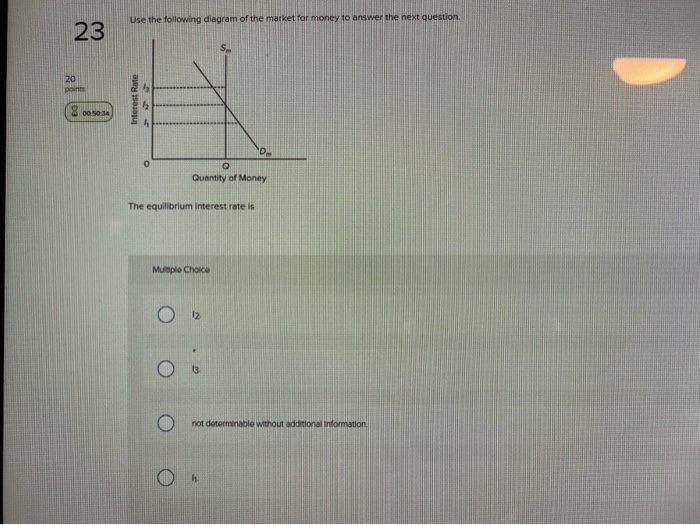
44 refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is
Module 8 Chapters 34 & 35 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall. IS-LM Curve (With Diagram): An Overview - Economics Discussion The right hand diagram [part (b)] shows the money market. The supply of money is the vertical line M, since it is fixed by the Central Bank. The two demand for money curves L 1 and L 2 correspond to two different income levels. When the income level is Y 1, the demand curve for money is L 1 and the equilibrium rate of interest is n.
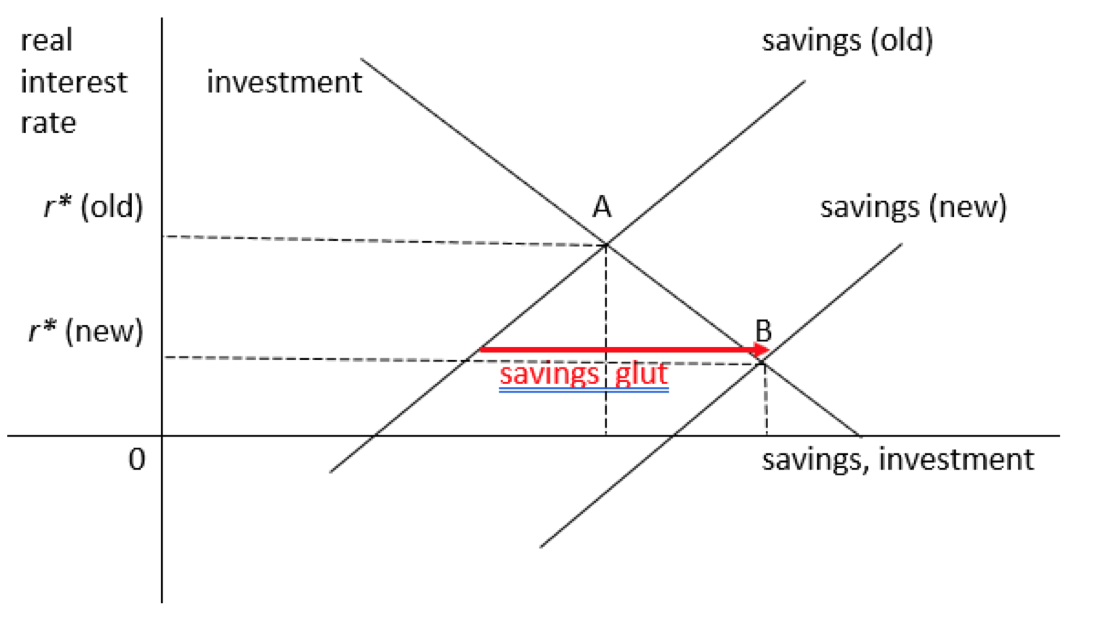
PDF Measuring the equilibrium real interest rate; The equilibrium real interest rate is a crucial concept in the new Keynesian class of models. This rate represents the real rate of return required to keep the economy's output equal to potential output, which, in turn, is the level of output consistent with flexible prices and wages and constant markups in goods and

Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is
Refer to the following table on the Money Market. Interest ... 3. Refer to the following table on the Money Market. Interest rate Demand for Money Supply of Money (peroent) (billions of dollars) (billions of dollars) 200 a. Determine the equilibrium interest rate using the data table above. b. Suppose the Central Bank increases the money supply by $100 billion. Expansionary Monetary Policy and Its Effects (With Diagram) Result: People will sell bonds and thus asset price will fall leading to rise in interest rate. Thus, due to increase in demand for money the interest rate will increase and, thus, move up on the LM 1 curve till a new equilibrium point is reached. This is at point E 2.. Thus, At point E 2: both product and money market is in equilibrium (IS = LM,). Interest Rate Determination - GitHub Pages Since the interest rate is identical to the rate of return on dollar assets from a U.S. dollar holder's perspective (i.e., RoR $ = i $), we can now place the RoR diagram directly on top of the rotated money market diagram as shown in Figure 18.8 "Money-Forex Diagram". The equilibrium interest rate (i′ $), shown along the horizontal axis ...
