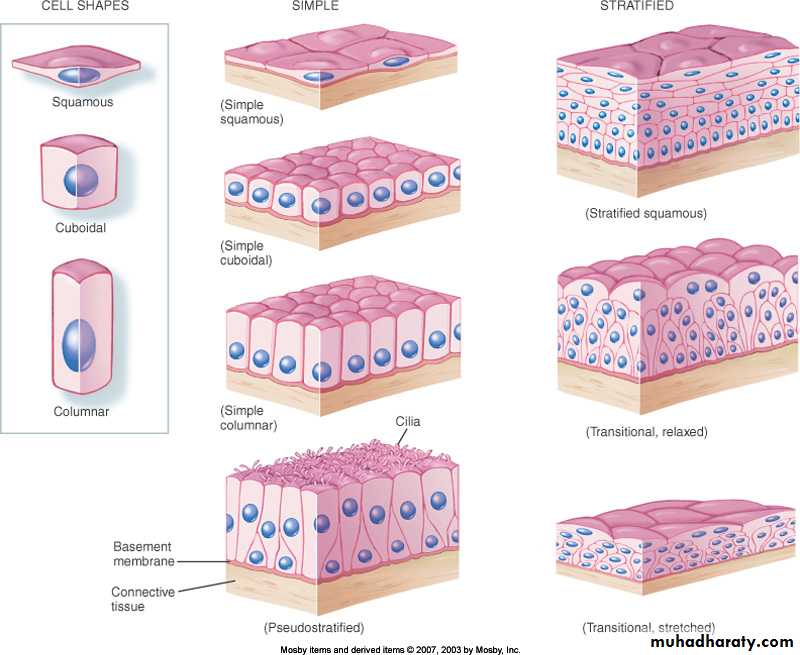
45 diagram of epithelial tissues
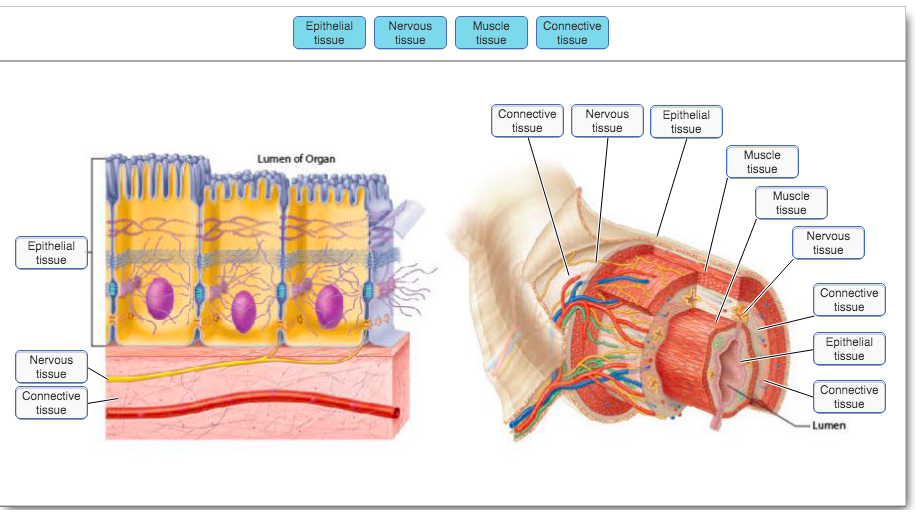
Epithelial Tissue Diagram. Epithelial Tissue Diagram. The epithelium is a complex of specialized cellular organizations arranged into sheets without significant intercellular substance. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells. The epithelial tissues perform many functions including protection from abrasion, radiation damage ... between epithelial cells. Lumen Epithelia usually separate two compartments. Often one compartment is an external space or lumen of a tube and the other is the rest of a tissue or organ. The apical side of the epithelial cells faces the external space or lumen and the basal side faces the rest of the organ. One role for epithelia is to control the
Epithelial cells nuclei (histological slide) Epithelial tissue is a highly cellular tissue that overlies body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands.In addition, specialized epithelial cells function as receptors for special senses (smell, taste, hearing, and vision).Epithelial cells are numerous, exist in close apposition to each other, and form specialized junctions to create a barrier ...
