43 Laws Of Reflection Diagram
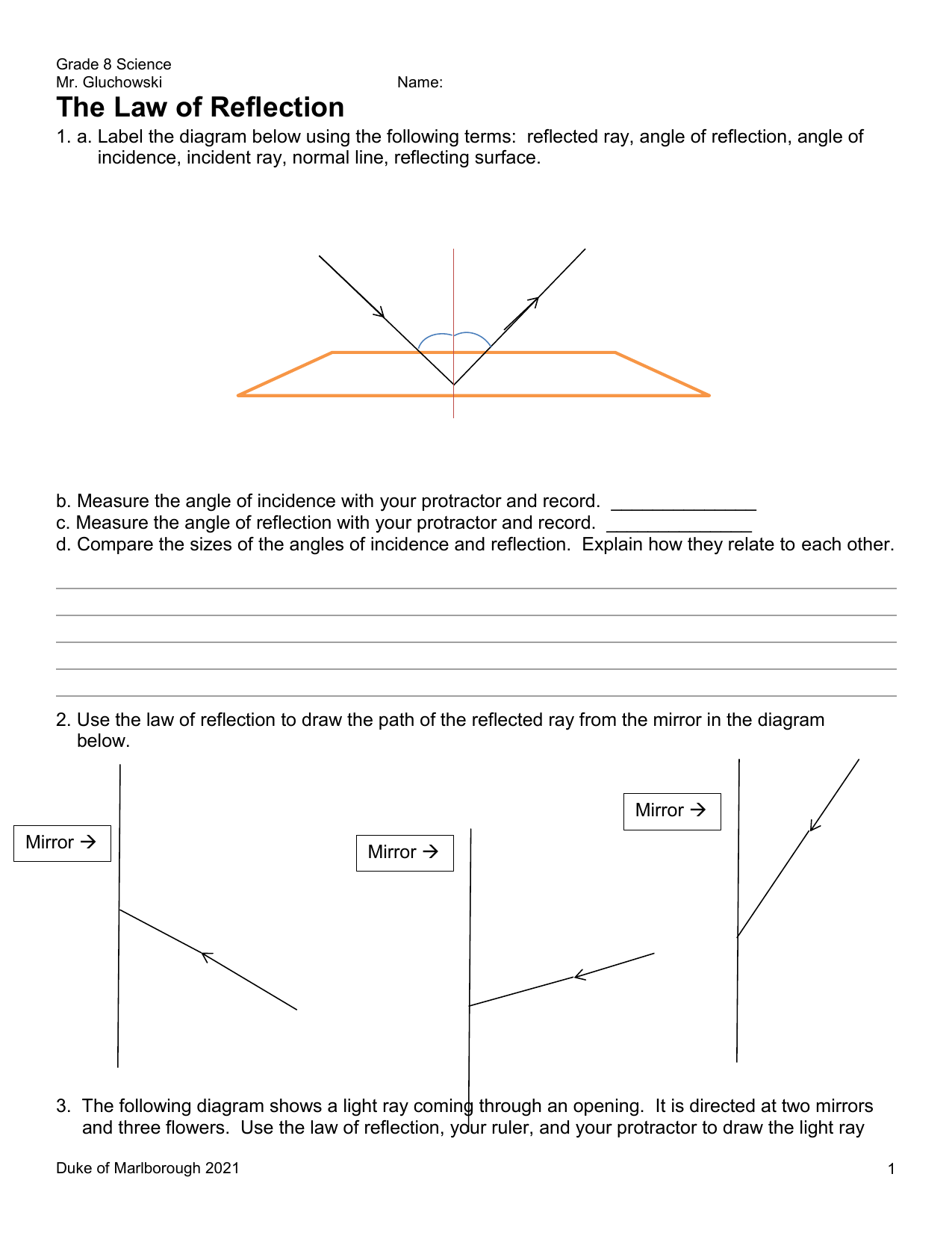
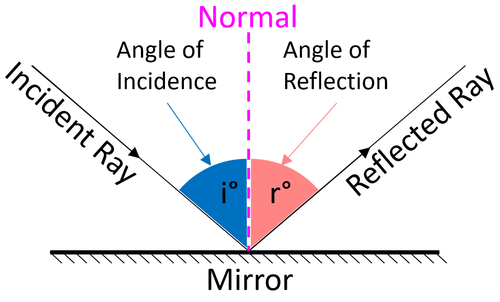
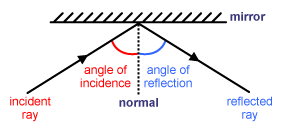
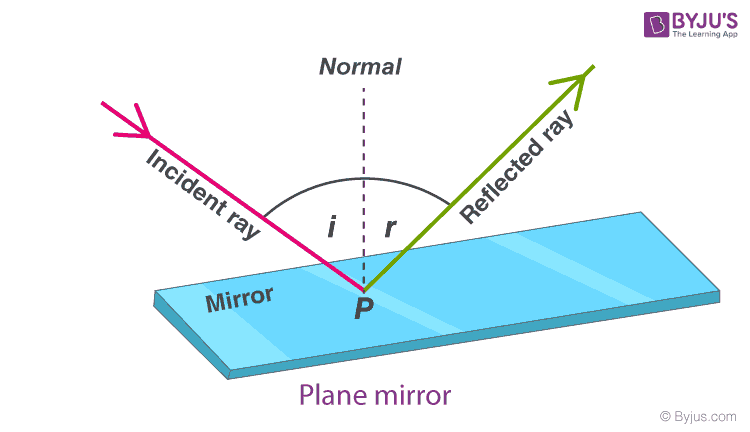
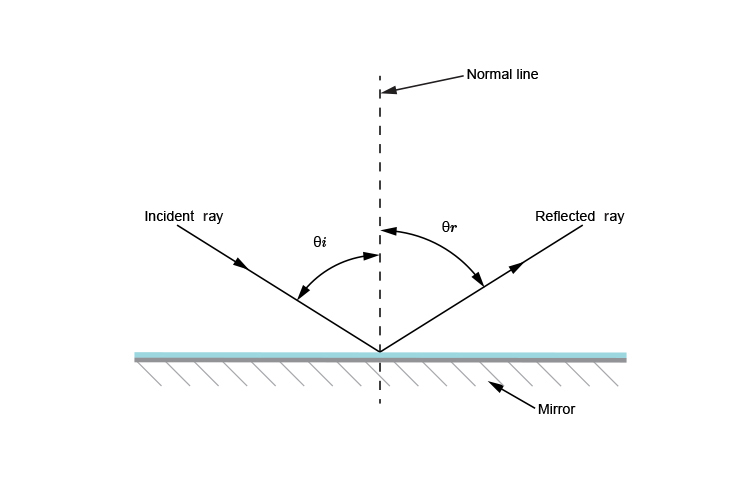
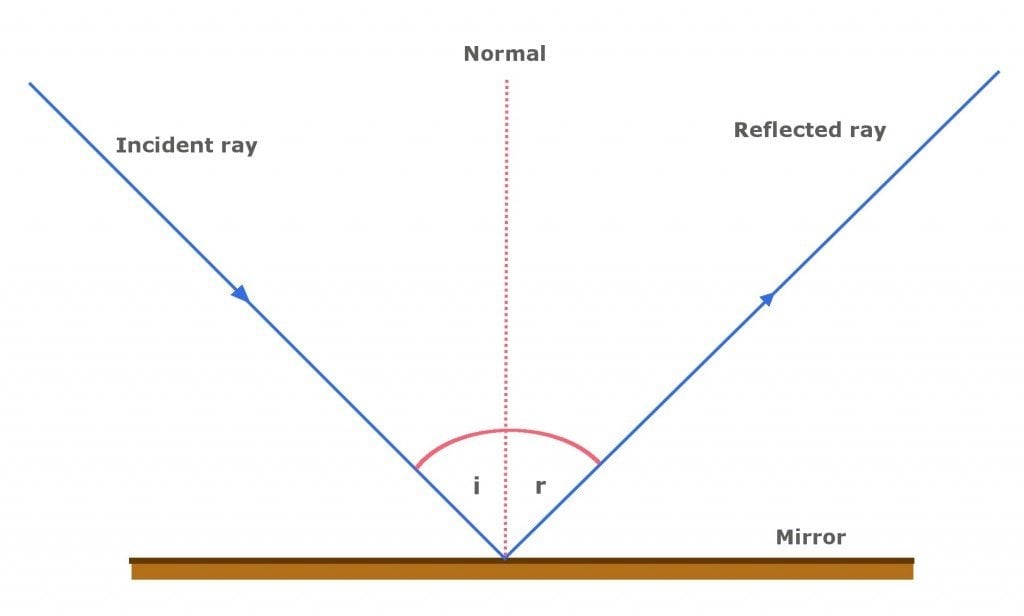
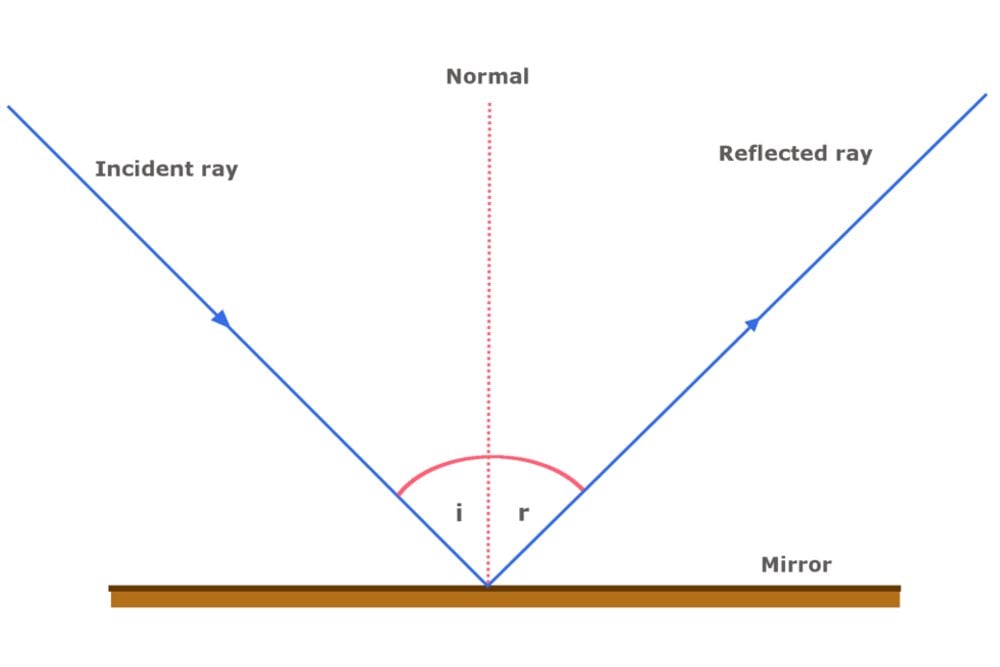
Reflection at Plane Surfaces: Laws of Reflection, Image ... Laws of Reflection Consider the diagram below to understand the laws of reflection: 1. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection when light is reflected on a plane surface. 2. The incident ray reflected the ray and the normal lie on the same plane. Image Formation Through a Plane Mirror Ray Optics & Light: Introduction, Properties, Applications ... Law of Reflection Light rays can reflect from any polished surface. Reflected ray, incident ray, and normal