43 antigen antibody reaction diagram
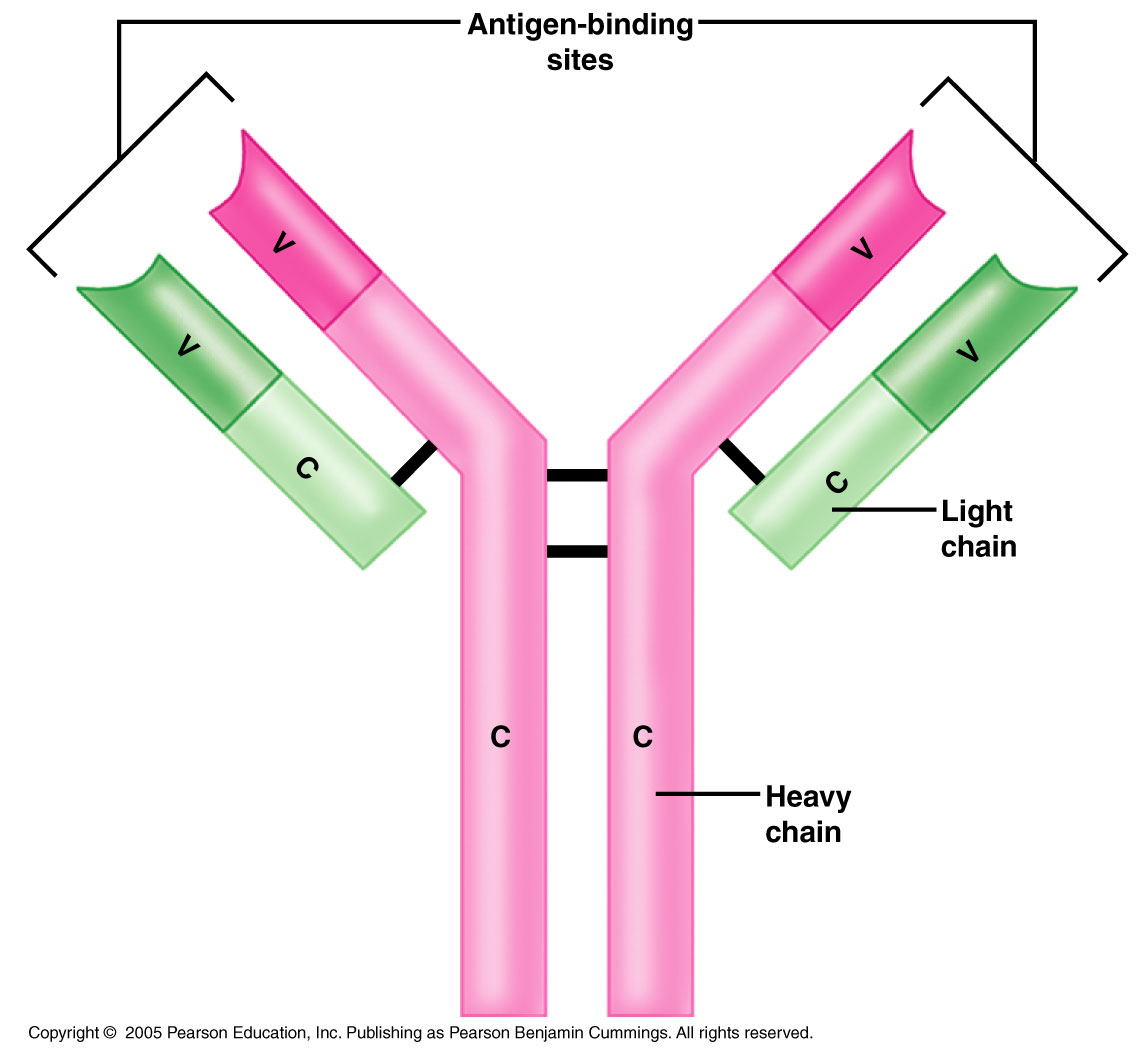
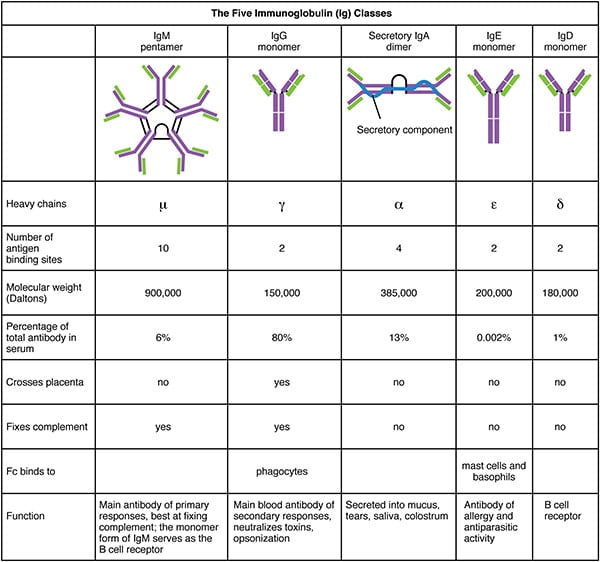
Each antibody has two identical antigen-binding sites and they differ in the antibodies. Different types of Antibody. There are 5 types of antibodies based on H chains: IgM. IgM is the largest antibody and is found in a pentameric which is produced in response to a microbial attack by B cells. November 8, 2013 - The function of antibodies (Abs) involves specific binding to antigens (Ags) and activation of other components of the immune system to fight pathogens. The six hypervariable loops within the variable domains of Abs, commonly termed complementarity determining ...
June 23, 2018 - Through activation of B cells by ... of a reaction. ... Foreign Microbes has surface proteins which acts like a key , which helps them to enter our Body Cell. So antibodies acts like a lock for there key. If No key is free then how they can enter?… No way ☺️ ... antigens are the attackers ...

Antigen antibody reaction diagram
The nature of the antigen-antibody reaction determines which way it becomes involved. Complement (C′) is a large group of more than twenty proteins present in abundance in the body, and in freshly drawn serum samples. Complement from one species is effective in antigen-antibody reactions in many other species. Just posted this in camping and hiking but figured it would be of particular relevance to this community as well. Forgive the cross post if that is bad etiquette, I am new to the reddit world! ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Hello, survival! I am a wilderness paramedic and snakebite specialist, and wanted to share a lifesaving pro-tip with all of you for your next adventure in the backcountry. The topic today will be anaphylactic shock. Q: What is a... Hello, camping and hiking! I am a wilderness paramedic and