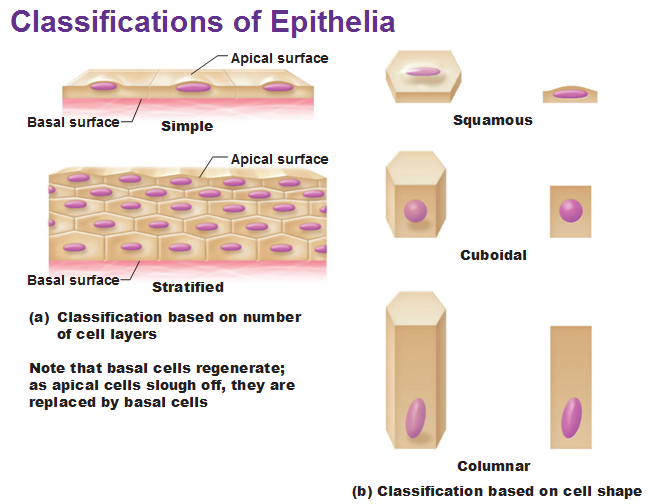
Diagram of epithelial tissues
The epithelial tissue is typically derived from the embryonic ectoderm and endoderm (not the mesoderm). There are four different specific types of epithelial tissues throughout the body. Epithelial Tissues Simple Squamous Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Simple Columnar Epithelium Stratified Epithelium Pseudostratified Epithelium ... diagrams that illustrate the diagnostic features of the following list of tissue types. Be sure to clearly label the significant features of that tissue type. Epithelium is one of only 4 types of human body tissues.Like all types, it is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM). The cells in this tissue are tightly packed within a thin ECM. Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces (surface epithelium) and secreting organs (glandular epithelium). Functions of epithelial tissue are secretion, protection, absorption ...
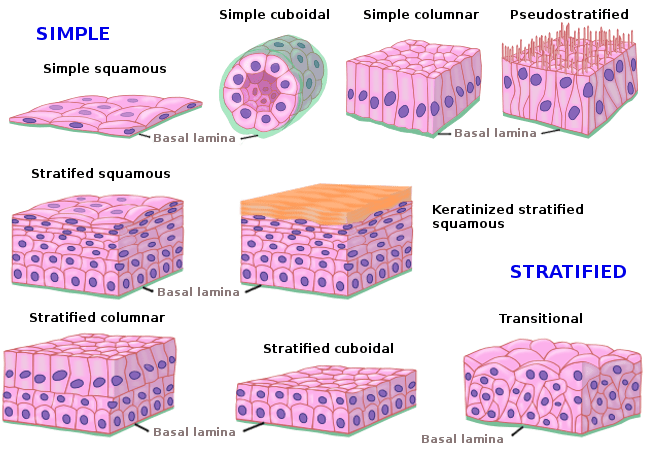
Diagram of epithelial tissues. Simple Columnar Epithelium: A Labeled Diagram and Functions Epithelium is a tissue that lines the internal surface of the body, as well as the internal organs. Simple epithelium is one of the types of epithelium that is divided into simple columnar epithelium, simple squamous epithelium, and simple cuboidal epithelium. Epithelium (/ ˌ ɛ p ɪ ˈ θ iː l i ə m /) is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue.It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with little intercellular matrix.Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities ... Epithelial tissues are composed of layers of tightly connected cells shaped into complex three-dimensional (3D) structures such as cysts, tubules, ... Epithelial tissue in the body is of two types -. A. Simple epithelium: It consists of a single layer of cells where cells are in direct contact with the basement membrane. It is further sub-divided into the following types: (i) Simple squamous epithelium: It consists of a single layer of flat cells with irregular boundaries.