all lie in the same plane in which they are propagating as shown in the figure below. Whereas the incident ray and reflected ray both lie on either side of the normal drawn which is perpendicular to the reflecting surface.
Light Reflection and Refraction Exam Questions Class 10 ... Question: (a) State Snell's law of refraction. (b) When a ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into a glass slab, it is observed that the light ray emerges parallel to the incident ray but it is shifted sideways slightly. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate it. Answer: (a) Snell's law sini/sinr=constant.
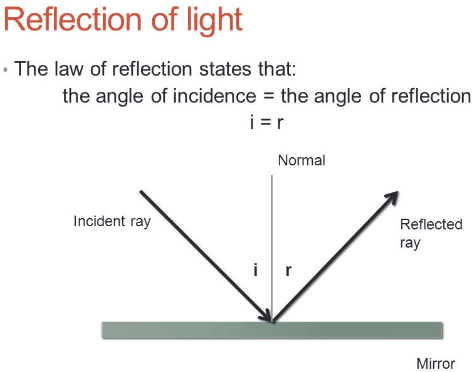
Laws of reflection diagram
Laws Of Reflection Of Light Class 12: Definition ... The first Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. For example, if an incident ray makes and angle of 45 degrees with the normal ray (line perpendicular to the surface at the point). The reflected ray would also make the angle of 45 degrees with the normal ray. Second law of reflection The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. Which ... Therefore, in the picture attached: - B is the angle of incidence. - C is the angle of reflection. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Answer from: ej02duncan1. SHOW ANSWER. The measure of angle B equals the measure of angle C. Explanation: Important Questions Light Reflection and Refraction Class ... Answer: Laws of Reflection. a. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence are always in the same plane. b. ∠i = ∠r. Question: Define the term reflection. Answer: The bouncing back of a ray of light in the same medium after striking on a surface of an object.