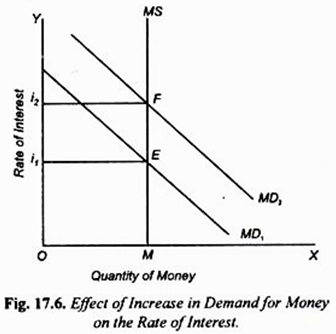
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is. Finance: Chapter 60-3: Derivation of the AA Curve The real money demand function with GNP level Y $ 1 intersects with real money supply at point G1 in the money market diagram determining the interest rate i $ 1. The interest rate in turn determines RoR $ 1 which intersects with RoR £ at point G 2 determining the equilibrium exchange rate E $/£ 1. These two values are transferred to the ... revmoney Refer to the above diagram of the money market. The equilibrium interest rate is: A. i *B 1. B. ... R-1 F13072: Refer to the above diagram of the money market. Other things equal, the money demand curve in the diagram would shift leftward if: A. the asset demand for money increased. B. the transactions demand for money increased. C. nominal GDP ... econ 1040- chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram of the market for money. The vertical money supply curve Sm reflects the fact that: the stock of money is determined by the Federal Reserve System and does not change when the interest rate changes. financial economics - What is the interest rate that on ... The money market diagram showing liquidity preference and money supply intersect at an equilibrium level of interest rate, but what interest rate is it? Within the teaching model, there is a portfolio allocation between "money" and some interest-paying instrument (labelled "bonds" or "bills").
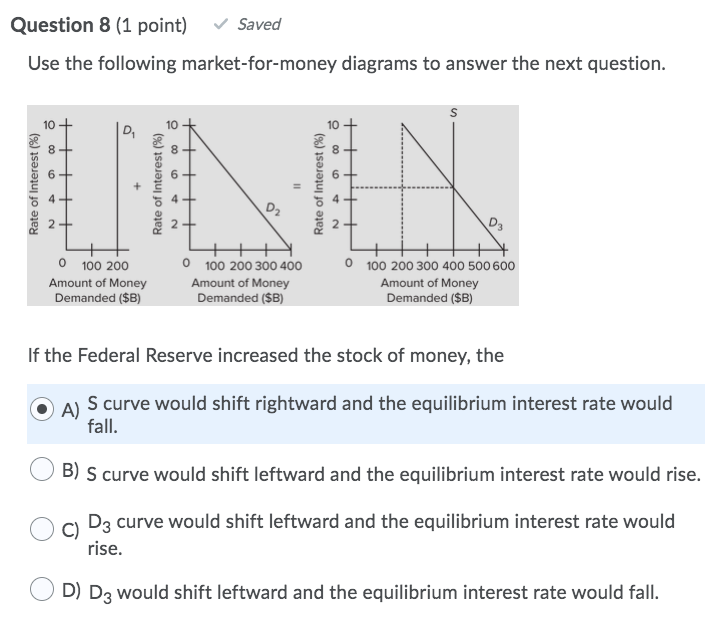
Refer to the above diagram of the money market The ... See Page 1. 89. Refer to the above diagram of the money market. The equilibrium interest rate is: A) i1. B) i2. C) i3. D) not determinable without additional information. Answer: B. McConnell/Brue: Economics, 16/e Page 417. Solved 27) 2 Quantity of Money Refer to the diagram of the ... Economics questions and answers. 27) 2 Quantity of Money Refer to the diagram of the market for money. The equilibrium interest rate is A) /3. C) /2. D) not determinable without additional information. 28) Which of the following is an asset on the consolidated balance sheet of the Federal Reserve Banks? econ ch.16 You'll Remember - Quizlet Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. Refer to the above diagram of the money market Given Dm ... 156. Refer to the above diagram of the money market. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: A) supply of bonds in the bond market will decline and the interest rate will rise. B) supply of bonds in the bond market will increase and the interest rate will decline.