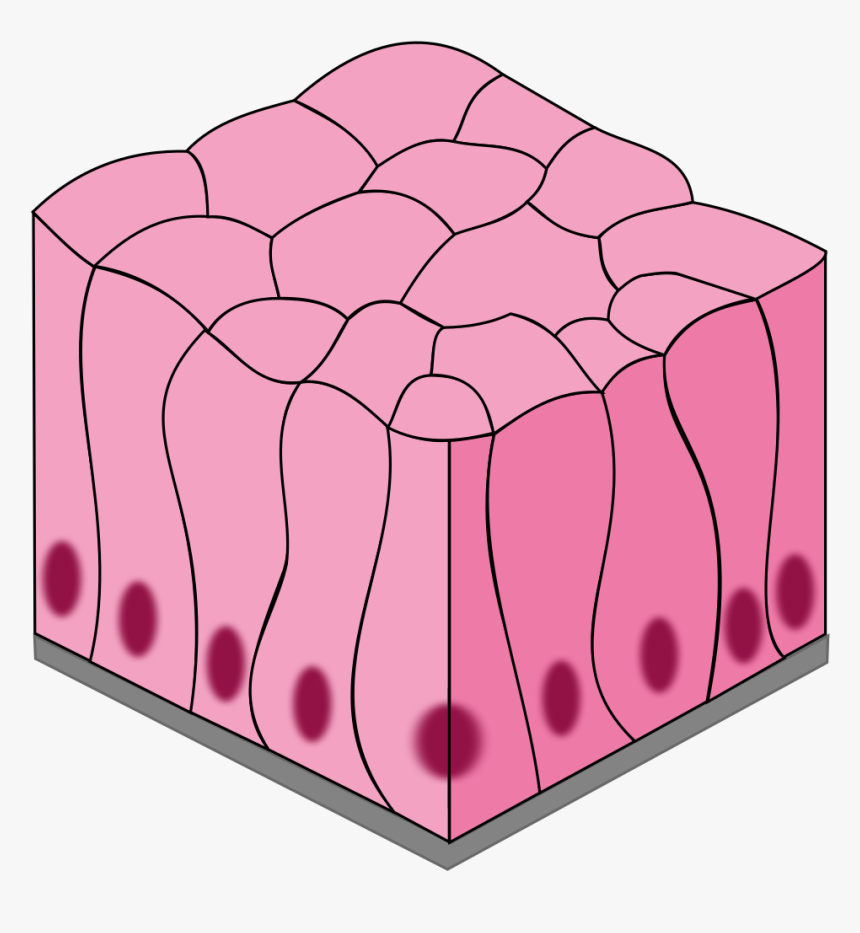
Epithelium is a tissue that lines the internal surface of the body, as well as the internal organs. Simple epithelium is one of the types of epithelium that is divided into simple columnar epithelium, simple squamous epithelium, and simple cuboidal epithelium. Bodytomy provides a labeled diagram to help you understand the structure and function of simple columnar epithelium. Epithelial Tissue definition. Epithelial Tissue is one of the four types of tissue (epithelial, muscular, connective, and nervous) in animals which consists of closely aggregated polyhedral cells adhering firmly to one another, forming cellular sheets that line the interior of hollow organs and cover the body surface. An epithelial tissue or epithelium (plural is epithelia) consists of cells ... cuboidal epithelial tissue | cuboidal epithelial tissue diagram | Biology boostupcuboidal epithelial tissuecuboidal epithelial tissue diagramcuboidal epithel... Epithelial tissues, the second type, are sheets of cells adhering at their side, or lateral, surfaces. They synthesize and deposit at their bottom, or basal, surfaces an organized complex of matrix materials known as the basal lamina or basement membrane. This thin layer serves as…
1 answerDraw diagram of each type of epithelial tissue. types of epithelium. Epithelial cells are the thin protective coverings that line most organs and cavities ... parts, epithelial tissues form the inner lining and external lining of body parts. To summarize, the apical pole faces the surface, while the basal pole is attached to the connective tissue located below the epithelium. Types of epithelial tissue. There are 3 different types of epithelial tissue: squamous, cuboidal, and columnar. Epithelial tissue was introduced by Rush. These cells consist of a basal surface and a free surface. There are two types of epithelial tissues, Simple and Compound tissues. -Simple Epithelial: It consists of a single layer of cells resting on the basement membrane. It lines the body cavity, ducts, and tubes. Start studying Epithelial Tissue. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Epithelial Tissue. Epithelial tissues are widespread throughout the body. They form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception. The cells in epithelial tissue are tightly packed together ...