Laws of reflection diagram. Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 4 ... - BYJUS We know from the laws of reflection that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Therefore, angle of reflection will be equal to 30 degrees. Q3. A ray of light strikes a plane mirror at an angle of 40 degrees to the mirror surface. What will be the angle of reflection? Answer: The angle to the mirror surface = 40 degrees 📐Q7 Explain how light can be reflected at lots of ... Q7 Explain how light can be reflected at lots of different angles from a rough surface and still obey the law of reflection. Use a diagram in your answer. Q8 Read the following statements. A: You can have refraction without dispersion B: You cannot have dispersion without refraction a Discuss a situation where statement A is true. Angle of Reflection Overview & Law | What is the Angle of ... The Law of Reflection states that the normal line bisects the angle formed between the incident and reflected rays. Therefore, the angle of incidence ( {eq}\theta_i {/eq}) and the angle of... The diagram below represents a light ray striking the ... The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal. The correct option for the angle between the given light ray and the reflected ray is the option;. 120° Reason:. The given parameter are; The angle formed by the light ray and the glass surface = 30°. Required:. To find the angle between the light ray and the reflected ray. Solution:. According to the laws of reflection, the angle ...
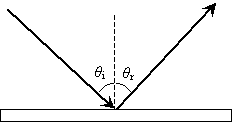
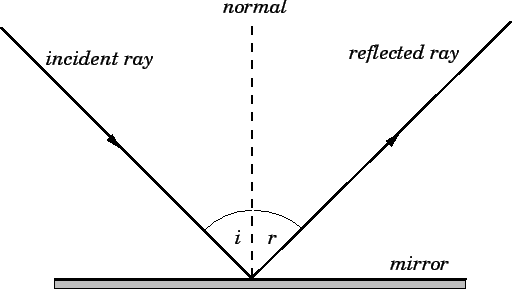
What is the Law of Reflection: Definition and A Simple ... This is basically what the law of reflection is all about. Here's a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray. Draw a ray diagram showing image formed when object is at 2 F. In reflection, a light ray strikes a smooth surface, such as a mirror, and bounces off. A reflected ray always comes off the surface of a material at an angle equal to the angle at which the incoming ray hit the surface. In physics, you'll hear this called the law of reflection.Reflection is when light bounces off an object. What is reflection? - Health and Care Professions Council Reflection is a process which helps you gain insight into your professional practise by thinking analytically about any element of it. The insights developed, and lessons learned, can be applied to maintain good practice and can also lead to developments and improvements for both the professional and their service users. Diffuse Reflection: Definition, Examples & Surfaces ... Since each ray is hitting the surface at the same angle - the angle of incidence - then each ray reflects at the same angle - the angle of reflection. A person standing in the path of the reflected...
Revision Notes for Reflection of Light Class 9 Physics ICSE Laws of Reflection. ∙ Reflection at a surface obeys two laws of reflection: First law of reflection: The incident ray, the normal to the surface at the point of incidence and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane. Second law of reflection: The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. What is reflection of light represent by ray diagram? 2022 ... The law of reflection In the ray diagram: the hatched vertical line on the right represents the mirror. the dashed line is called the normal , drawn at 90° to the surface of the mirror. the angle of incidence , i, is the angle between the normal and incident ray. What is the purpose of ray diagram? What are the two major types of reflection? Reflection And Refraction of Light: Laws, Formulas ... Reflection And Refraction of Light: Laws, Formulas, Scattering, Dispersion and Conditions. Reflection and Refraction of light are results of light waves interacting with different media. Light waves generally travel in a straight line in any media. But when it falls on the boundary of a different media, it either undergoes Reflection or Refraction. explain the laws of motion, reflection. label a diagram of ... Law of reflection The principle when the light rays fall on the smooth surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, also the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane. Law of motion Newton's laws of motion relate an object's motion to the forces acting on it.
