41 co2+ orbital diagram
File:MO Diagram CO2.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 406 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 162 × 240 pixels | 325 × 480 pixels | 406 × 600 pixels | 520 × 768 pixels | 694 × 1,024 pixels | 1,387 × 2,048 pixels | 420 × 620 pixels.
Answer (1 of 3): The atomic orbitals of oxygen are uniformly lower in energy than the corresponding atomic orbitals of element C because of the increased stability of the electrons in oxygen. The molecular orbitals are no longer symmetrical, and the energies of the bonding molecular orbitals are ...
The formation of CO2 consists of two particles: Oxygen and Carbon. Carbon is in group 4, whereas oxygen is in group 6. Furthermore, there are 2 Oxygen atoms. Therefore, CO2= 4 + 6 (2) = 16. So, the total valence electrons are 16. Carbon is the least electronegative, which means it stays at the centre.

Co2+ orbital diagram
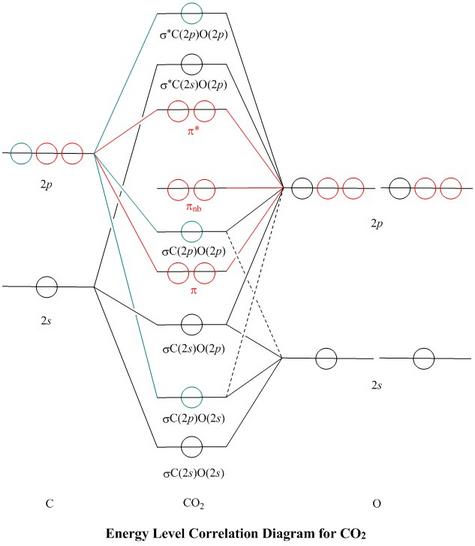
5.4.2 Carbon Dioxide's Molecular Orbital Diagram O=C=O D∞h-> D 2h 5.4 Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 5.4.2 Carbon Dioxide's Molecular Orbital Diagram O=C=O D∞h-> D 2h Oxygen Group Theory Carbon Group Theory