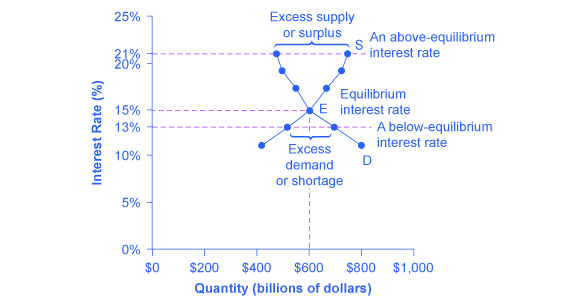
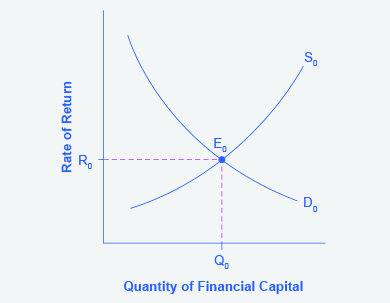
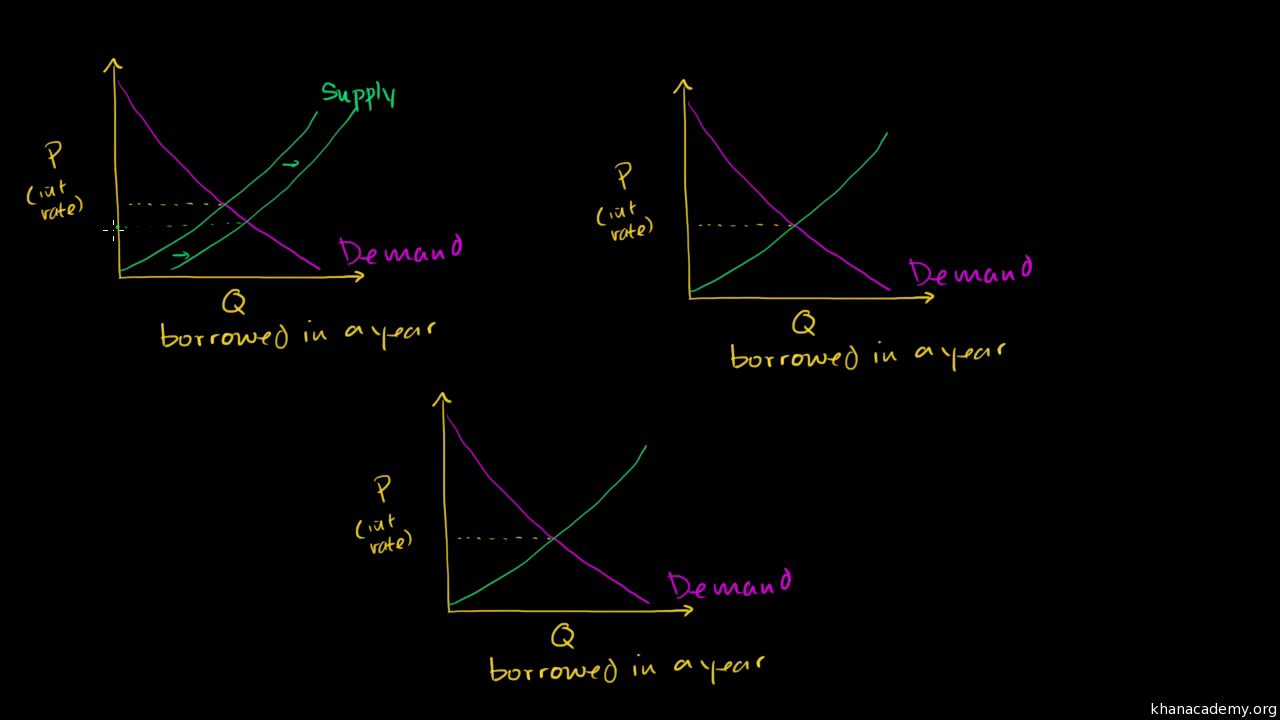
4.2 Demand and Supply in Financial Markets - Principles of ... In this market for credit card borrowing, the demand curve (D) for borrowing financial capital intersects the supply curve (S) for lending financial capital at equilibrium €. At the equilibrium, the interest rate (the "price" in this market) is 15% and the quantity of financial capital being loaned and borrowed is $600 billion. Integrating the Money Market and the Foreign Exchange Markets The equilibrium interest rate ( i ′ $ ), shown along the horizontal axis above the rotated money market diagram, determines the position of the RoR$ line in the Forex market above. This combined with the RoR£ curve determines the equilibrium exchange rate, E ′ $/£, in the Forex market. PDF PRACTICE- Unit 6 AP Economics - St. Johns County School ... If the interest rate is above the equilibrium rate, there will be an _____ money and the interest rate will _____. A. excess demand for; rise B. excess supply of; fall C. excess demand for; fall D. excess supply of; rise E. excess supply of; remain the same 35. Use the "Money Market II" Figure 28-1. If the rate of interest is below the ... Loanable Funds Market: Concept and How it Works - Penpoin. Suppose the market interest rate is higher than the equilibrium interest rate. In that case, the market faces an excess supply of loanable funds. As a result, interest rates have a tendency to fall. Because interest rates are higher, borrowing costs are more expensive. This causes the demand for loanable funds to decrease.
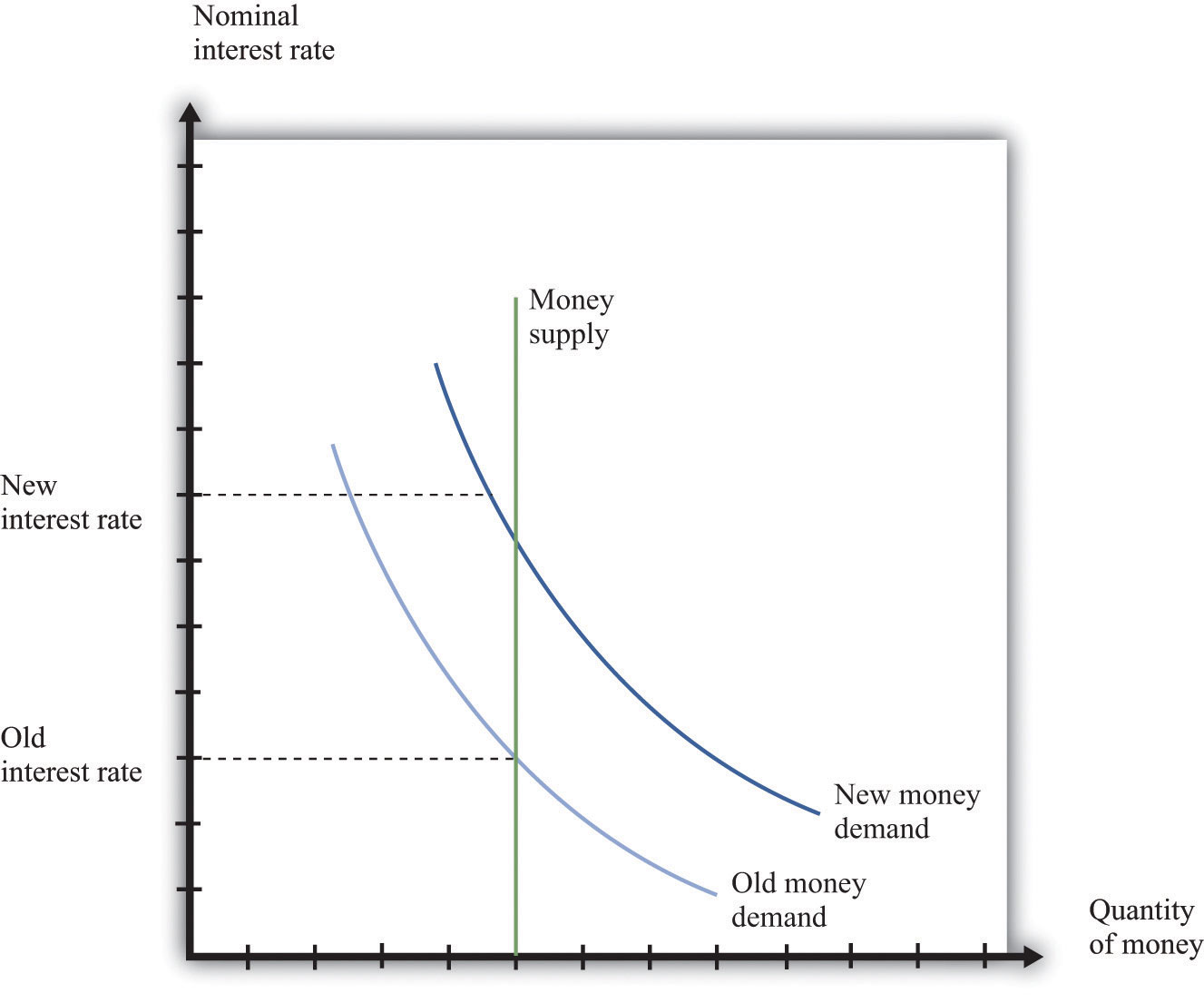
25.2 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in the Money Market ... Figure 25.12 An Increase in the Money Supply. The Fed increases the money supply by buying bonds, increasing the demand for bonds in Panel (a) from D1 to D2 and the price of bonds to Pb2. This corresponds to an increase in the money supply to M ′ in Panel (b). The interest rate must fall to r2 to achieve equilibrium.
Derivation of the AA Curve - GitHub Pages The real money demand function with GNP level Y $ 1 intersects with real money supply at point G 1 in the money market diagram determining the interest rate i $ 1. The interest rate in turn determines RoR $ 1, which intersects with RoR £ at point G 2, determining the equilibrium exchange rate E $/£ 1.
ECON 131 Homework Chapter 16 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall.
