ATC Unit Costs O, Q2 Q3 Output Refer to the diagram.
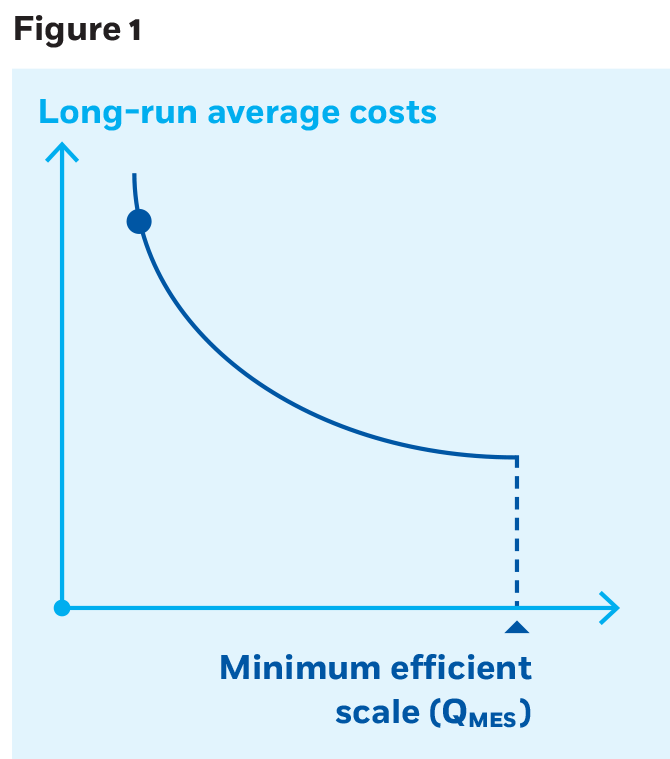
Refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale
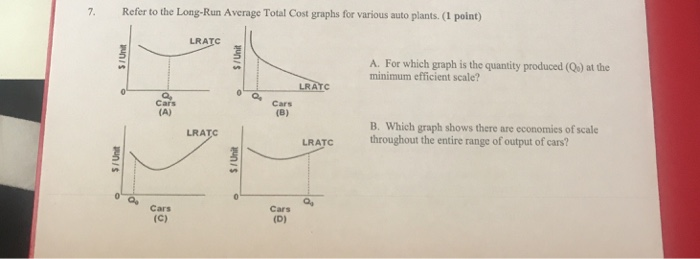
169. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q 3 . B. is achieved at Q 1 . C. is achieved at Q 3 . D. cannot be identified in this diagram. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Bloom's: Level 3 Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 07-04 Use economies of scale to link a firm's size and its ... 3. firms must be large both absolutely and relative to the market to employ the most efficient productive techniques available. 4. beyond some point marginal product declines as additional units of a variable resource (labor) are added to a fixed resource (capital). 9. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: In the above diagram, with a U-shaped LRAC curve, the minimum efficient scale is Q 0. The size of a firm is often measured by its long-run output level which depends to a large extent on the minimum efficient scale. If the minimum efficient scale is low, the firm will tend to be small. Conversely, if the minimum efficient scale is high, the ...
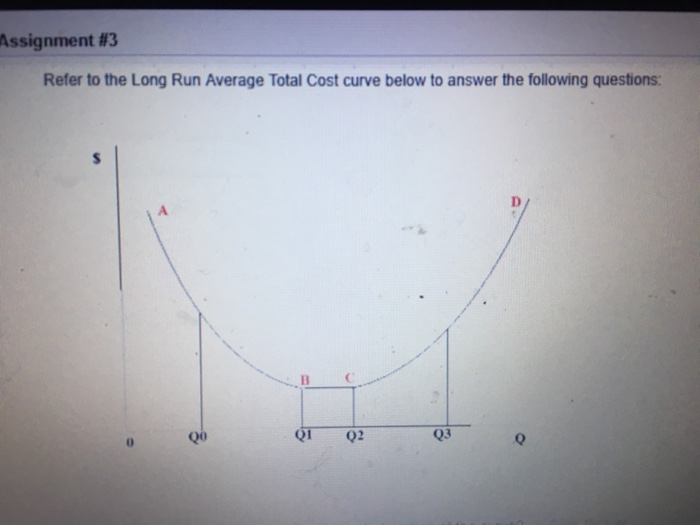
Refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale. The minimum efficient scale (MES) is the balance point at which a company can produce goods at a competitive price. Achieving MES minimizes long-run average total cost (LRATC). The minimum efficient scale of a firm: A. is realized somewhere in the range of dis-economies of scale. ... Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q3. B. is achieved at Q1. C. is achieved at Q3. D. cannot be identified in this diagram. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q 3. B. is achieved at Q 1. C. is achieved at Q 3. D. cannot be identified in this diagram. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Skills Bloom's: Application Learning Objective: 8-4 Topic: Long-run costs 191. Refer to the above diagram. Constant returns to scale: A ... Minimum efficient scale corresponds to the lowest point on the long run average cost curve and is also known as an output range over which a business achieves productive efficiency.. MES is not a single output level - more likely, the MES is a range of outputs where the firm achieves constant returns to scale and has reached the lowest feasible cost per unit.