11.12.2017 · This is the general MO diagram you need to fill with the valence electrons of BN Boron has 3 valence electrons, and nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, this makes 8 electrons. You have to start filling the orbitals from those with lowest energy to those with higher energy. So, 2 electrons on σ2s , two electrons on σ∗2s, two electrons on σ2p . You have now 2 electrons left, …
Carbon dioxide (CO2), molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride (BeH2) However, unlike hydrogen as peripheral atoms in BeH2, there are oxyge...
Co2+ orbital diagram.
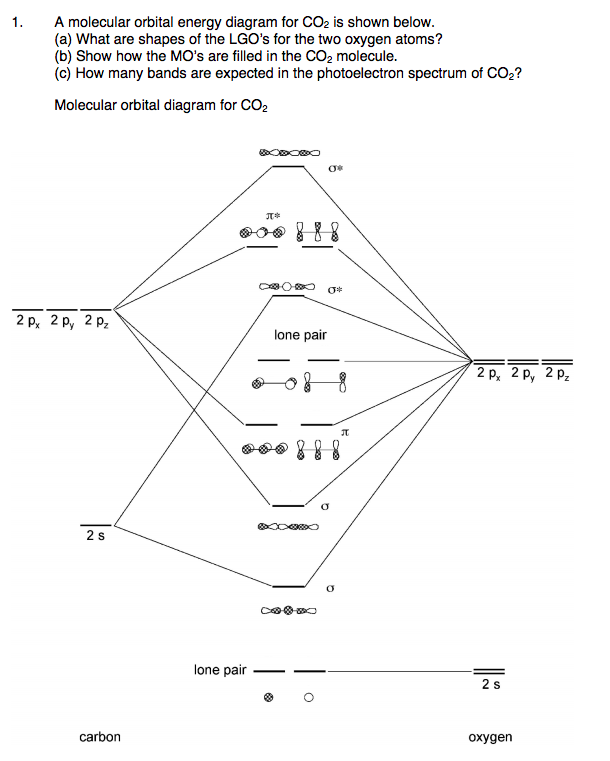
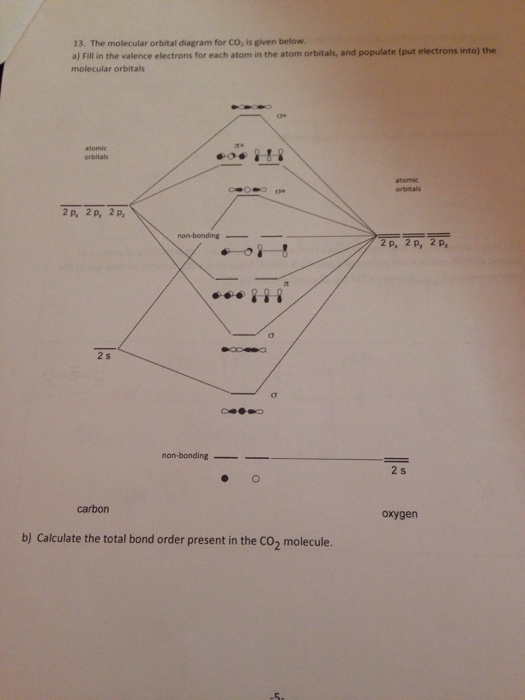
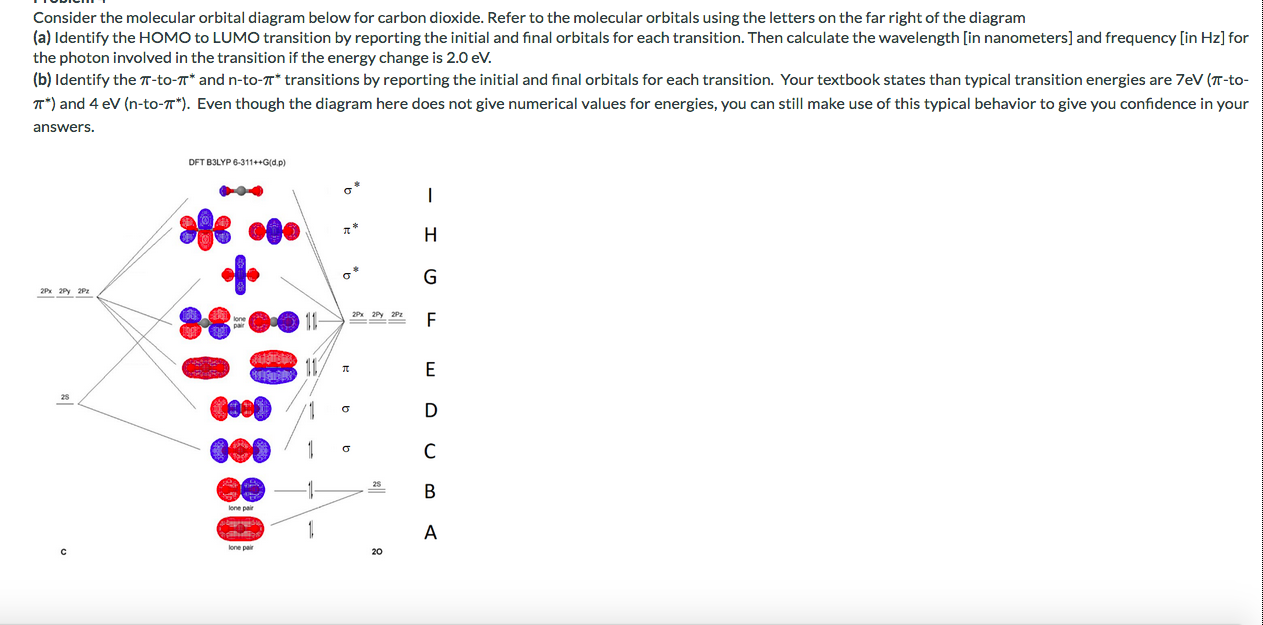
CO2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
However, the diagram is more correctly called a Perrin-Jablonski diagram to recognise the important contributions in its development by French physicists Jean Baptist Perrin, winner of the 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics, and his son Francis Perrin who both contributed greatly to the theory of fluorescence in the 1920s and 1930s. 2,3 Jean Perrin introduced the concept of resonant …
A description of the hybridization of CO2 including sigma and pi bonds.Note that the CO2 hybridization is sp for the central carbon atom. It's sp2 for each ...
Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital …
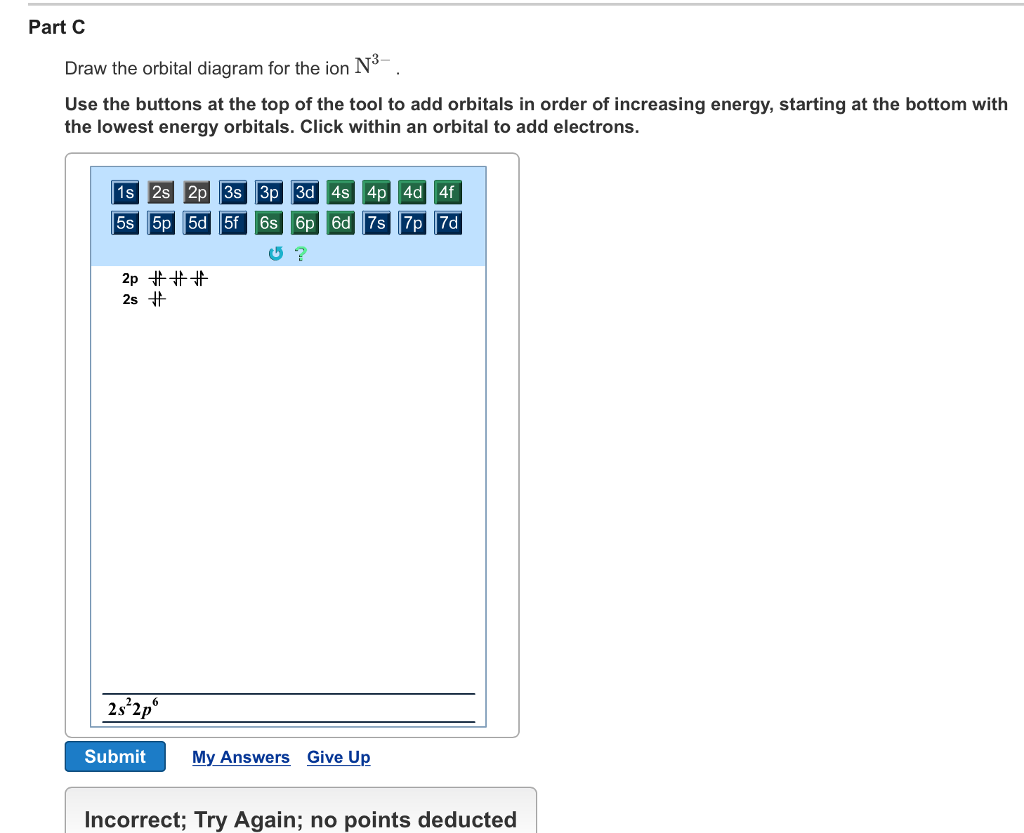
Part B. Draw the orbital diagram for the ion Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting at the bottom with the lowest energy orbitals. Click within an orbital to add electrons. Part C. Draw the orbital diagram for the ion N3−.
The valence molecular orbital diagram for Li2- is shown. THe molecular orbital bond order for this species is equal to _____ and Li2- is _____ stable than Li2-1/2-less. correctly describe sigma and pi molecular orbitals -Both atomic s and p orbitals can form sigma molecular orbitals-atomic p orbitals can combine to form either sigma or pi molecular orbitals-a pi bonding molecular …
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO 2) is an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas.The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of …
In carbon dioxide molecule, oxygen also hybridizes its orbitals to form three sp 2 hybrid orbitals. The p orbital in oxygen remains unchanged and is mainly used to form a pi bond. However, out of the three sp hybrid orbitals, only one will be used to form a bond with the carbon atom.
