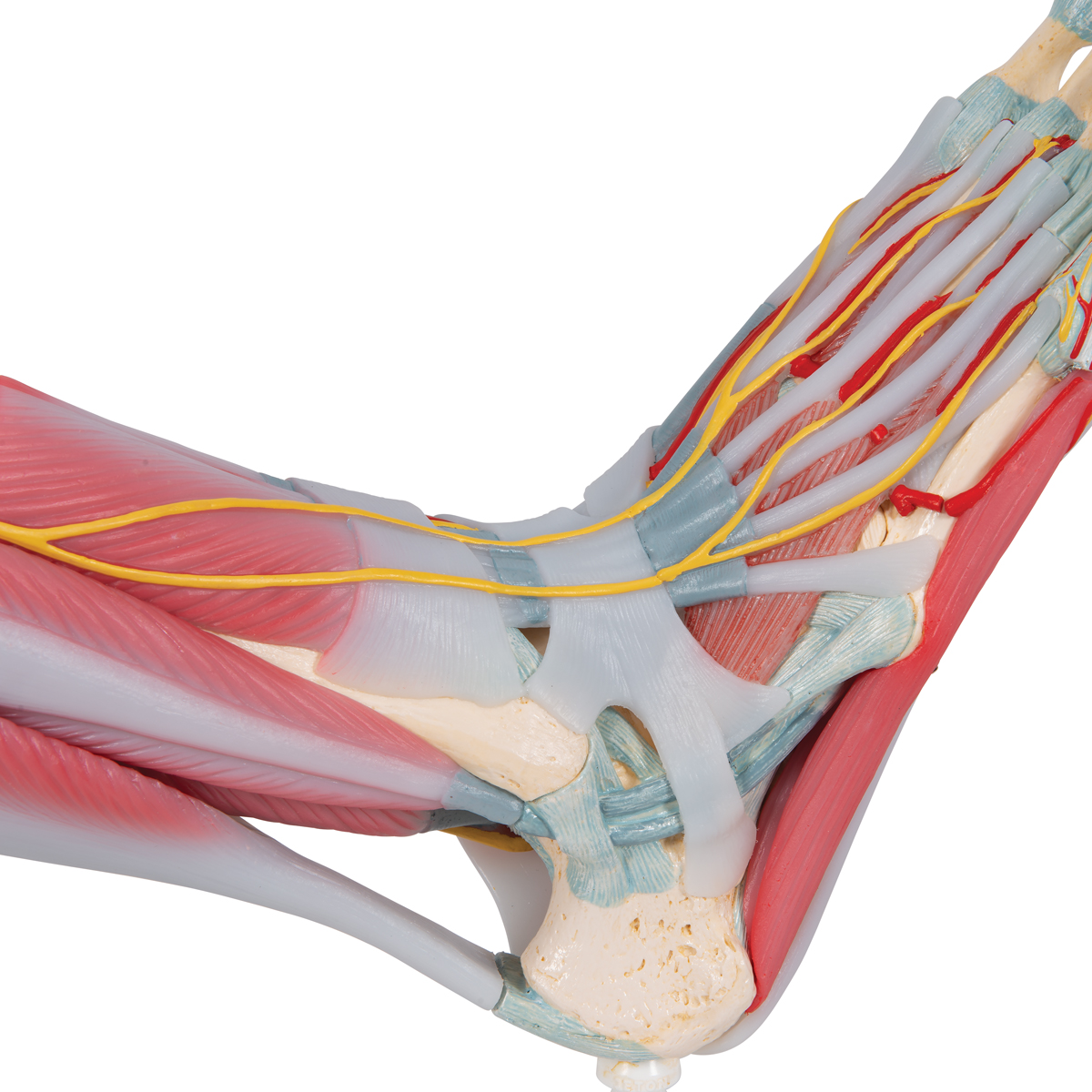
42 nerves of the foot and ankle diagram
Physical Examination of the Foot and Ankle | Musculoskeletal Key Epidemiologically, foot and ankle complaints are the third most common musculoskeletal reason for adult patients to present in a primary care setting This chapter provides a review of foot and ankle anatomy and examination followed by an evidence-based discussion of the major provocative tests... Foot Arthritis, Nerve and Tendon Issues Treatment for foot arthritis, bunions, flat feet, pinched nerves and other foot and ankle problems at Froedtert & the Medical College of Wisconsin. There may be weakening of the supporting structures of the joints, and bunions, claw toes, hammer toes or rheumatoid nodules may develop.
Ankle and Foot - Physiopedia Original Editor - Rachael Lowe Top Contributors - Rachael Lowe , Iva , Admin , Kim Jackson , Leana Louw , Candace Goh , Samson Chengetanai , Nikhil Benhur Abburi , Xiomara Hernandez , Rania Nasr , Alex Benham , Tony Lowe , Tyler Shultz , Sharon Schumacher , Cath Young , Didzis Rozenbergs...

