41 rocket free body diagram
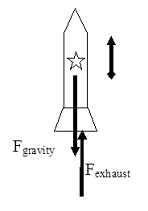
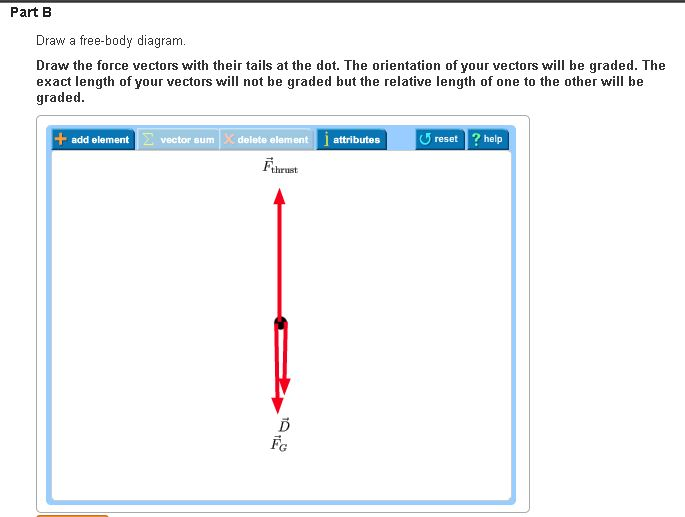
A rocket is being launched straight up. Air resistance is not negligible. Draw a free-body diagram for the rocket. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. rocket. Free-Body Diagram: 2 . F Net = F a - F o Force Opposing (F drag) Force Applied ma = F g - F drag (F g) The applied force is the weight, Fg Free-Body Diagram: 3 . Title: Chapter 6 and 7.1 Author: Friendswood High School Science Department Created Date:
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
Rocket free body diagram
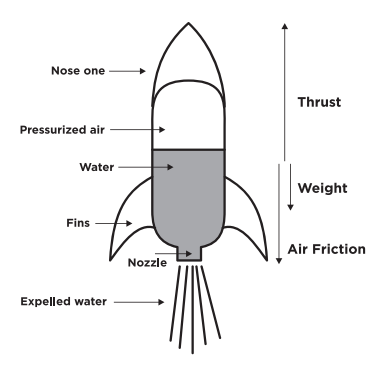
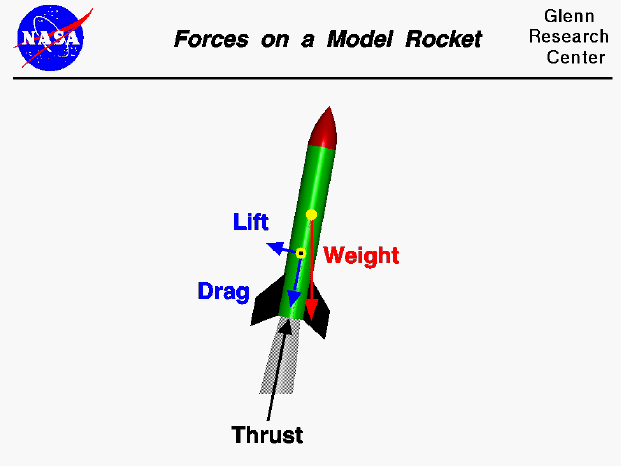
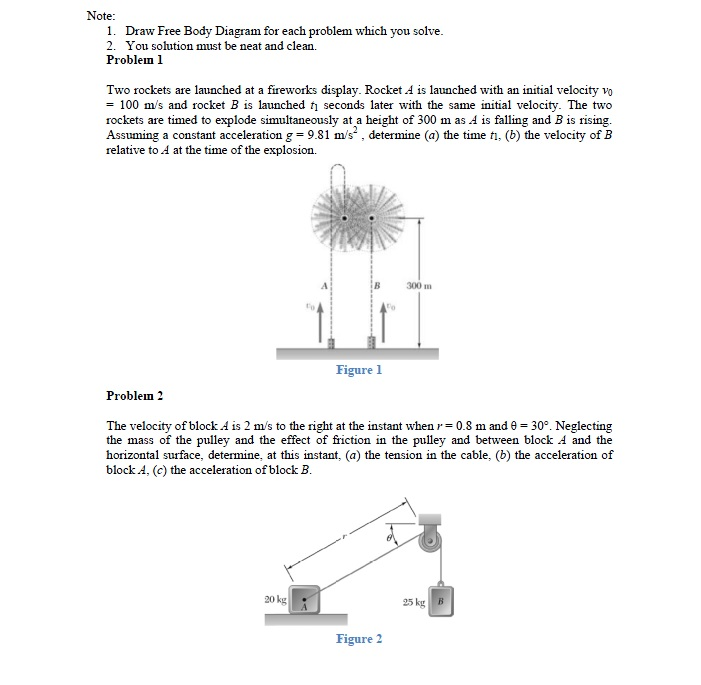
The free body diagram, shown below, clearly illustrates that the rocket body will be subjected to an axial force as well as a bending moment. The axial force is generated by thrust from the motor, the weight of the rocket and drag. The rocket moving through the air with an angle of attack α, creates the bending moment. Figure 4: Free Body Diagram free-body diagram: A diagram that shows all the forces acting upon an object. Newton's first law : If the forces are balanced, the body will stay at rest or continue with the same velocity, neither accelerating nor decelerating. Example: A rocket on the launch pad will not move without an outside force. 