The regular reflection and irregular reflection of light ... The light reflection is the returning back of light waves in the same medium on meeting a reflecting surface, and the surface at which the reflection takes place is called the reflecting surface, The light reflection is classified according to the nature of the reflecting surface into the regular (uniform) reflection, and the irregular (non-uniform)
Laws of reflection - Optography Two laws of reflection are followed during the process. They are: 1. The angle of reflection with which the light bounces off the surface should be equal to the angle of incidence with which the light is incident on the surface. That is i=r 2. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
With the help of a neat diagram, explain the reflection of ... This explains laws of reflection of light from plane reflecting surface on the basis of Huygens' wave theory. Note: 1. Frequency, wavelength and speed of light do not change after reflection. 2. If reflection takes place from a denser medium, then phase changes by π radian.
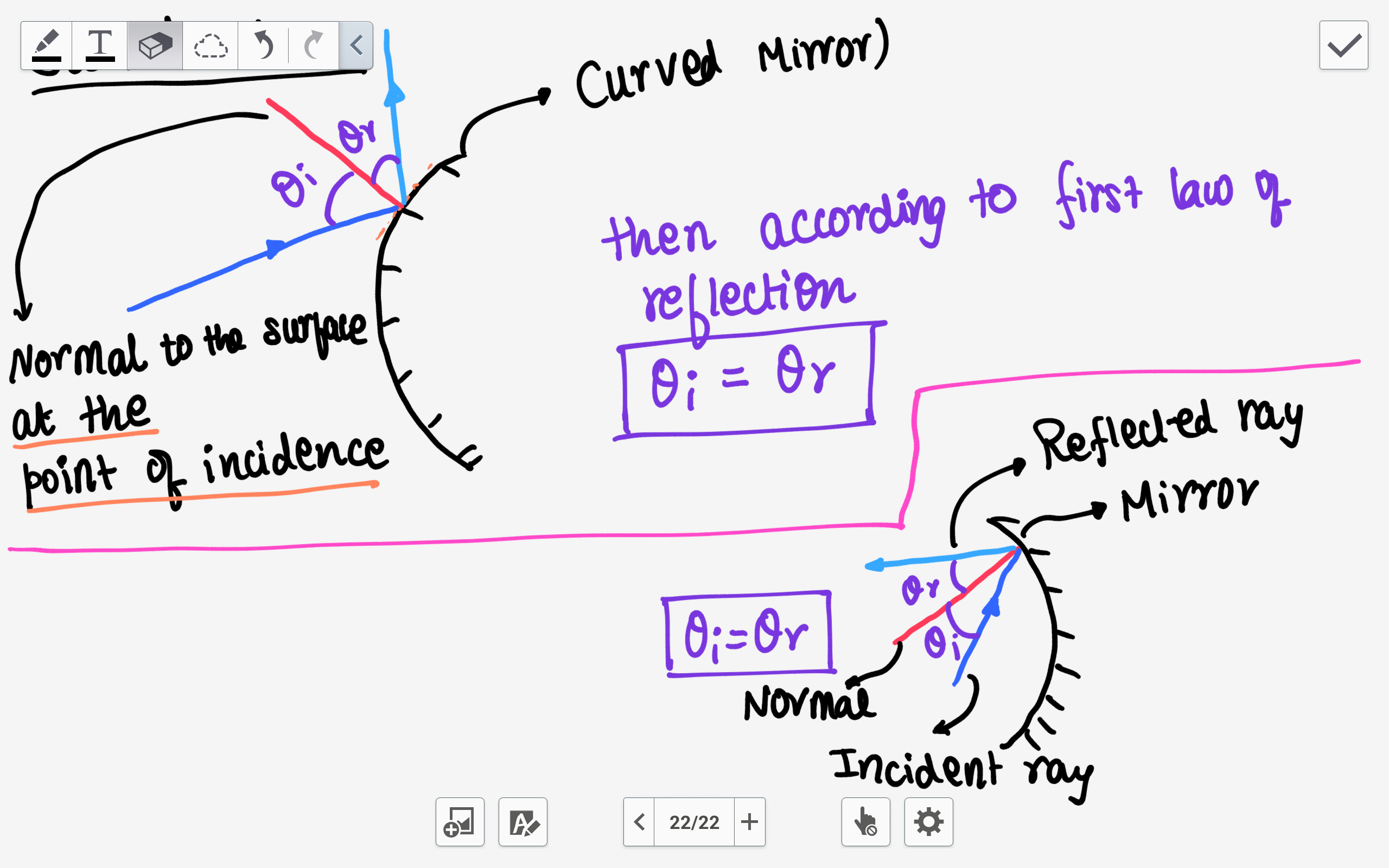
Uses of Spherical Mirrors: Law of Reflection, Types, Diagrams Laws of Reflection. Before we understand the uses of spherical mirrors, we need to understand the law of reflections. The laws of reflection apply to all types of surfaces: smooth or rough, plane or curved, dull or shiny. To understand the laws of reflection, first, we have to understand few terms related to it.