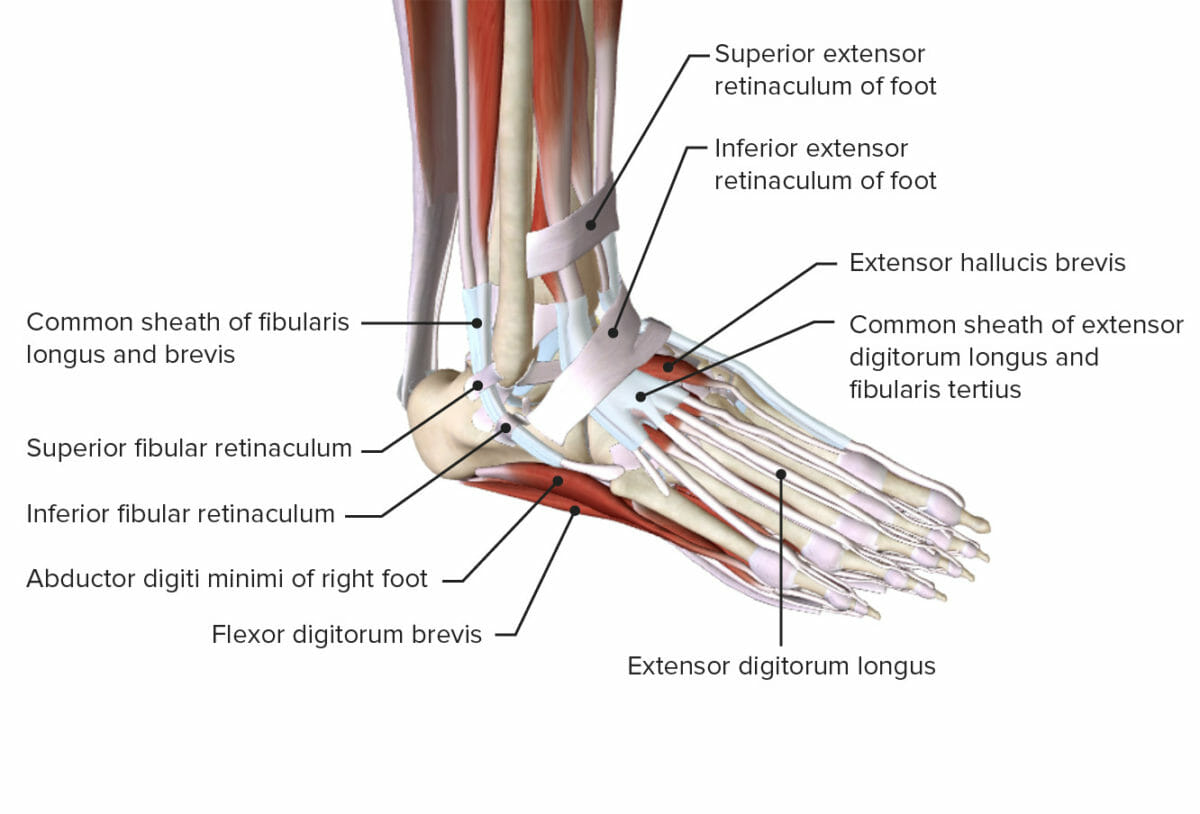
Nerves of the foot and ankle diagram
Ankle Block - Landmarks and Nerve Stimulator Technique... | NYSORA Anesthesia of the foot can be accomplished by blocking the five peripheral nerves that innervate the area at the level of the ankle. Ankle block impairs ambulation on the affected leg, but to a lesser degree than sciatic or popliteal block, and patients can be discharged home before the block wears off. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Foot Nerves Article Embryological derivatives of the foot nerves arise from the development of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neuropathies of the ankle and foot are uncommon and often underdiagnosed. Neuropathies may arise from metabolic processes, such as diabetes or alcohol abuse, or as a result... The Foot and Ankle: Congenital and Developmental Conditions Treatment aims to preserve the foot, stabilize the ankle, and correct leg length discrepancies. The ball-and-socket ankle is characterized by a hemispheric configuration of the articular surface of the talus on both frontal and lateral radiographs, with corresponding congruent concavity of the distal...