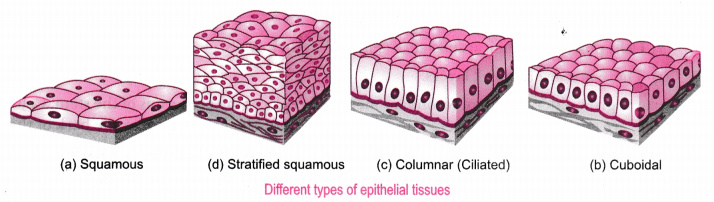
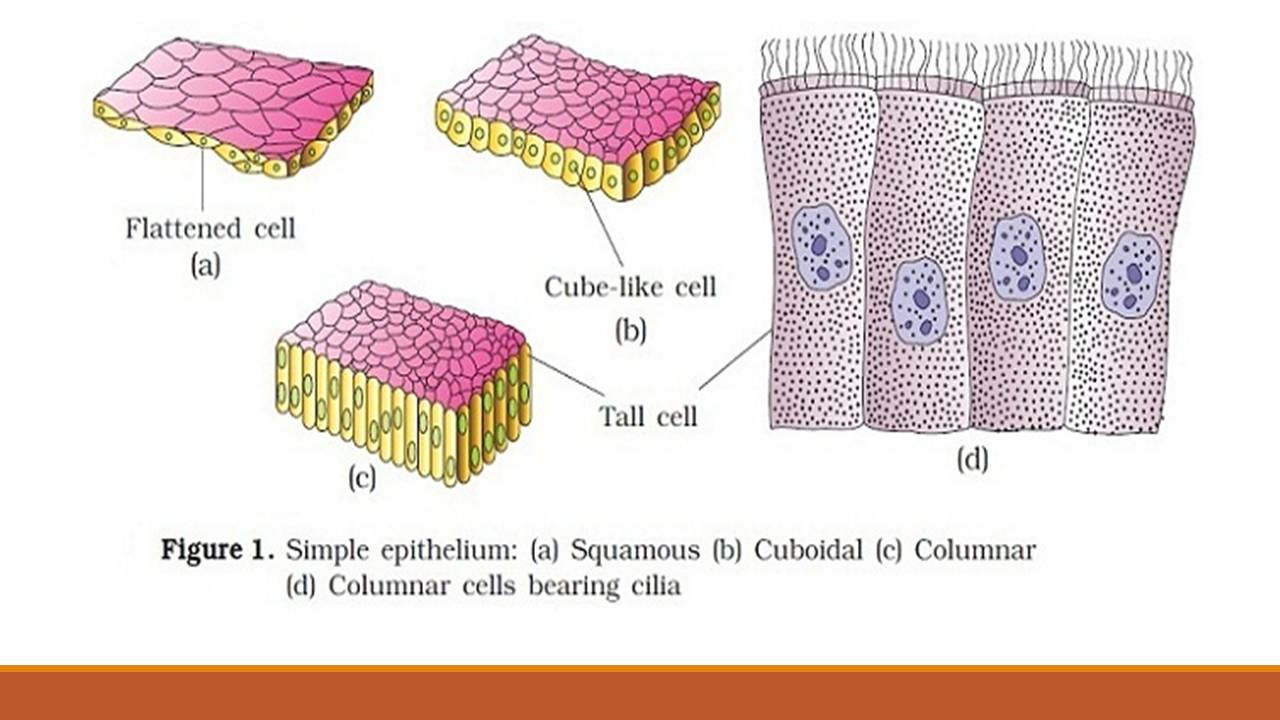
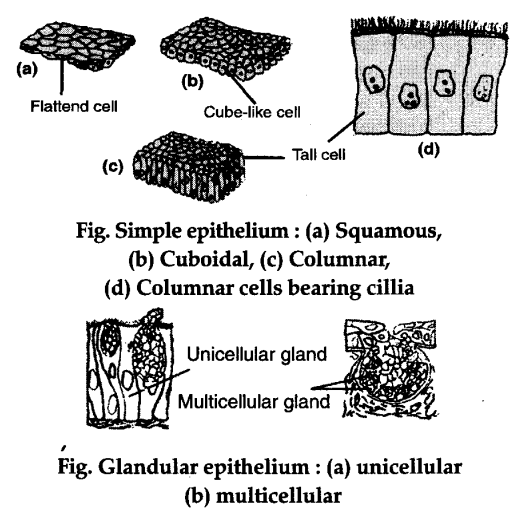
Simple Epithelial Tissue. This type of epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells which mainly make up the linings of ducts, tubes and other cavities in the body. Based on the structure of the cell, the simple epithelial tissue is classified into three types viz.: Squamous epithelium: It is a simple single-layered epithelium.