Reflection of Light: Definition, Types, Laws & More ... Using these laws, the reflection of the incident ray on various surfaces like a plane mirror, water, metal surfaces, etc can be determined. For instance, if we consider a plane mirror, here are the laws of reflection: The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray must lie in the same plane.
prove thesurfacelaw OF Refltion ata plain with diagram ... Find an answer to your question prove thesurfacelaw OF Refltion ata plain with diagram patilsonali13512 patilsonali13512 4 days ago Physics Secondary School answered Prove the surface law OF Refltion at a plain with diagram 1 See answer patilsonali13512 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points.
Regular and Diffused Reflection - GeeksforGeeks Regular Reflection. The bouncing back of the incident light from the surface is known as reflection. If the reflection occurs following the laws of reflection it is known as the regular reflection. It follows both the laws of reflection. The reflected ray from the surface forms the same angle of reflection which is equal to the angle of incidence.
Selina Chapter 4 Light Energy Questions Answers Class 7 ... Draw a diagram showing the reflection of a light ray from a plane mirror. Label on it the incident ray, the reflected ray, ... Describe an experiment to verify the laws of reflection of light. Ans. Laws of reflection. Answer (i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, lie in the.
Draw neat and labelled ray diagram of reflection of light ... This explains laws of reflection of light from plane reflecting surface on the basis of Huygens' wave theory. Note: 1. Frequency, wavelength and speed of light do not change after reflection. 2. If reflection takes place from a denser medium, then phase changes by π radian.
State and explain the laws of reflection of light - Tutorix Answered on 22nd Mar, 2021 (a) The two laws of reflection are as follows: 1. The angle of incidence (∠ i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠ r), which is given as, ∠ i = ∠ r . For example, if we measure the angle of reflection ∠ NOB in the figure given above, we will find that it is exactly equal to the angle of incidence ∠ AON. 2.
REFLECTION AT CURVED SURFACES - Form 2 Physics Notes ... Sketch on the same diagram the path of the rays after striking the mirror. Relationship between Radius of Curvature and Focal Length. It can be shown through geometry that the radius of curvature is twice the focal length i.e. r=2f. Laws of Reflection in Curved Mirrors. Reflection at curved surfaces also obeys laws of reflection:
Important Questions Light Reflection and Refraction Class ... Answer: Laws of Reflection. a. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence are always in the same plane. b. ∠i = ∠r. Question: Define the term reflection. Answer: The bouncing back of a ray of light in the same medium after striking on a surface of an object.