8. A large model rocket engine can produce a thrust of 12.0 N upon ignition. This engine is part of a rocket with a total mass of 0.288 kg when launched. a. Draw a free-body diagram of the rocket just after launch. b. What is the net force that is acting on the model rocket just after it leaves the ground? F net! F thrust $ F g! 12.0 N $ (0.288 ...
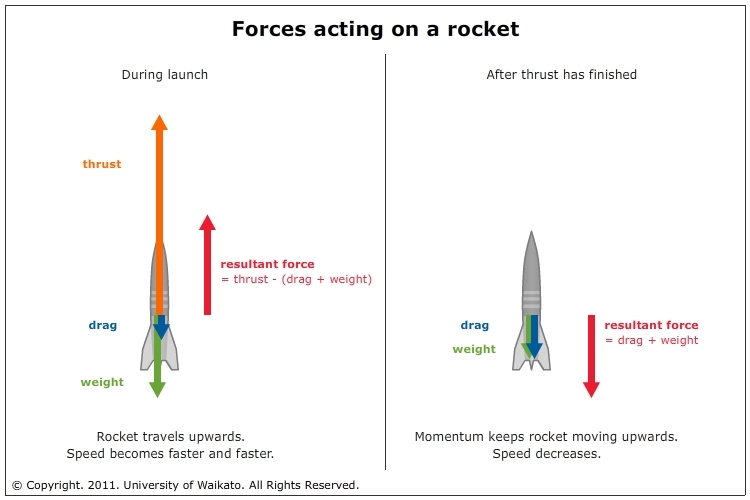
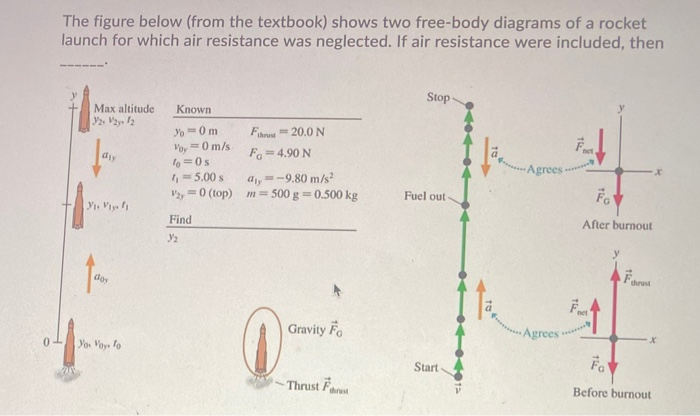
Rocket free body diagram. Our free body diagram looks like: There are only two forces acting on the rocket - the weight of the rocket down (i.e.the force on the rocket due to gravity, F g or mg) and the Normal Force (the force of the launch pad pushing back up on the rocket, F N ). Free Body Diagram: Data: Rocket’s Stats Speed Mass Height Force 0 m/s 1,638 kM-26,201 N Analysis: The data reveals that as the number of seconds in space increases, speed and force become zero, however the height of flight increases due to its fuel to push to the boundaries of its force termed thrust. Nov 23, 2021 · Students are introduced to statics and dynamics, free-body diagrams, combustion and thermodynamics to gain an understanding of the forces needed to lift rockets off the ground. They learn that thrust force is needed to launch rockets into space and the energy for thrust is stored as chemical energy in the rocket's fuel. Then, using the law of conservation of energy, students learn that the ... Download scientific diagram | Free-body Diagram of Rocket (Rocket Physics). The forces the rocket experiences can be written as the sum of the forces in the í µí±¦-direction: from publication ...