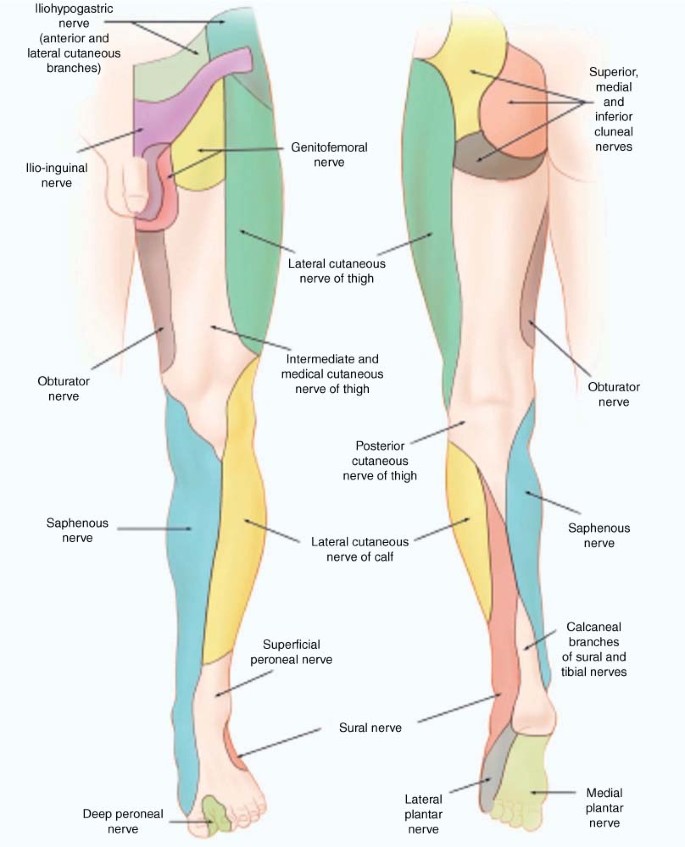
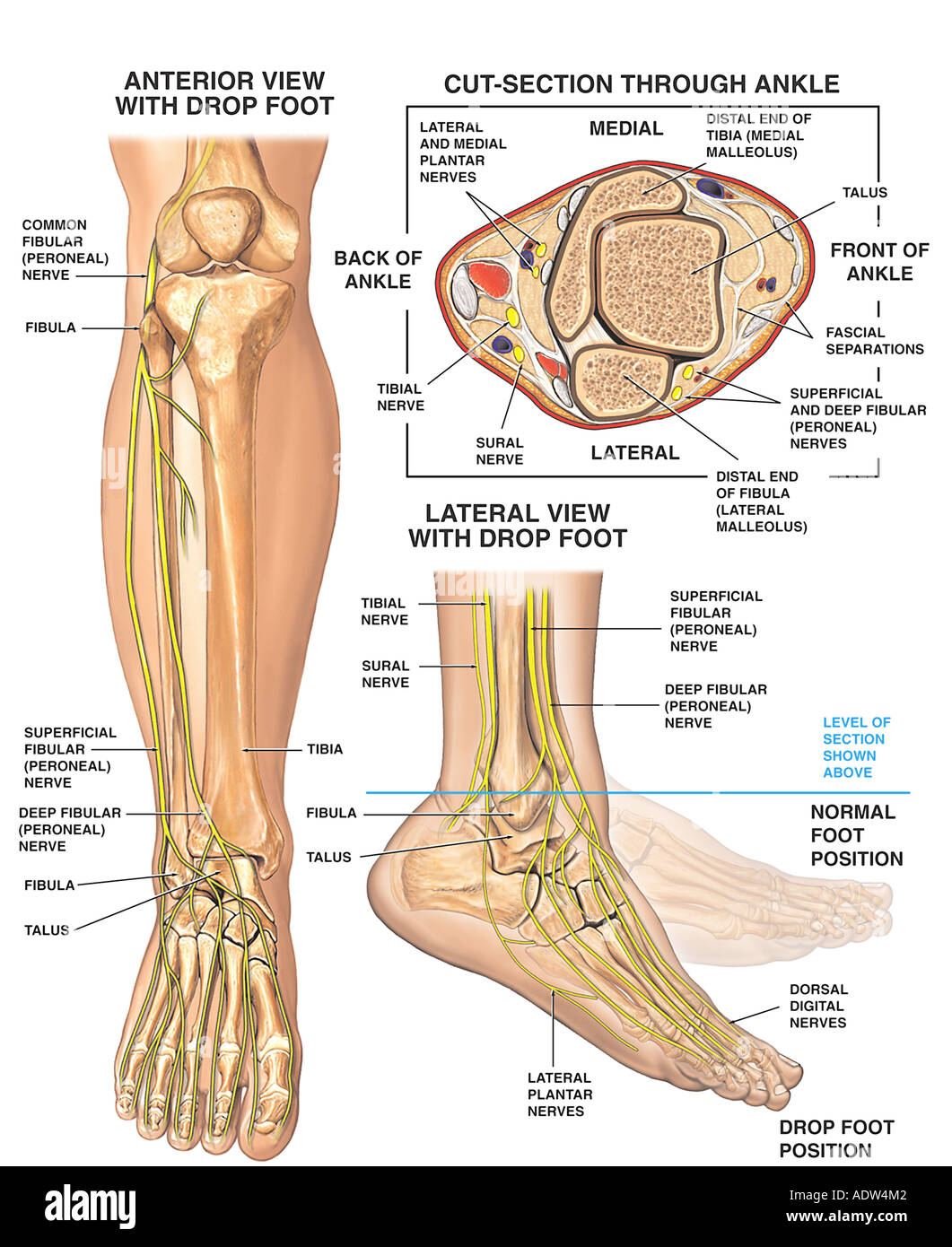
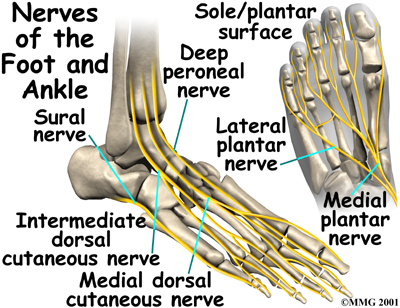
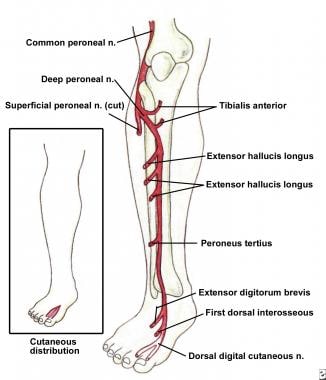
Nerves of the foot and ankle diagram. Foot Drop: Background, Anatomy, Pathophysiology The foot and ankle dorsiflexors include the tibialis anterior, the extensor hallucis longus (EHL), and Diagram of ground reaction vector during heel strike. View Media Gallery. This causes the foot to The peroneal nerve crosses laterally to curve over the posterior rim of the fibular neck to the anterior... Dorsal digital nerves of foot - Wikipedia Dorsal digital nerves of foot are branches of the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve, medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, sural nerve and deep fibular nerve. There are 10 total dorsal digital branches: The medial terminal branch (internal branch) divides into two dorsal digital nerves... Nerves of Foot - Earth's Lab Main innervation of foot is done by the: Tibial Nerve Deep Fibular Nerve Superficial fibular Nerve Sural Nerve Saphenous Nerves The tibial nerve travels inside… Terminal branches supply skin on the medial side of the proximal foot and enter the foot in superficial fascia on the medial part of the ankle. Anatomy of the foot | Structural diagram of foot | Patient Between them, the two feet need to balance the weight of the body, redistributing it in response to The talus connects with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint, and the calcaneum is the bone The muscles are located mainly in the sole of the foot and divided into a central (medial) group and a...