snakebite specialist, and wanted to share a lifesaving pro-tip with all of you for your next adventure in the backcountry. The topic today will be anaphylactic shock. Q: What is anaphylactic shock? Anaphylaxis is the ultimate one-two punch of hypersensitivity reactions. Basically, something triggers an immunologic response that begins to spread like wildfire throughout the body. Take, for example, a bee sting: when a sting occurs, your...
Antigen antibody reaction diagram. Antibodies are Y shaped tetra-peptide molecules consisting of two identical heavy (H) chains and two identical light (L) chains, held together by disulfide bonds. Each light chain is bound to a heavy chain by a disulfide bond to form a heterodimer (H-L).Two identical heavy and light (H-L) chain combinations are also held together by disulfide bridges forming a basic four-chain (H-L)2 antibody ... One of the antibodies called nanobody is a novel and unique class of antigen-binding fragments (Fab) with superior characteristics, such as small size, robust antigen-binding affinity, high stability, access to more epitopes, and low production expense, which make it a suitable antibody for the treatment (Jovcevska and Muyldermans, 2020; Koenig et al., 2021). October 8, 2013 - The function of antibodies (Abs) involves specific binding to antigens (Ags) and activation of other components of the immune system to fight pathogens. The six hypervariable loops within the variable domains of Abs, commonly termed complementarity determining regions (CDRs), are widely assumed ... When the amount of antigen in the reaction system is very small but excess antibodies, after the reaction reaches equilibrium [AB]<[A ]; 3. When the amount of antigen and antibody in the reaction system is just right, the reaction is in a half-saturated state after reaching equilibrium, at this time [AB]=[A], then Kd=[A][B]/[AB]=[B ].