Cooling Incubator,Vacuum Oven,Shaking Incubator lcd,Plant Growth Chamber,Yiheng Group,Yiheng China,Shanghai bluepard instruments Co.,ltd.
18.12.2021 · CO2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Likewise, the left side has …
However, the diagram is more correctly called a Perrin-Jablonski diagram to recognise the important contributions in its development by French physicists Jean Baptist Perrin, winner of the 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics, and his son Francis Perrin who both contributed greatly to the theory of fluorescence in the 1920s and 1930s. 2,3 Jean Perrin introduced the concept of resonant …
Carbon dioxide is electron-poor at the central carbon and acts as an electrophile. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxideis very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen.
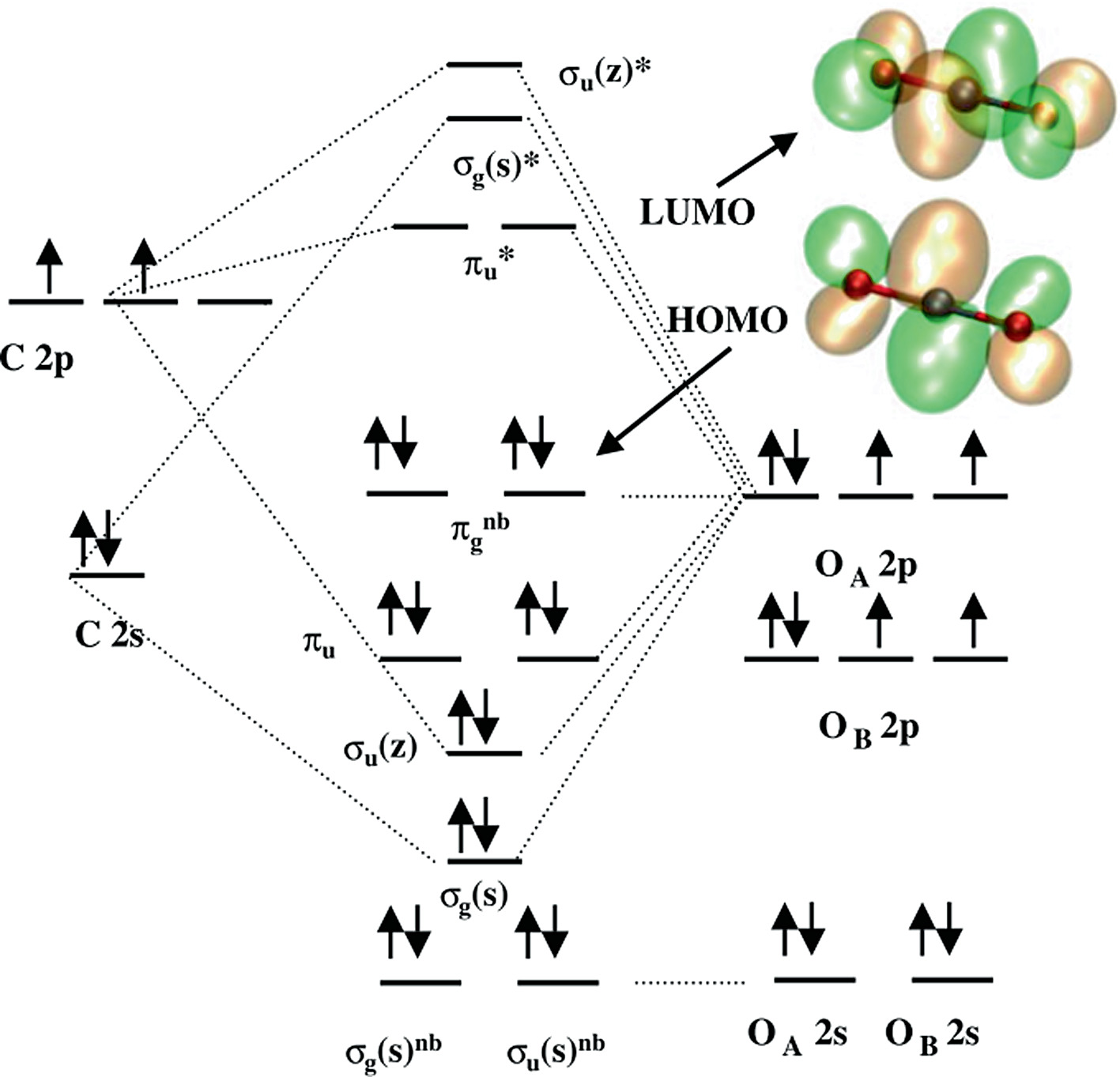