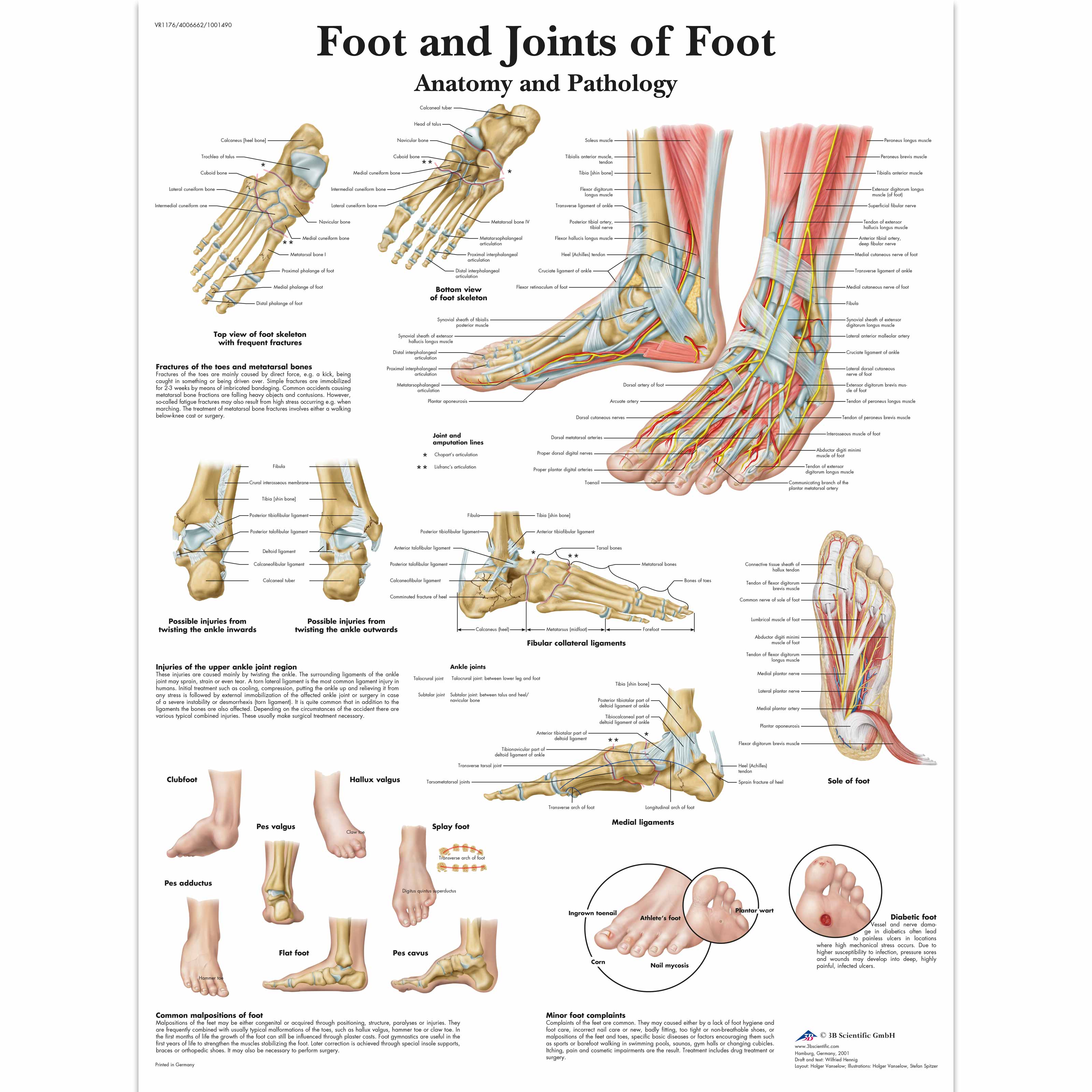
Human Anatomy Fundamentals: How to Draw Feet The foot may well be the most neglected part of the body, largely because it's so often hidden inside a shoe, or simply left outside the frame of the drawing - out of sight and out of mind. The bones of the foot are arranged to form 3 arches that give it the strength to support our bodies. Ankle and foot anatomy: Bones, joints, muscles | Kenhub Ankle and foot (left lateral view). If you've watched a documentary film about primates likes chimps or orangutans you may have thought how useful it Bones and ligaments of the foot (diagram). Tarsals make up a strong weight bearing platform. They are homologous to the carpals in the wrist and are... PDF joints of the foot Arches of the foot - ligaments. • Plantar aponeurosis: from calcaneal tubercle to the plantar surfaces of toes. Works when the body is standing; stabilizes During walking, many anatomical features of the lower limbs contribute to minimizing fluctuations in the body's center of gravity and thereby reduce the... Foot Anatomy Dr Rania Gabr. - ppt video online download Objectives Know the retinaculae around the ankle and their relations. Discuss the characteristic features of joints of foot. 17 Sole : DEEP FASCIA The plantar aponeurosis is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia that protects the underlying nerves, blood vessels, and muscles.