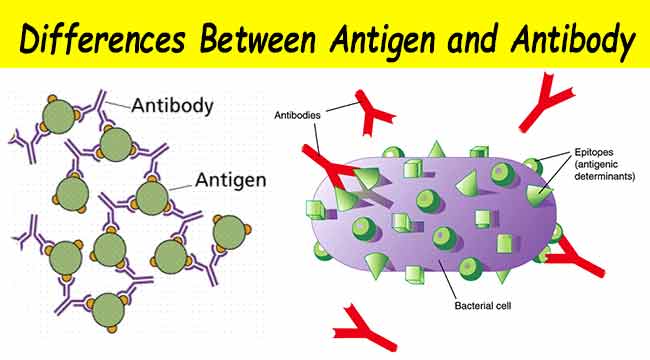
June 26, 2020 - Here we outline the differences between antigens and antibodies, and the roles that the two play in vaccination. meanwhile, antigen presentation takes place with the activation of specific T helper cells; CD4 helper T cells then co-ordinate a targeted antigen-specific immune response involving two adaptive cell systems: humoral immunity from B cells and antibodies, and cell-mediated immunity from cytotoxic CD8 T cells; Let's start at the very beginning. December 16, 2020 - Using the "lock and key" metaphor, the antigen can be seen as a string of keys (epitopes) each of which matches a different lock (antibody). Different antibody idiotypes, each have distinctly formed complementarity-determining regions. Allergen – A substance capable of causing an allergic reaction ... Antigen Antibody Interactions . Antigen Antibody Reaction Virus Neutralization Virus Neutralization Tests 1 Hemagglutination Inhibition Test Hemagglutination Inhibition Test Is Widely Ppt Download . Overview Of Microneutralization Assay The Main Steps Of The Download Scientific Diagram . Lab Dig Virus
September 28, 2021 - In other cases the antibody-coated antigen is subject to a chemical chain reaction with complement, which is a series of proteins found in the blood. The complement reaction either can trigger the lysis (bursting) of the invading microbe or can attract microbe-killing scavenger cells that ingest, ... Die ATTO-LAB GmbH wurde 2003 auf dem Innovationscampus in Lübeck gegründet und verfügt über modern ausgestattete S2 und S3**- Laboratorien · Gegenstand des Unternehmens ist die Entwicklung, Herstellung, Anwendung und der Vertrieb von Analysegeräten bzw. Analysemethoden Antibody Test . An antibody test works differently than the antigen test in the sense that it can be done after the antigens have left the body. This test is used to determine whether or not an infection had ever occurred by singling out the antibodies that were created when the immune response took place. Hence, the antibody activates the complement system only when bound to an antigen. C1 is a large, multimeric, protein complex composed of one molecule of C1q and two molecules each of C1r and C1s subunits. C1q binds to the antigen bound antibody (Fc portion). C1r and C1s are proteases which help to cleave C4 and C2.
Can't sign in? Forgot your username · Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
Primary Immune Response. Secondary Immune Response. After initial exposure to a foreign antigen, there is a lag phase where B cells are differentiating into plasma cells, but not yet producing antibodies. Antibody generation can take anything from 2 days to several months. If a previously encountered antigen enters the body again, a few days up ...
Biochemistry of Antibody-Antigen Interactions. The interaction between antigens and antibodies, also called immunoglobulins, underpins the immune response. Antigens are typically exogenous and endogenous molecules that can engage the body's immune system. Antigens include metabolites or products produced from cellular processes to a host of ...
When the cross-linking involves cell-bound antigens, the process causes clumping of the foreign cells, a process called agglutination; this type of antigen-antibody reaction occurs when mismatched blood is transfused and is the basis of tests used for blood typing. Precipitation.
In the three-dimensional (tertiary) ... up the antigen-combining site. For this reason, the hypervariable regions are also called complementarity determining regions (CDRs). The diagram on the left (courtesy of A. G. Amit) shows · the tertiary structure of one arm of an antibody specific for ...
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. In human blood transfusions it is the most important of the 38 different blood type (or group) classification systems currently recognized. A mismatch (very rare in modern medicine) in this, or any other serotype, can cause a potentially fatal adverse reaction after a ...