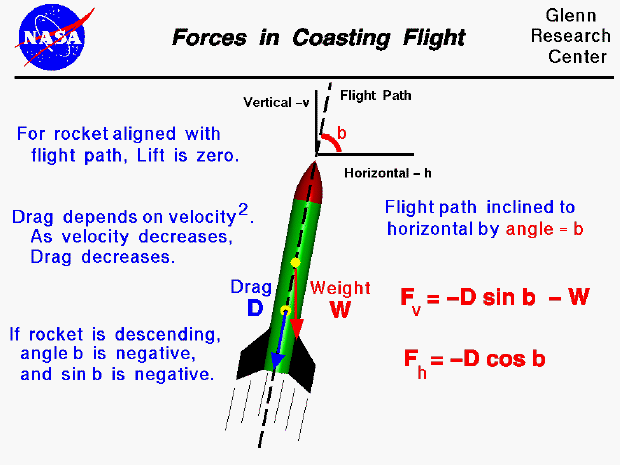
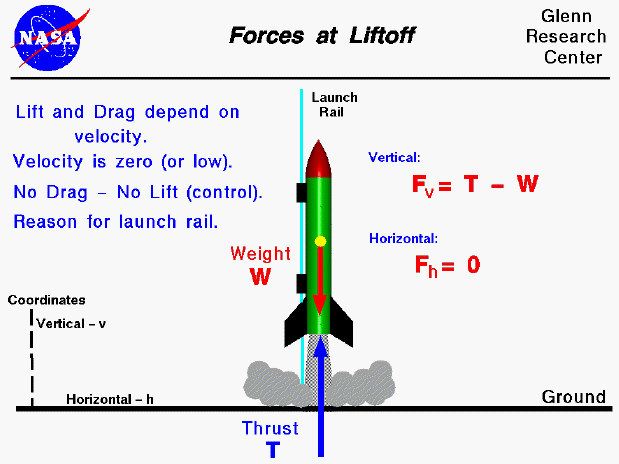
In order to begin finding the maximum height, a free-body diagram is used to find all of the forces a rocket body experiences in its flight. This diagram (Figure 3) shows the thrust, T, force of gravity, F G, and force of drag, F D, on the rocket. Figure 3: Free-body Diagram of Rocket (Rocket Physics). Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit.These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. 8. A large model rocket engine can produce a thrust of 12.0 N upon ignition. This engine is part of a rocket with a total mass of 0.288 kg when launched. a. Draw a free-body diagram of the rocket just after launch. b. What is the net force that is acting on the model rocket just after it leaves the ground? F net! F thrust $ F g! 12.0 N $ (0.288 ...
free-body diagram: A diagram that shows all the forces acting upon an object. Newton's first law : If the forces are balanced, the body will stay at rest or continue with the same velocity, neither accelerating nor decelerating. Example: A rocket on the launch pad will not move without an outside force. The free body diagram, shown below, clearly illustrates that the rocket body will be subjected to an axial force as well as a bending moment. The axial force is generated by thrust from the motor, the weight of the rocket and drag. The rocket moving through the air with an angle of attack α, creates the bending moment. Figure 4: Free Body Diagram





















0 Response to "41 rocket free body diagram"
Post a Comment