Molecular Orbitals for CO2. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on an orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown Mouse Control of Models. Left mouse drag rotate; Shift Left drag resize; Shift Right drag z-rotate; Right click for menu Notes
The energy diagram for carbon in CO 2 is shown below. What is the hybridization of oxygen in CO 2. Each oxygen has two lone pairs and forms one s bond and one p bond. This means that there must be three hybridized orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital to make the p bond. This is sp 2 hybridization.
Our videos prepare you to succeed in your college classes. Let us help you simplify your studying. If you are having trouble with Chemistry, Organic, Physics, Calculus, or Statistics, we got your back! Our videos will help you understand concepts, solve your homework, and do great on your exams.
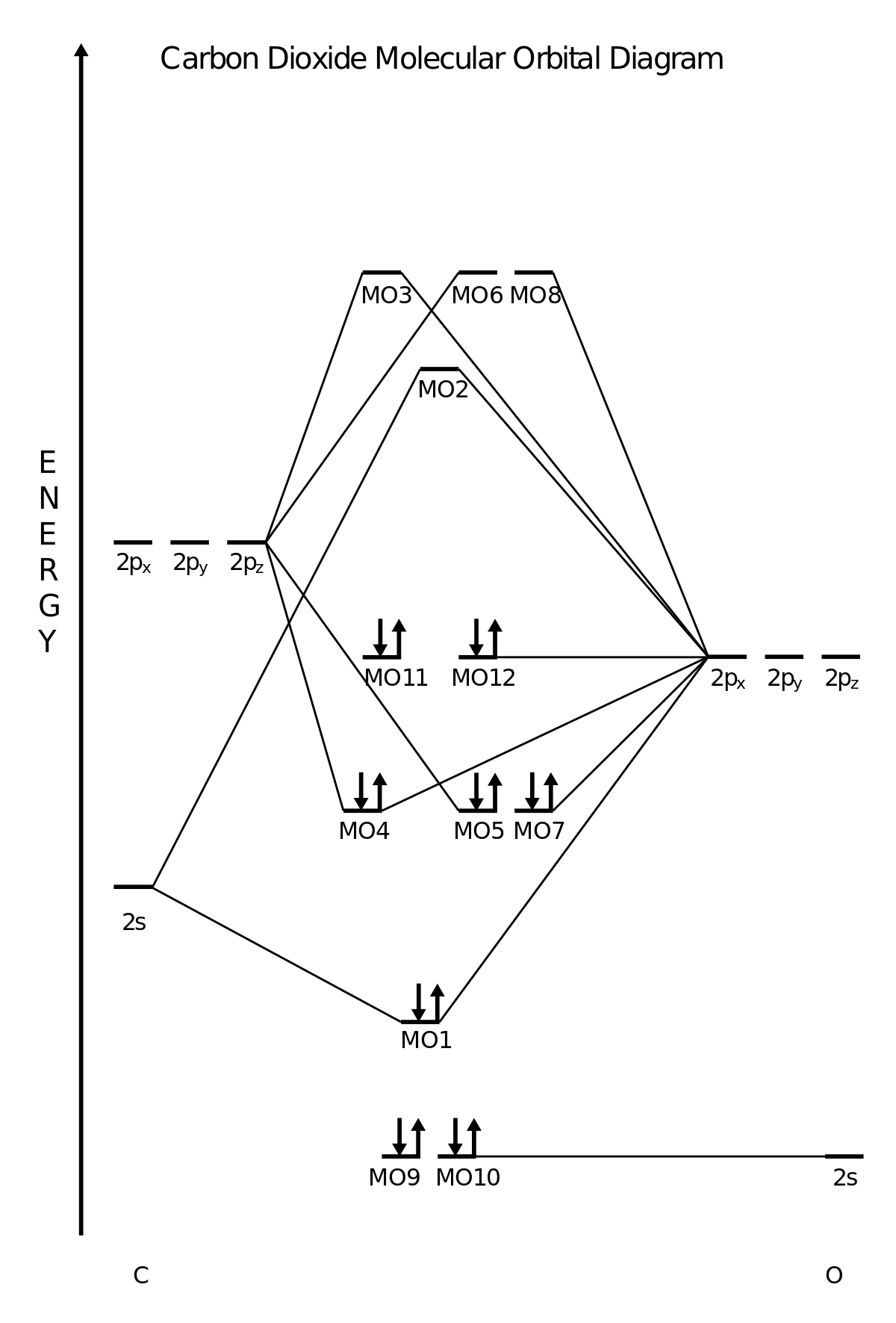
The molecular orbitals for the CO2 (O1=C=O2) molecules are given by, in order of increasing energy 14. CO2 MOs MO Diagram for CO2 C 2p C 2s bonding MOs antibonding MOs C AOs O LCAOs 1 3 u 3 g 2 u 1 g 1 u 2 u 2 g 1 u 1 g 15.