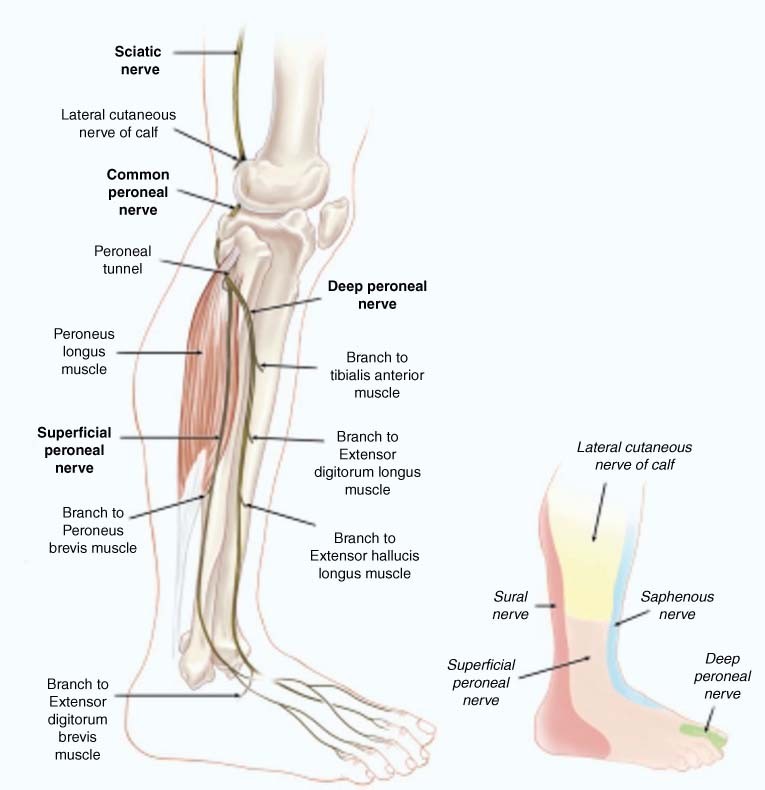
Nervous System: Explore the Nerves with Interactive Anatomy Pictures The Human Nervous System - Interact with diagrams and descriptions of the nervous system anatomy of the human body, everything from the brain to The sensory nerves and sense organs of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) monitor conditions inside and outside of the body and send this... IX. Neurology. 6e. The Sacral and Coccygeal Nerves. Gray, Henry. The nerves forming the sacral plexus converge toward the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen, and unite to form a flattened band, from the anterior and It runs forward below the lateral malleolus, and is continued as the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve along the lateral side of the foot and little toe... The Ankle Joint - Articulations - Movements - TeachMeAnatomy The ankle joint (or talocrural joint) is a synovial joint, formed by the bones of the leg and the foot - the tibia, fibula, and talus. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the ankle joint; the articulating surfaces, ligaments Innervation is provided by tibial, superficial fibular and deep fibular nerves. Ankle/ foot nerves Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Ankle/ foot nerves. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. sensory- posterior heel and plantar surface of foot. motor- semitendonosus/membranosus, biceps femoris, Magnus, gastroc, soleus, plantaris, flexor hallucis...