Principle of ELISA. ELISA is a plate-based assay technique. Along with the enzyme-labelling of antigens or antibodies, the technique involves following three principles in combination which make it one of the most specific and sensitive than other immunoassays to detect the biological molecule: An immune reaction i.e. antigen-antibody reaction.
refers to an acquired unresponsiveness to a specific antigen. radical mastectomy. the surgical removal of an entire breast and many of the surrounding tissues. streptococci. bacteria that form a chain. antibody. disease-fighting protein created by the immune system in response to the presence of a specific antigen.
We have described the structure of the antibody molecule and how the V regions of the heavy and light chains fold and pair to form the antigen-binding site. In this part of the chapter we will look at the antigen-binding site in more detail. We will discuss the different ways in which antigens ...
The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining health and protecting the human body against microbial invasions. However, this same system can lead to exaggerated immune and inflammatory responses that result in adverse outcomes known as hypersensitivity reactions. There are four traditional classifications for hypersensitivity reactions, and these include Type I, Type II, Type III, and ...
3. Antigen-antibody ratio- there is a zone of equivalence that gives the equivalence of antigen reactive sites and antibody so a visible lattice is formed, too much antibody = false negative, too much antigen = false negative. 4. Antigenic determinants- number of antigens on the carrier surface. 5.
When the antibody sticks to the antigen it neutralises it so that the foreign organism can no longer enter a human cell or cause harm (see Figure 15). Once an infectious agent is neutralised it dies. Figure 14: Diagram of a Y-shaped antibody. The variable region - the antigen binding site (in yellow) and the constant region (in light blue)
Something went wrong. Wait a moment and try again
Precipitation reactions are based on the interaction of antibodies and antigens. They are based on two soluble reactants that come together to make one insoluble product, the precipitate. These reactions depend on the formation of lattices (cross-links) when antigen and antibody exist in optimal proportions. Excess of either component reduces ...
Agglutination reactions produce visible aggregates of antibody - antigen complexes when antibodies or antigens are conjugated to a carrier. Carriers used in agglutination methods could be artificial (e.g., latex or charcoal) or biological (e.g., erythrocytes ).
Blood clots in arteries, for example in the coronary vessels, can be dissolved by injecting streptokinase into the blood. Streptokinase is formed by bacteria and rapidly breaks down the blood clot. The first treatment with streptokinase is much more effective than the second treatment. The diagram below shows the concentration of anti-streptokinase antibodies in the blood after the first and second injection of streptokinase, respectively. The second injection occurred 10 weeks after the first. ...
Watch for any signs of elliptical precipitin arcs as they indicate antigen-antibody interaction. There is no reaction if no precipitation is formed. By checking the result, you can identify different antigens according to the shape, intensity, and the precipitation line placement. (8, 9, and 10) Uses of immunoelectrophoresis
Agglutination definition. Agglutination is an antigen-antibody reaction in which a particulate antigen combines with its antibody in the presence of electrolytes at a specified temperature and pH resulting in the formation of visible clumping of particles. It occurs optimally when antigens and antibodies react in equivalent proportions. This reaction is analogous to the precipitation reaction ...
The antigen is then chemically bound by and subsequently held together by that antibody. When a clump of antigen-antibody complexes occurs, it is called agglutination, which helps cells in the ...
The reaction rate depends on the concentration of the antigen in the sample. Here the measurements are taken as a function of time, so the first measurement is taken at time "zero" (t = 0). Kinetic nephelometry is the most widely used technique, since the study can be carried out in 1 hour, compared to the long period of time of the end ...
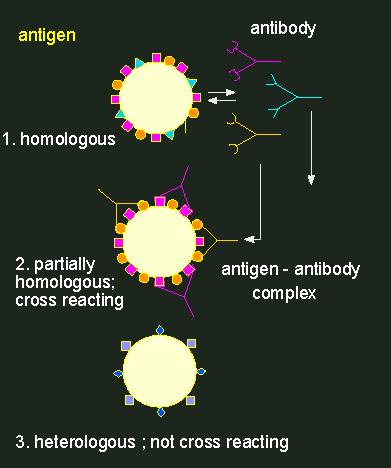
For example, infection with Treponema pallidum (syphilis) causes the production of antibodies that cross-react with a substance found in cardiac muscle, cardiolipin. Since it is much easier to obtain pure cardiolipin than pure Treponemal antigens, this cross-reaction is used to test for syphilis ...