The angular overlap diagrams for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital .. For Co2+: High-spin octahedral d7 has LFSE = -∆o. Tetrahedral d7 has. As it is sometimes explained, the statement that 4 s orbital is lower in energy than 3 d But while you fill 3 d orbital with electrons it becomes lower and lower in. Part B.
Watching the Earth breathe from space... Measuring carbon dioxide from space
Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Click within the orbital to add.
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. By. All About Chemistry - July 2, 2020. 1. 231. Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post, If you find ...
Why does Co2+ have 7 electrons in the 3d orbital, and not 5 like Mn? Ask Question Asked 7 years, 4 months ago. Active 3 years, 4 months ago. ... But while you fill $3d$ orbital with electrons it becomes lower and lower in energy and eventually ends up lower in energy than the $4s$ orbital. Thus, when electrons are lost from $\ce{Co}$ atom, they ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
24.10.2018 · diagram for CO2 in Figure can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO 2 in Figure The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total …
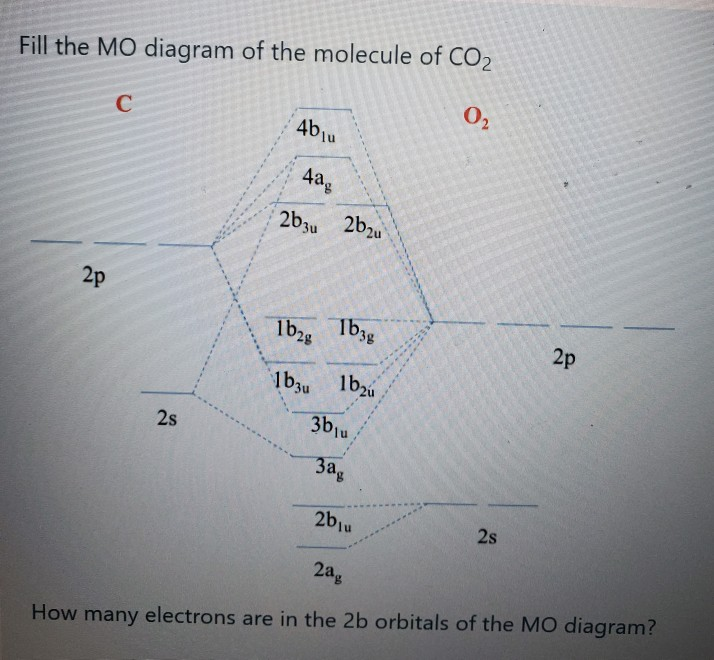
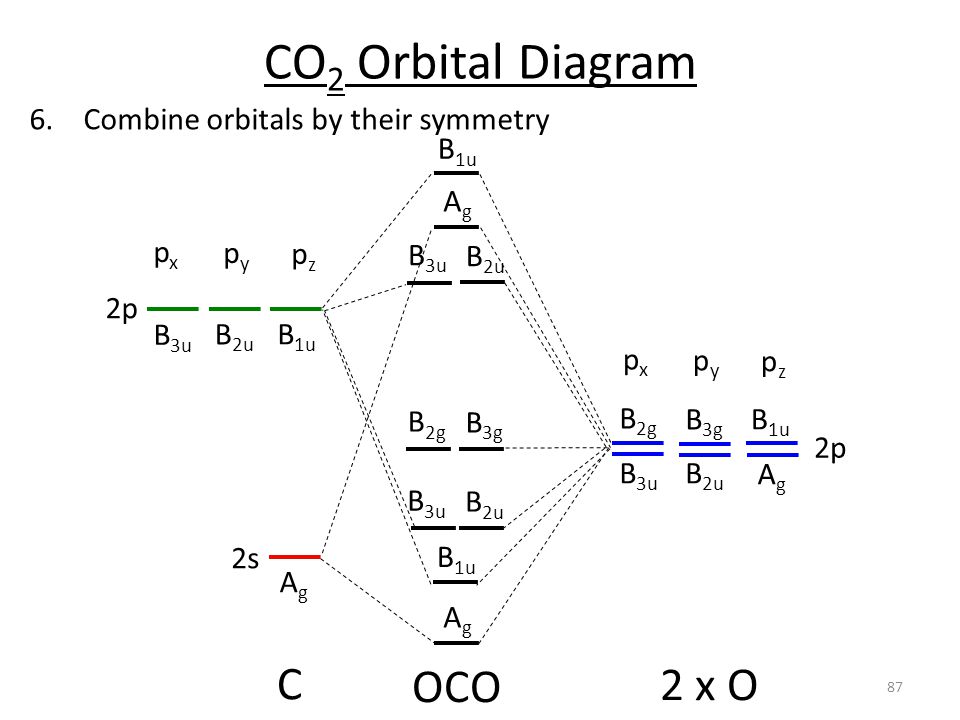
6.2: CO₂. Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for CO 2. Step 1. Find the point group of the molecule and assign Cartesian coordinates so that z is the principle axis. Step 2. Identify and count the pendant atoms' valence orbitals. Step 3. Generate the Γ 's. Step 4.
Draw the orbital diagram for the ion Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting at the bottom with the lowest energy orbitals. Click within an orbital to add electrons. Part C. Draw the orbital diagram for the ion N3−.