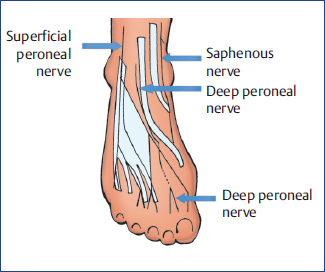
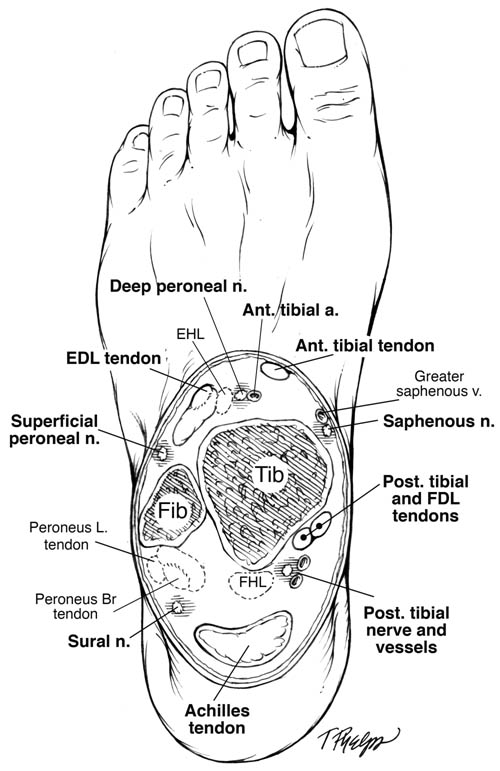
Nerve Blocks of the Foot and Ankle — Downeast Emergency Medicine The superficial peroneal, sural, and saphenous nerves are located in the subcutaneous tissue encircling the ankle. The tibialis interior can be located by having the patient dorsi flex the foot and invert the ankle. The injection site should be at the level of the superior malleolus and between the...
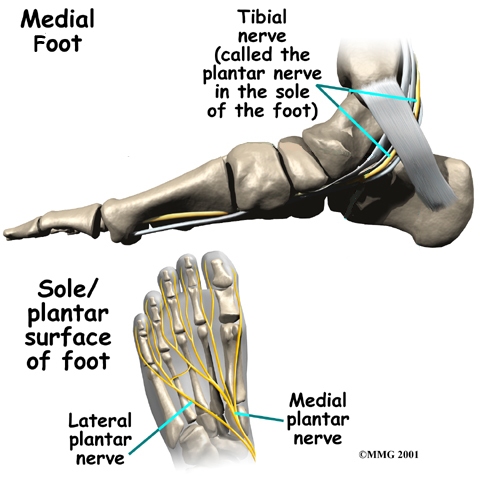
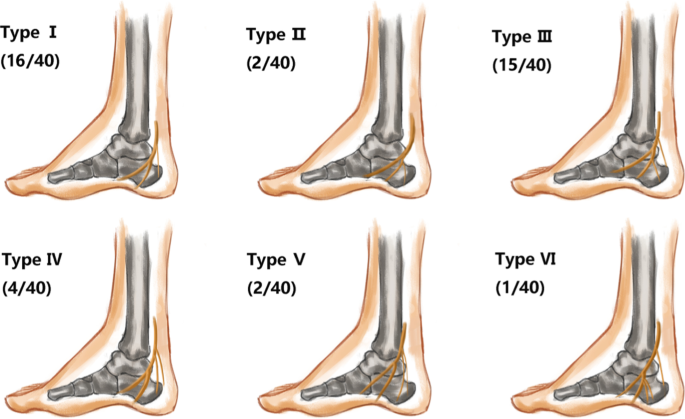
Nerves of the Foot - Foot & Ankle - Orthobullets Nerves of the Foot branches of the tibial nerve. What is the first branch off of the lateral plantar nerve and what specific muscle does it innervate?