The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. Which ... Therefore, in the picture attached: - B is the angle of incidence. - C is the angle of reflection. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Answer from: ej02duncan1. SHOW ANSWER. The measure of angle B equals the measure of angle C. Explanation:
Laws Of Reflection Of Light Class 12: Definition ... The first Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. For example, if an incident ray makes and angle of 45 degrees with the normal ray (line perpendicular to the surface at the point). The reflected ray would also make the angle of 45 degrees with the normal ray. Second law of reflection
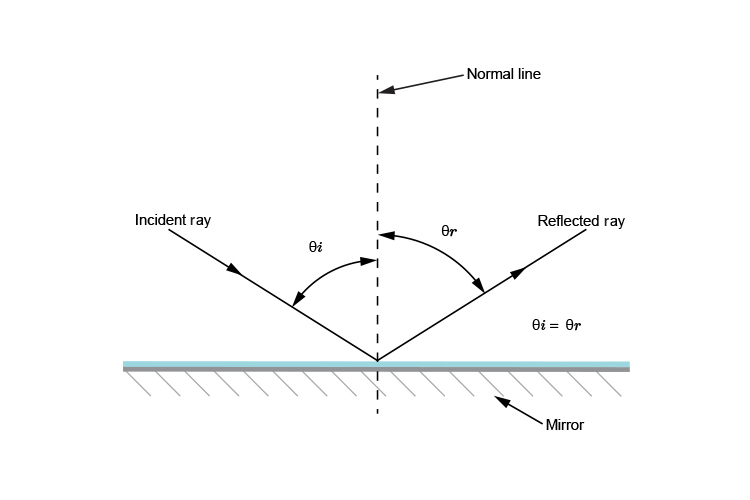

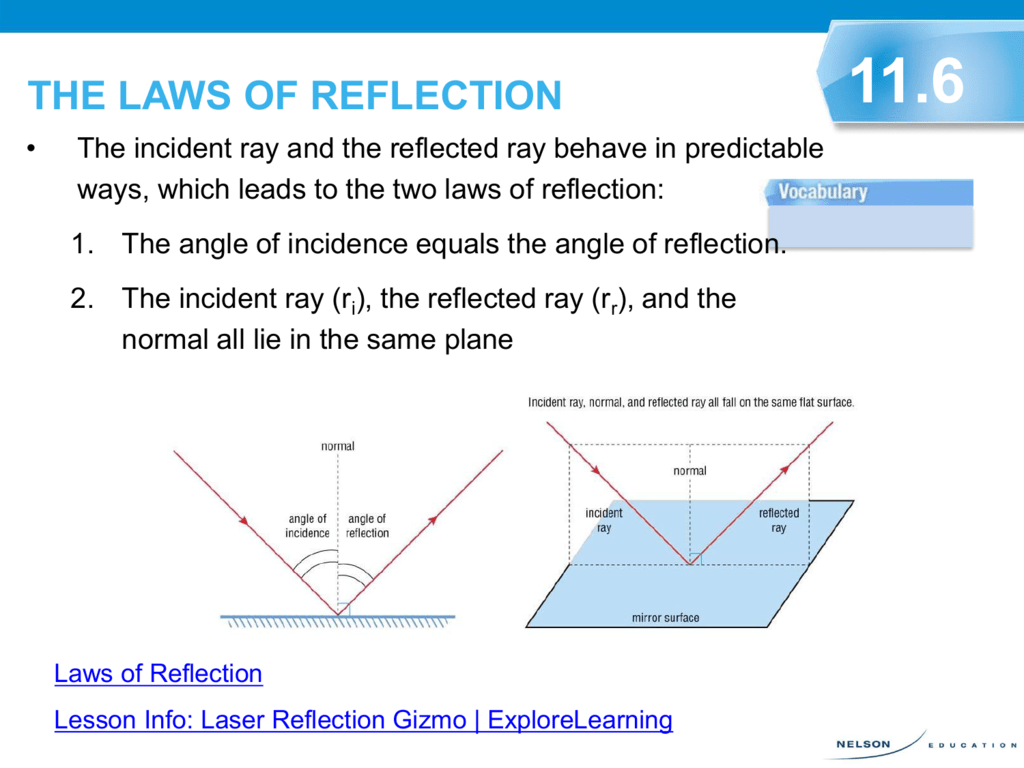


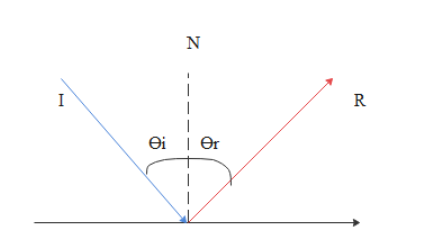



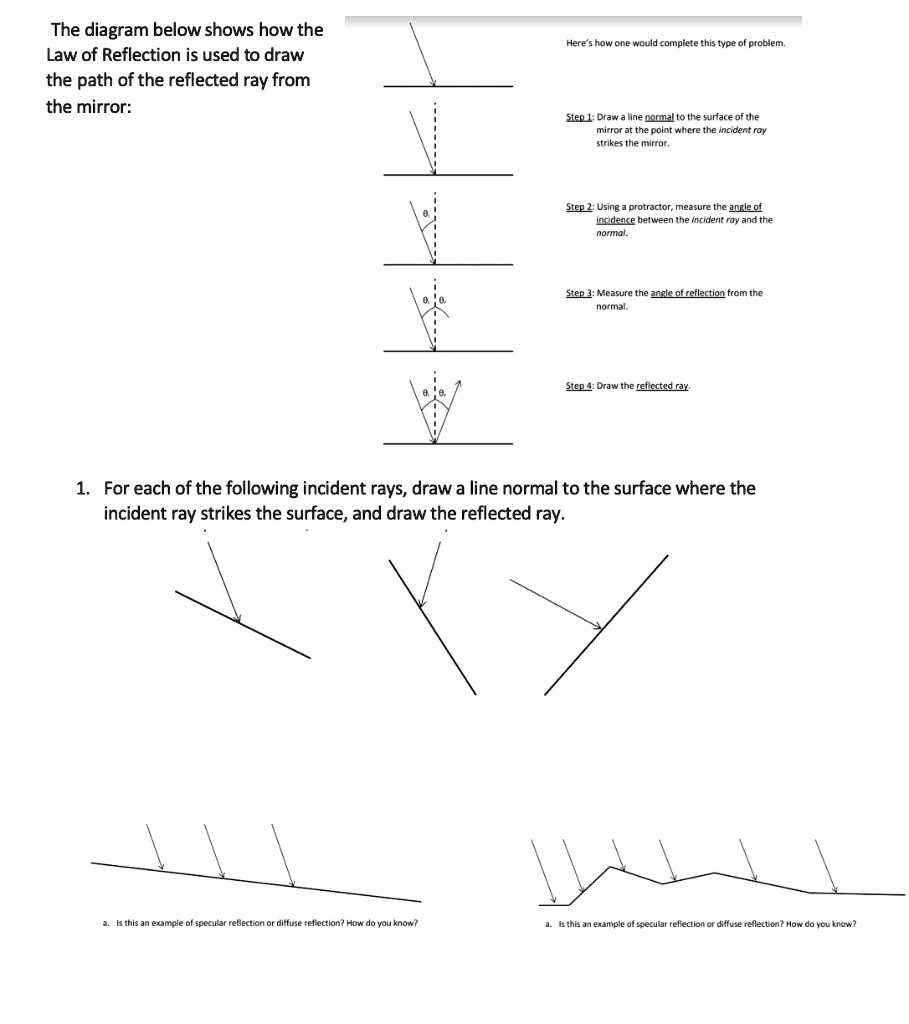


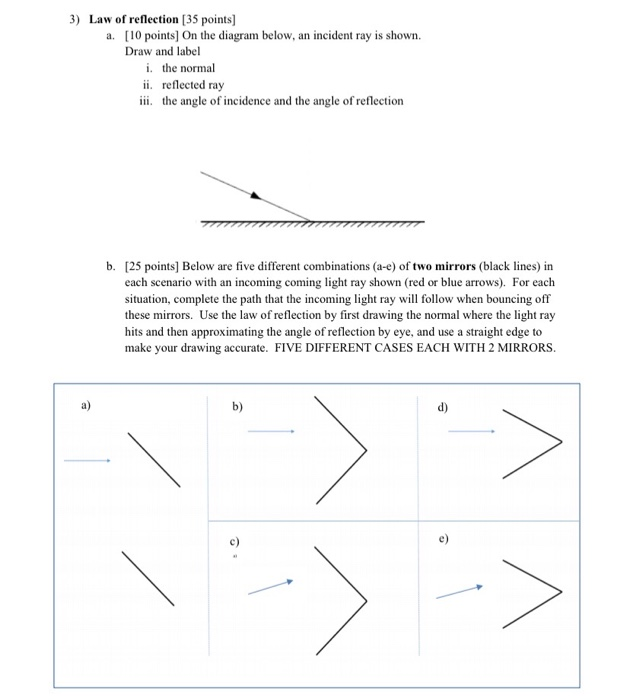
![Solved 2) Law of reflection [35 points] a. [10 points] On ...](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media%2F1eb%2F1ebb8037-d34b-45a6-a7dd-e7d711b040c5%2FphpB6Fcqx.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)









0 Response to "43 Laws Of Reflection Diagram"
Post a Comment