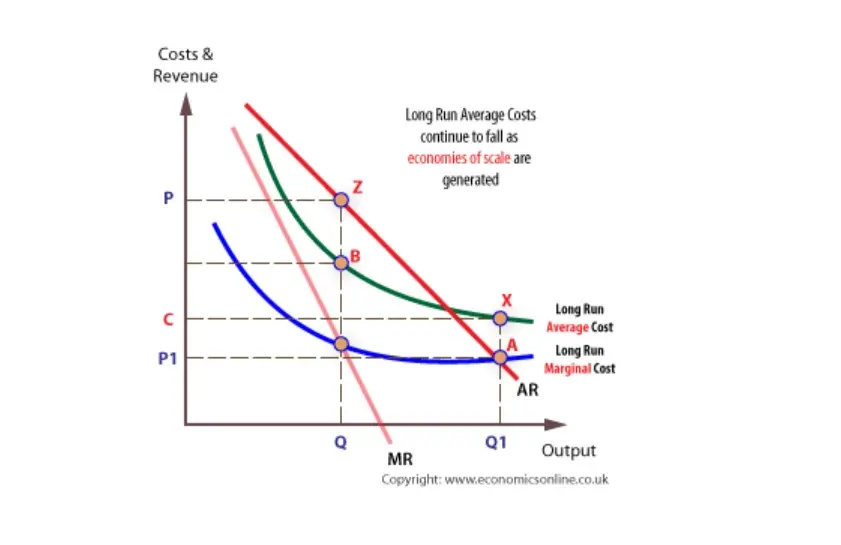
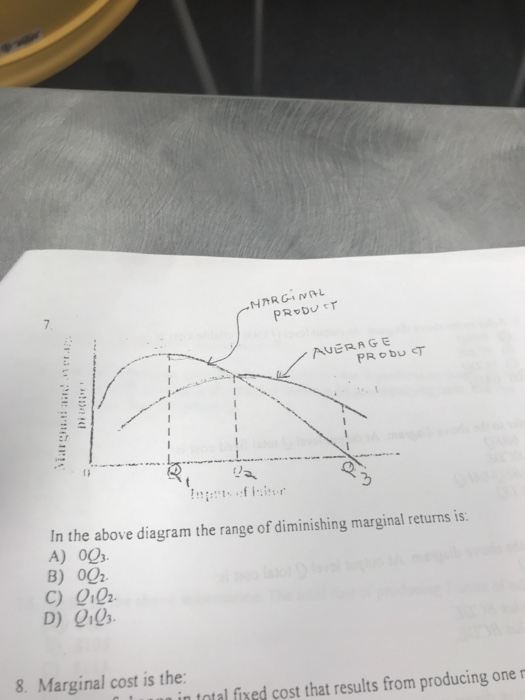
Refer to the above diagram Diseconomies of scale A begin at output Q 1 C begin. Refer to the above diagram diseconomies of scale a. ... Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A) occurs at some output greater than Q 3. C) is achieved at Q B) is achieved at Q 1. D) cannot be identified in this diagram. This is a good question Minimum efficient scale is the point where average cost is minimum. Minimum eff …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Long-Run ATC Unit Costs 0 Q2 Q3 Output Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale occurs at some output greater than Q3. is achieved at Q1 О O is achieved at Q3 cannot be identified in ... Refer to the above table. There are increasing marginal returns through the: A. ... In the diagram above LRTC = long-run total costs. The firm is experiencing: A. economies of scale. B. diseconomies of scale. C. constant returns to scale. D. minimum efficient scale. 16. R-16 REF 22-139: Q38. Refer to the short-run production and cost data above. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: A) marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. B) marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. C) marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same output. D) AVC cuts MC at the latter's minimum point.
In the above diagram it is assumed that:all costs are variable. Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale:occur over the 0Q 1 range of output. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale:begin at output Q 3. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale:is achieved at Q 1. 9. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q3. B. is achieved at Q1. C. is achieved at Q3. D. cannot be identified in this diagram. 10. Suppose a firm is in a range of production where it is experiencing economies of scale. Refer to the above short-run production and cost data. The curves of Figures A and B suggest that: O A. marginal product and marginal cost reach their maximum points at the same output. O B. marginal cost reaches a minimum where marginal product is at its maximum. O C. marginal cost and marginal product reach their minimum points at the same ... 9. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: 1. occurs at some output greater than Q3. 2. is achieved at Q1. 3. is achieved at Q3. 4. cannot be identified in this diagram. 10. Suppose a firm is in a range of production where it is experiencing economies of scale.