This means each antibody wages war against one target antigen. Once antibodies detect antigens, they bind and neutralize them. This knowledge is stored in your immune system's long-term memory ...
I was going to make a throwaway for this but lol fuck it, full steam ahead boys and girls. Long time lurker, sporadic commenter, first time poster. This is the creature that spawned me, in case the title doesn't make it clear. &nbsp; Before I start, don't you worry, I've been NC with this raging cuntbag since I was 20 - and I'm coming up on the big 3-0 soon - but she still tries to occasionally lovebomb me. One of these popped up in my spam folder today, so I'm sharing it unedited (save for...
About the BP Project History What People Say Kudos & Awards Project Team Site Credits Copyright Statement Linking to Site BP Style Manual Instructional Design · Graduate Studies in The Life Sciences
August 19, 2021 - The most important and common process in our immune system is the formation of antigen-antibody complexes. But first… What is an Antibody? Antibody is a protein found in our body, also known as Immunoglobins (Ig). They are serum proteins, meaning they are usually found in blood and belong ...
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website · If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked
Introduction to Antigen-Antibody Reactions. The interactions between antigens and antibodies are known as antigen-antibody reactions. The reactions are highly specific, and an antigen reacts only with antibodies produced by itself or with closely related antigens. Antibodies recognize molecular shapes (epitopes) on antigens.
Vertebrates inevitably die of infection if they are unable to make antibodies. Antibodies defend us against infection by binding to viruses and microbial toxins, thereby inactivating them (see Figure 24-2). The binding of antibodies to invading pathogens also recruits various types of white ...
Antibodies attach to a specific antigen and make it easier for the immune cells to destroy the antigen. T lymphocytes attack antigens directly and help control the immune response. They also release chemicals, known as cytokines, which control the entire immune response.
The first step is also to passively adsorb the antigen to the surface of the multiwell plate, wash and seal the excess area, add the analysis sample containing the antibody to be tested, incubate until the specific binding is complete, then wash and incubate the secondary antibody, and finally add the substrate Perform color reaction detection (Figure 4), so this method is mostly used for ...
Transfer characteristics were taken with V G = 0 to 1 V and V DS = 0.05 V, and the relative change of the gate voltage ΔV G was calculated after the antigen-antibody reaction. Electrolytes with different concentrations were obtained by diluting the standard PBS solution with DI water, and HCl was added to adjust the pH value.
May 15, 2012 - 1. Introduction. 2. Salient Features of Antigen – Antibody Reaction. 3. Strength of Antigen – Antibody Reaction. 4. Properties of Antigen – Antibody Reaction. …
Hello, camping and hiking! I am a wilderness paramedic and snakebite specialist, and wanted to share a lifesaving pro-tip with all of you for your next adventure in the backcountry. The topic today will be anaphylactic shock. Q: What is anaphylactic shock? Anaphylaxis is the ultimate one-two punch of hypersensitivity reactions. Basically, something triggers an immunologic response that begins to spread like wildfire throughout the body. Take, for example, a bee sting: when a sting occurs, your...
Just posted this in camping and hiking but figured it would be of particular relevance to this community as well. Forgive the cross post if that is bad etiquette, I am new to the reddit world! ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Hello, survival! I am a wilderness paramedic and snakebite specialist, and wanted to share a lifesaving pro-tip with all of you for your next adventure in the backcountry. The topic today will be anaphylactic shock. Q: What is a...
The nature of the antigen-antibody reaction determines which way it becomes involved. Complement (C′) is a large group of more than twenty proteins present in abundance in the body, and in freshly drawn serum samples. Complement from one species is effective in antigen-antibody reactions in many other species.









.png)




















0 Response to "43 antigen antibody reaction diagram"
Post a Comment