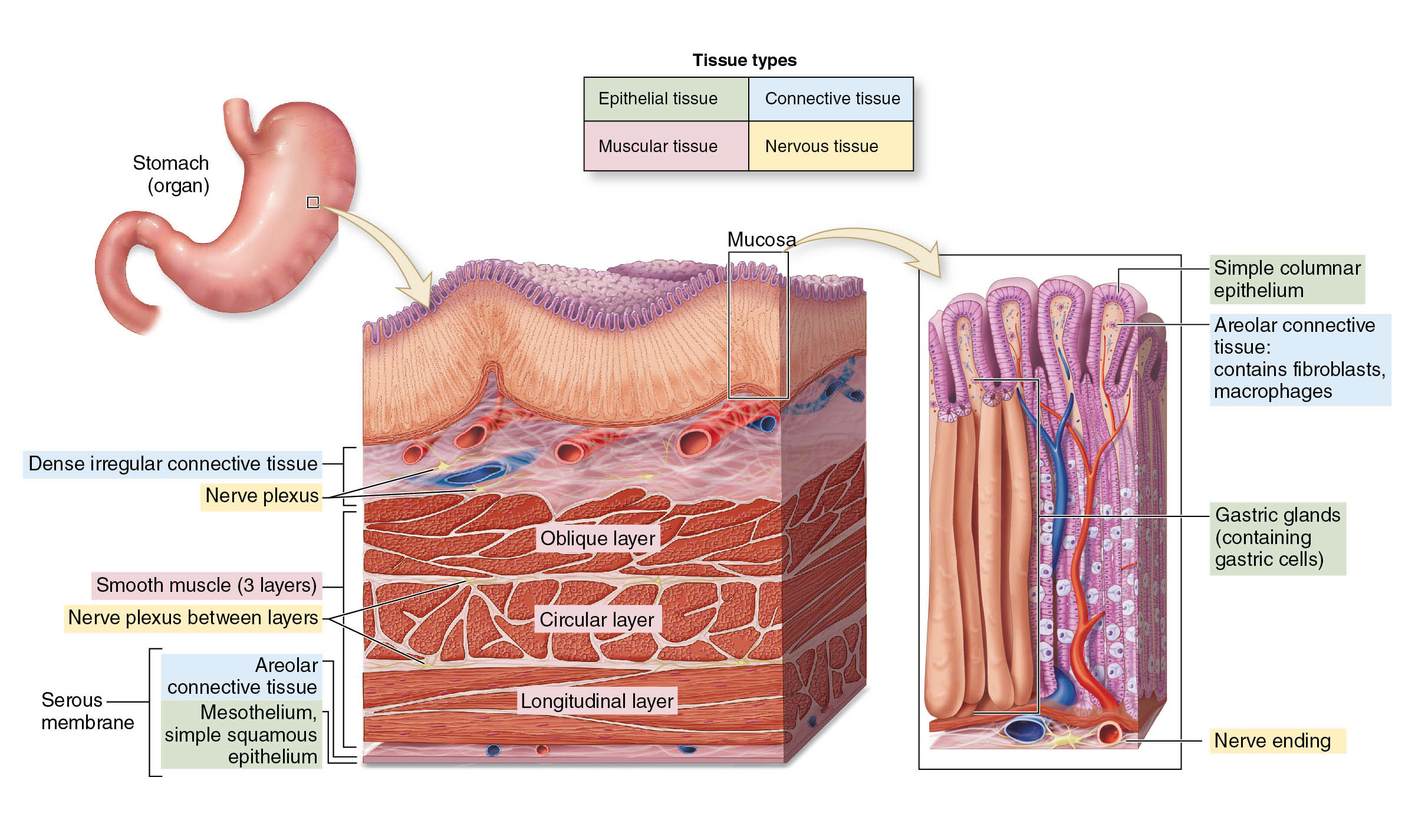
Figure 3.19d-f Connective tissues and their common body locations. Ligament (d) Diagram: Dense fibrous connective tissue from a tendon (475 Photomicrograph: Dense fibrous ×) Collagen fibers Nuclei of fibroblasts Nuclei of fibroblasts Collagen fibers Tendon Mucosa epithelium Lamina propria Fibers of matrix Nuclei of fibroblasts Elastic
Ciliated epithelium is an important tissue found in various parts of the body and aids in everyday health. Explore what ciliated epithelial is and its function, its structure using a diagram, why ...
Epithelial tissues provide the body's first line of protection from physical, chemical, and biological wear and tear. The cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the body controlling permeability and allowing selective transfer of materials across a physical barrier. All substances that enter the body must cross an epithelium.
Epithelial Tissue Definition. Epithelial tissues are thin tissues that cover all the exposed surfaces of the body. They form the external skin, the inner lining of the mouth, digestive tract, secretory glands, the lining of hollow parts of every organ such as the heart, lungs, eyes, ears, the urogenital tract, as well as the ventricular system of the brain and central canals of the spinal cord.
Types of Epithelial Tissue · Simple squamous epithelium. the cells are flattened and single-layered · Simple cuboidal epithelium · Simple columnar epithelium.Simple squamous epithelium: Air sacs of the lu...Simple columnar epithelium: Ciliated tissues i...Simple cuboidal epithelium: In ducts and secre...Stratified cuboidal epithelium: Sweat glands, s...
The simple epithelial tissue is a closed network of flat epithelial cells. These are located on the basal membrane. It is composed of a single layer of cells that are specialized in diffusion, osmosis, filtration, secretion, and absorption.The simple epithelial tissue is found in the alveolar epithelium (pulmonary alveolus), the endothelium (lining of blood vessels and lymph vessels), and the ...