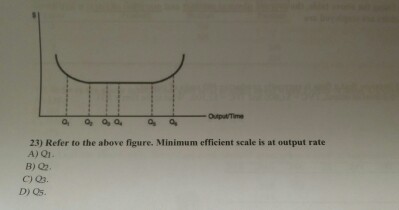
23. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q3. B. is achieved at Q1. C. is achieved at Q3. D. cannot be identified in this diagram. 24. Refer to the above diagram. Constant returns to scale: A. occur over the 0Q1 range of output. B. occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. C. begin at output Q3.
Refer to the diagram. Minimum efficient scale. Multiple Choice. occurs at some output greater than Q3. is achieved at Q1. is achieved at Q3. cannot be identified in this diagram. At what point does marginal product equal average product? Multiple Choice. where average product is equal to its minimum value; where average product is equal to its ...
Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale? Occur over the 0q1 range output. Refer to the diagram above. Minimum efficient scale? Is achieved at q1. Assume a firm closes down in the short run and produces no out put. Under these conditions: TFC and TC are positive, but TVC is Zero.
185. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: A) begin at output Q1. C) begin at output Q3. B) occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. D) are in evidence at all output levels. Answer: C. Type: G Topic: 6 E: 407 MI: 163 186. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A) occurs at some output greater than Q3. C) is achieved at Q3 ...
In the above diagram, with a U-shaped LRAC curve, the minimum efficient scale is Q 0. The size of a firm is often measured by its long-run output level which depends to a large extent on the minimum efficient scale. If the minimum efficient scale is low, the firm will tend to be small. Conversely, if the minimum efficient scale is high, the ...
3. firms must be large both absolutely and relative to the market to employ the most efficient productive techniques available. 4. beyond some point marginal product declines as additional units of a variable resource (labor) are added to a fixed resource (capital). 9. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale:
169. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A. occurs at some output greater than Q 3 . B. is achieved at Q 1 . C. is achieved at Q 3 . D. cannot be identified in this diagram. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Bloom's: Level 3 Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 07-04 Use economies of scale to link a firm's size and its ...









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)
/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)




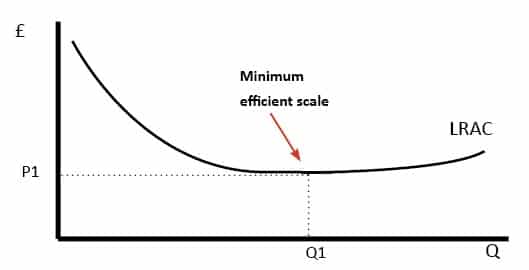



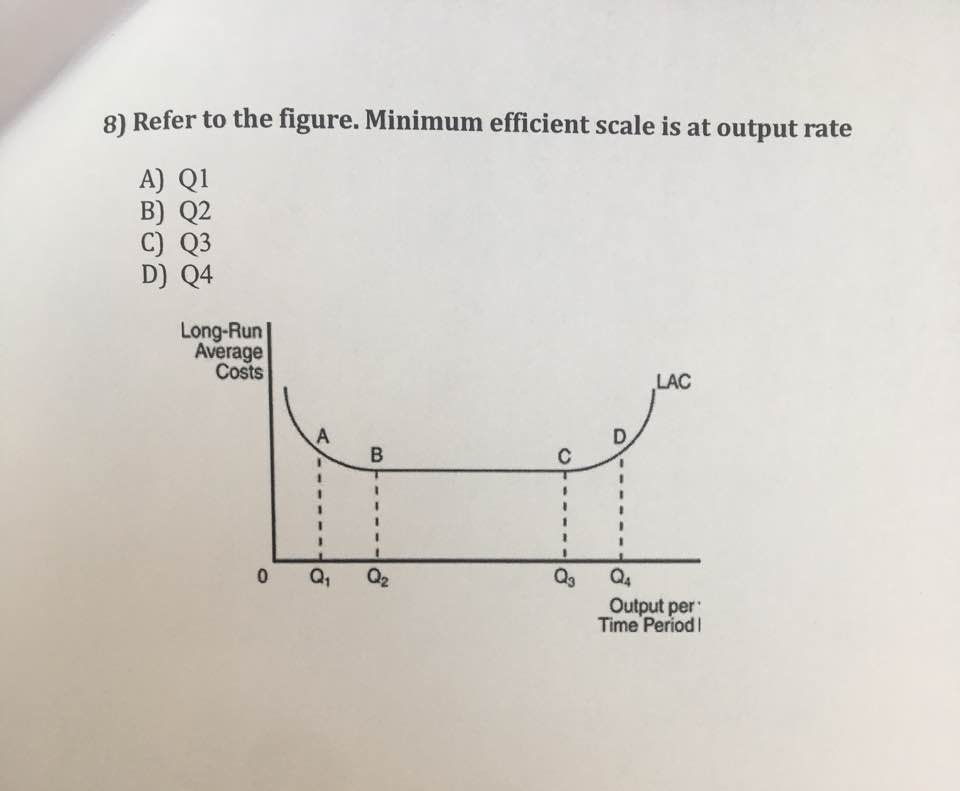


0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram. minimum efficient scale"
Post a Comment