Damage to the Nerves in the Foot... - Merck Manuals Consumer Version The nerves that supply the bottom of the foot and toes (interdigital nerves) travel between the bones of the toes. Pain in the ball of the foot may be Many factors contribute to nerve irritation, particularly nonsupportive or poorly fitting shoes. Other factors include thinning of the fat around the nerves, poor...
Muscles of the Foot | Intrinsic | Function | Geeky Medics The foot is anatomically defined as the distal part of the lower extremity and encompasses all structures below the ankle joint . All intrinsic muscles of the foot are innervated by branches of the tibial nerve except for extensor digitorum brevis, which is innervated by the deep fibular nerve .
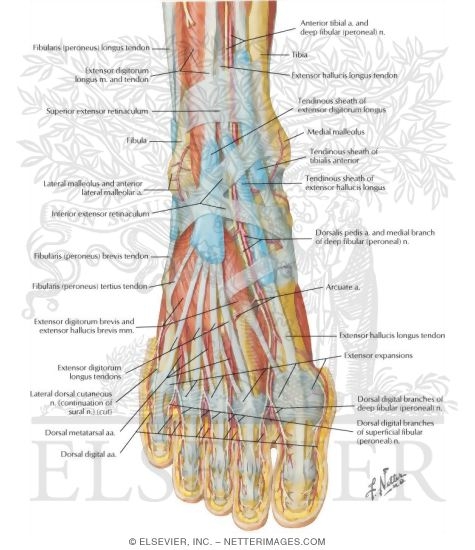
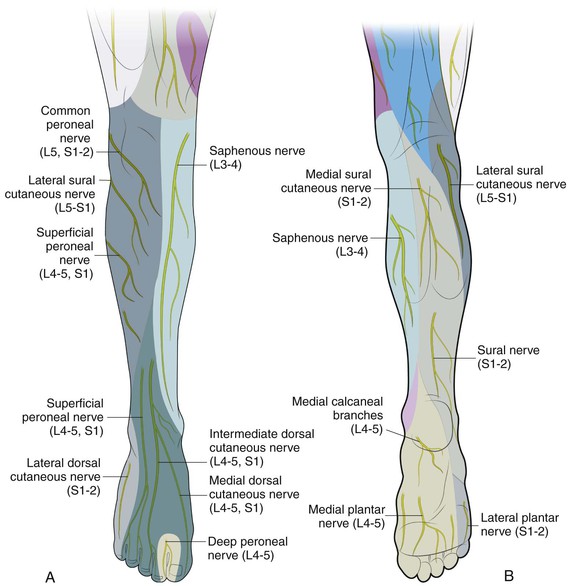
Anatomy of the foot | Osmosis | Labeled Diagrams Figure 9. Cutaneous Innervation of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot B. Anterior View of Left Foot and Ankle. Finally, the medial plantar nerve terminates near the bases of the metatarsals by dividing into three sensory branches called the common plantar digital nerves.
Feet (Human Anatomy): Bones, Tendons, Ligaments, and More WebMD's Feet Anatomy Page provides a detailed image and definition of the parts of the feet and explains their function. The feet are flexible structures of bones, joints, muscles, and soft tissues that let us stand upright and perform activities like walking, running, and jumping.
Foot (Anatomy): Bones, Ligaments, Muscles, Tendons, Arches and Skin The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animal's weight and allowing for locomotion on land. Here we will discuss the most important parts of the anatomy of the foot, and some injuries and disorders that can occur when these parts are damaged.
Nerves Of The Leg & Foot - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil... Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes the nerves of the lower leg in a very easy and simple animation.Lateral cutaneous nerve of the calfSural...
Foot Anatomy, Physiology, and Common Conditions | Verywell Health The foot contains many bones, muscles, tendons, and other structures. Learn how they work together, plus what can go wrong due to overuse or injury. This article offers a brief overview of the structures of the foot and how they work together. It also looks at some common problems that can arise from...
Foot Condition By Area | Top of Foot | Sol Foot & Ankle Centers Match the corresponding numbers on the foot diagram below for a list of conditions that may be causing your foot and ankle pain. Morton's Neuroma - A painful condition that most commonly affects the ball of the foot and is caused by a thickening of the nerve tissue.
Foot Pain Diagram - Why Does My Foot Hurt? | F. Ankle Sprain A foot pain diagram is a great tool to help you work out what is causing your ankle and foot pain. There are a whole range of structures e.g. bones, muscles, tendons and nerves which will each give slightly different foot pain symptoms. The foot pain identifier diagrams you find here will help you to...