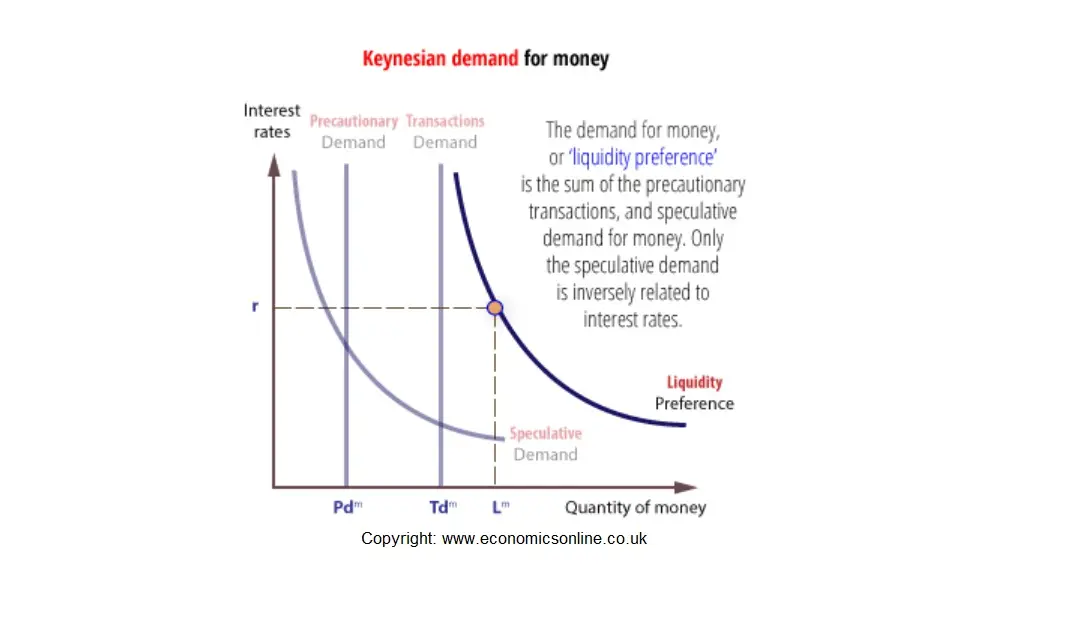
macro chapter 16 Flashcards - Quizlet On a diagram where the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded are shown on the vertical and horizontal axes respectively, the transactions demand for money can be represented by: a line parallel to the horizontal axis. a vertical line. a downsloping line or curve from left to right. an upsloping line or curve from left to right.
The equilibrium rate of interest in the market for money ... Accessibility: Keyboard Navigation Difficulty: Medium Learning Objective: 15-01 Discuss how the equilibrium interest rate is determined in the market for money. McConnell - Chapter 15 #47 Topic: 15-02 The Demand for Money Type: Application McConnell - Chapter 15 48. Refer to the above table. Suppose the transactions demand for money is equal to 20 percent of the nominal GDP, the supply of ...
Answered: Refer to the graph. If the initial… | bartleby Business Economics Q&A Library Refer to the graph. If the initial equilibrium interest rate was 5 percent and the money supply increased by $100 billion, then the new interest rate would be 6.
Refer to the above diagram of the market for money The ... Refer to the above market for money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the: S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D 3 would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
Derivation of the AA Curve - lardbucket The real money demand function with GNP level Y $ 1 intersects with real money supply at point G 1 in the money market diagram determining the interest rate i $ 1. The interest rate in turn determines RoR $ 1, which intersects with RoR £ at point G 2, determining the equilibrium exchange rate E $/£ 1.
Interest Rate Determination - GitHub Pages Since the interest rate is identical to the rate of return on dollar assets from a U.S. dollar holder's perspective (i.e., RoR $ = i $), we can now place the RoR diagram directly on top of the rotated money market diagram as shown in Figure 18.8 "Money-Forex Diagram". The equilibrium interest rate (i′ $), shown along the horizontal axis ...
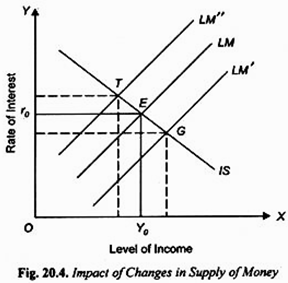
Expansionary Monetary Policy and Its Effects (With Diagram) Result: People will sell bonds and thus asset price will fall leading to rise in interest rate. Thus, due to increase in demand for money the interest rate will increase and, thus, move up on the LM 1 curve till a new equilibrium point is reached. This is at point E 2.. Thus, At point E 2: both product and money market is in equilibrium (IS = LM,).
Refer to the following table on the Money Market. Interest ... 3. Refer to the following table on the Money Market. Interest rate Demand for Money Supply of Money (peroent) (billions of dollars) (billions of dollars) 200 a. Determine the equilibrium interest rate using the data table above. b. Suppose the Central Bank increases the money supply by $100 billion.




/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-hand-giving-paper-money-to-iron-clip-with-conveyor-belt-depicting-investment-170886383-59f0db1d9abed500108ee1ac.jpg)










0 Response to "44 refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is"
Post a Comment