Epithelial cells attach to a specialized kind of extracellular matrix called the basal lamina or basement membrane that separates epithelial cells from the underlying tissue. Epithelia cells are polarized with an apical surface that faces the lumen of a tube or the external environment and a basal surface that attaches to the basement membrane.
A. Simple columnar epithelium. Slide 29 (small intestine) View Virtual Slide Slide 176 40x (colon, H&E) View Virtual Slide Remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. In slide 29 and slide 176, this type of epithelium lines the luminal (mucosal) surface of the small and large intestines, respectively. Refer to the diagram at the end of this chapter for the tissue orientation and consult ...
Epithelial tissues are classified according to the shape of the cells composing the tissue and by the number of cell layers present in the tissue. Figure 4.2.2 ) Cell shapes are classified as being either squamous (flattened and thin), cuboidal (boxy, as wide as it is tall), or columnar (rectangular, taller than it is wide).
Part of the epithelial tissue that is exposed to an open area (either the external environment or to the inside of a hollow organ). basement membrane (basal lamina) attaches epithelia to underlying connective tissues
Types of Epithelial Tissue. There are three types of epithelial cells, which differ in their shape and function. Squamous- thin and flat cells Cuboidal- short cylindrical cells, which appear hexagonal in cross-section Columnar- long or column-like cylindrical cells, which have nucleus present at the base On the basis of the number of layers present, epithelial tissue is divided into the simple ...