Carbon Dioxide by Reducible Representations Γ2s= Ag+ B1u Γ2pz= Ag+ B1u Γ2px= B2g+ B3u Γ2py= B3g+ B2u B3u B2u Ag Ag 2p x 2p y 2p z 2s B2g B3g B1u B1u These are the same group orbital symmetries that we got using inspection. We can (re)draw them. 5. Find matching orbitals on central atom Ag B1u B3u B2u 6. Build MO diagram…
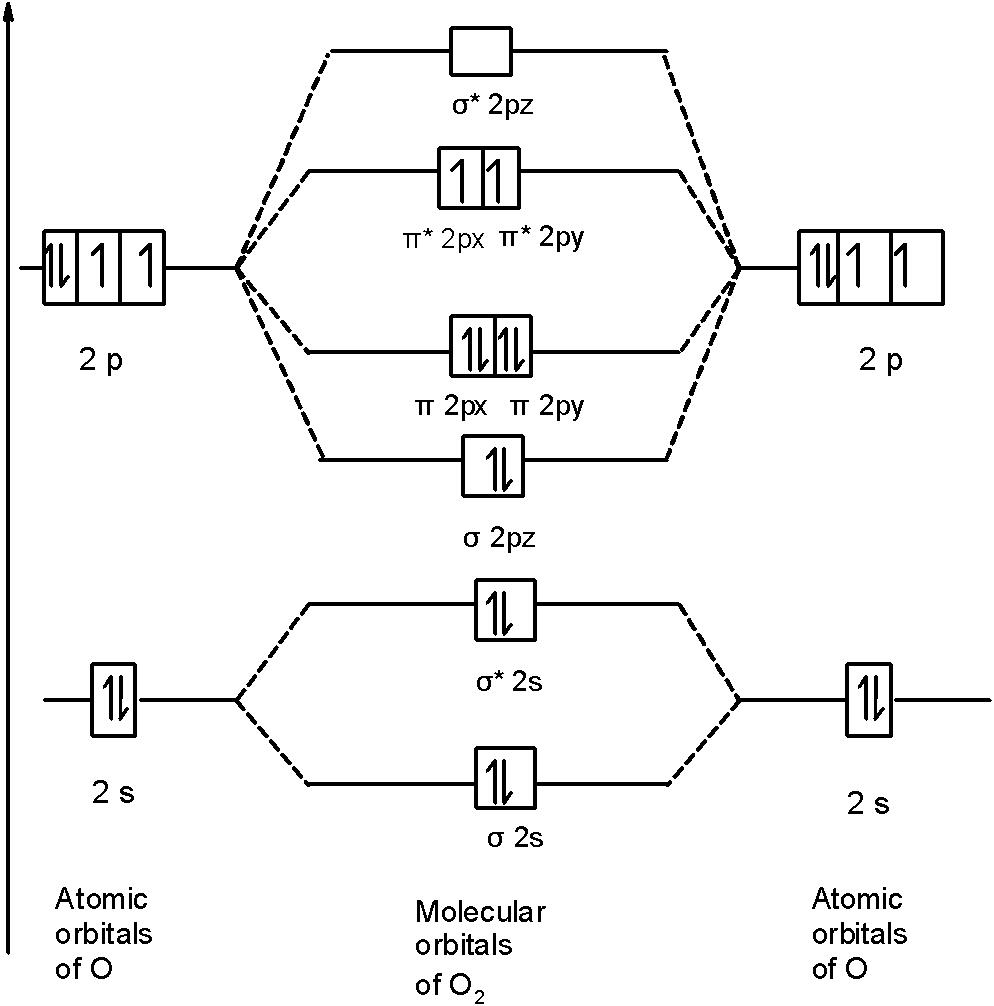
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
For simple polyatomic molecules with a "central atom" such as methane (CH4) or carbon dioxide (CO2), a MO diagram may show one of the identical bonds to the central atom. The following molecular orbital diagrams contain the chemical bonding of carbon, Co2, and He2.
CO2 or Carbon Dioxide is made up of two types of atoms: Carbon and Oxygen. ... In its excited state, the atom's electronic configuration becomes 1s2 2s1 2p3, so now every p-orbital of the atoms has one electron each. Here the 2s orbitals and one of the p-orbitals will hybridize to form 2 sp orbitals. In contrast, the Oxygen atom hybridizes to ...
Draw an orbital diagram for the Zn2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ ions in the presence of solvent molecules. Use up and down arrows to represent the spin of electrons. Only two electrons can occupy a single box. Fill the lower three boxes before filling the upper two and make sure to follow Hund's rule as you fill the orbitals with electrons.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.




















0 Response to "41 co2+ orbital diagram"
Post a Comment