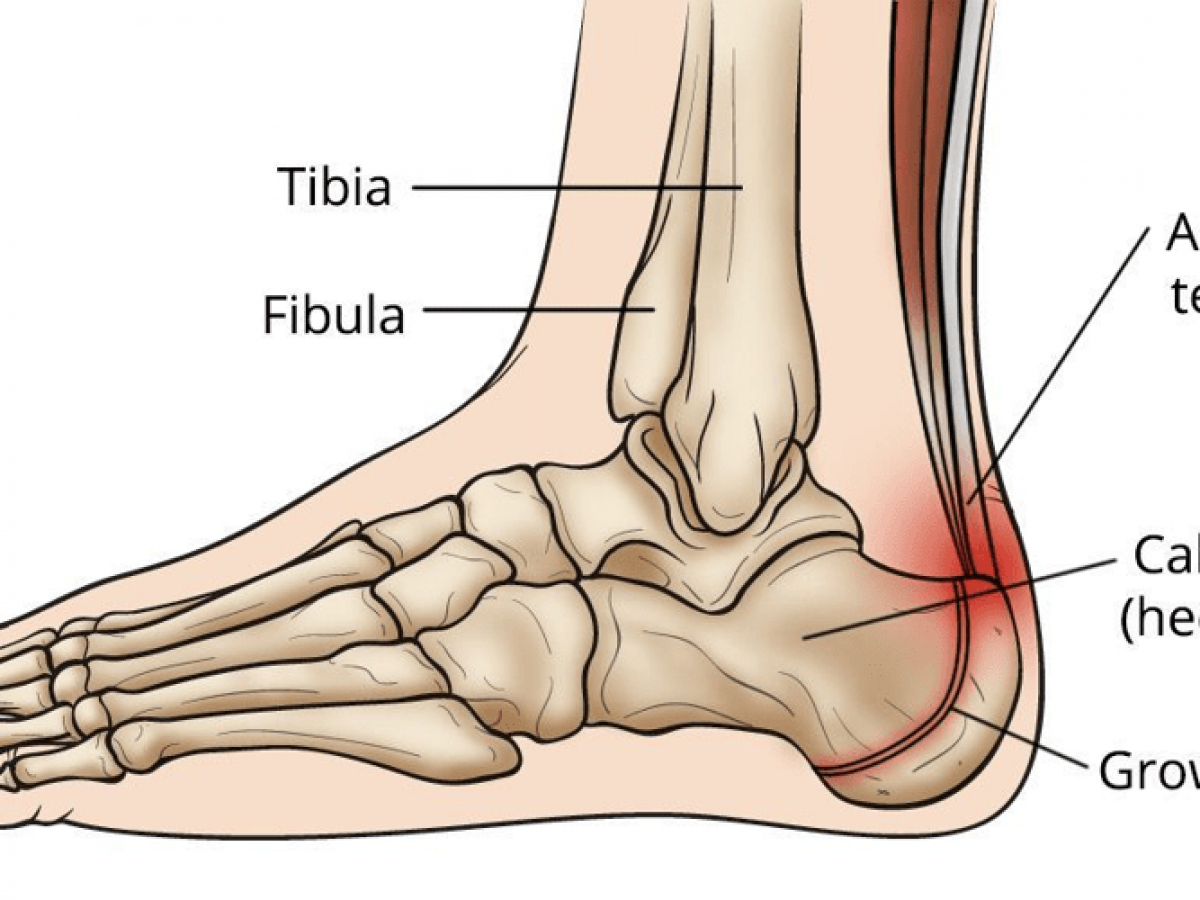
The leg, ankle, and foot - Knowledge @ AMBOSS The foot has one transverse and two longitudinal arches that help distribute body weight. The leg (crus) has an anterior, posterior, and lateral compartment. The anterior compartment (extensor compartment), which is innervated by the peroneal nerve, contains muscles involved in ankle dorsiflexion and foot...
The Foot and Ankle: Congenital and Developmental Conditions Treatment aims to preserve the foot, stabilize the ankle, and correct leg length discrepancies. The ball-and-socket ankle is characterized by a hemispheric configuration of the articular surface of the talus on both frontal and lateral radiographs, with corresponding congruent concavity of the distal...
Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Foot Nerves Article Embryological derivatives of the foot nerves arise from the development of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Neuropathies of the ankle and foot are uncommon and often underdiagnosed. Neuropathies may arise from metabolic processes, such as diabetes or alcohol abuse, or as a result...
Ankle Block - Landmarks and Nerve Stimulator Technique... | NYSORA Anesthesia of the foot can be accomplished by blocking the five peripheral nerves that innervate the area at the level of the ankle. Ankle block impairs ambulation on the affected leg, but to a lesser degree than sciatic or popliteal block, and patients can be discharged home before the block wears off.









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/footpainfinal-01-d507e82b3e844d068c0089cbb7004d76.png)






:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11040/537_m_lumbricales_fkt.png)





0 Response to "42 nerves of the foot and ankle diagram"
Post a Comment