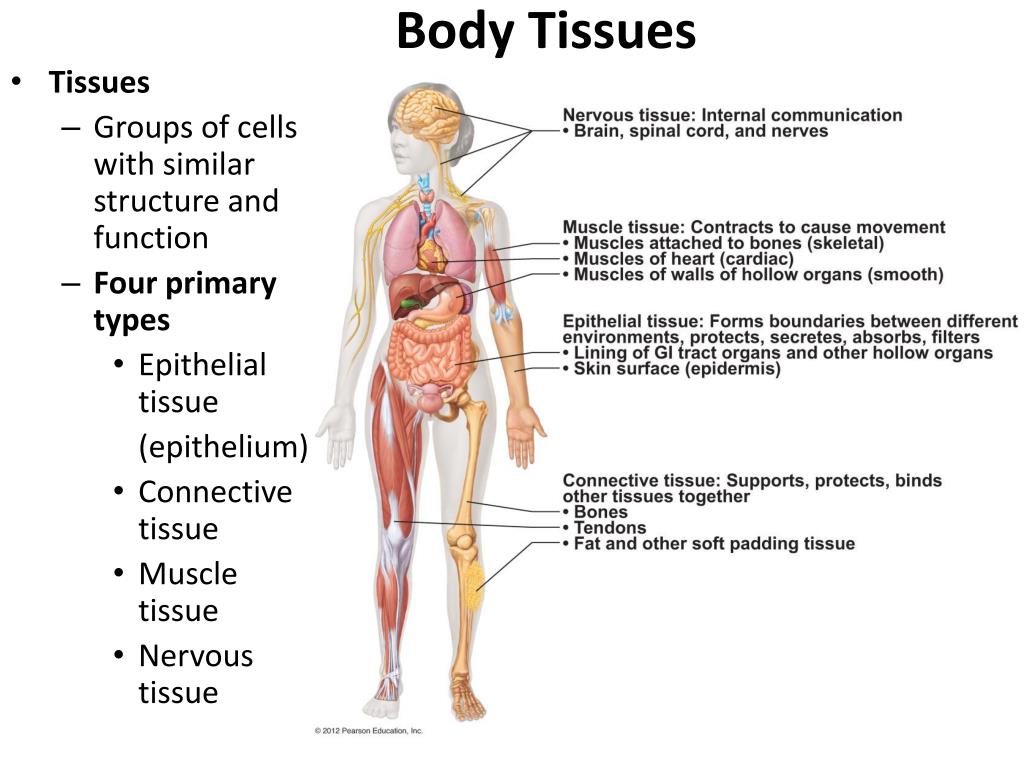
Animal tissues: The cheek cells are a type of epithelial tissue, while blood is a kind of connective tissue. There are two other types of animal tissue—muscular and nervous. Epithelial tissue: This tissue covers the surface of the body and lines the internal organs. Its main function is protection.
Epithelium is one of only 4 types of human body tissues.Like all types, it is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM). The cells in this tissue are tightly packed within a thin ECM. Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces (surface epithelium) and secreting organs (glandular epithelium). Functions of epithelial tissue are secretion, protection, absorption ...
Epithelial Tissues Simple Squamous Epithelium Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Simple Columnar Epithelium Stratified Epithelium Pseudostratified Epithelium ... diagrams that illustrate the diagnostic features of the following list of tissue types. Be sure to clearly label the significant features of that tissue type.
The epithelial tissue is typically derived from the embryonic ectoderm and endoderm (not the mesoderm). There are four different specific types of epithelial tissues throughout the body.























![Image from page 346 of "Elements of biology; a practical text-book correlating botany, zoology, and human physiology" ([c1907])](http://live.staticflickr.com/5715/21230952532_ebea6a93f9_c.jpg)





0 Response to "45 diagram of epithelial tissues"
Post a Comment