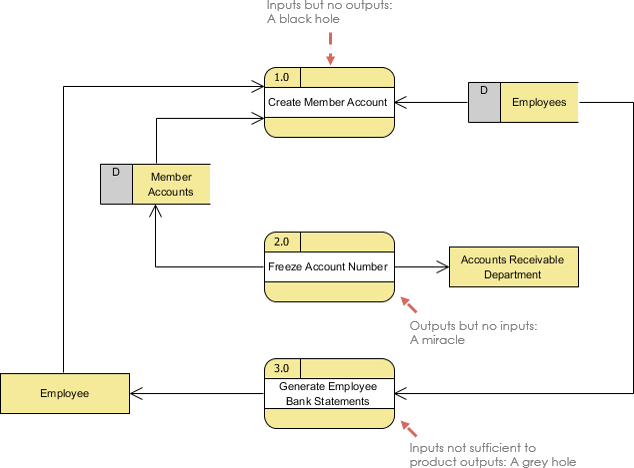
43 in a data flow diagram (dfd), a gray hole is a process that has _____.
1. Data source ——- Data source: Wrong 2. Data store ——- Data store: Wrong. 3. Data source ——- Data store: Wrong. 4. A processing step may have input flows but no output flows. This situation is sometimes called a black hole. 5. A processing step may have output flows but now input flows. This situation is sometimes called a miracle. 6. A gray hole process is a process that has ____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown ____ is/are logically impossible in a DFD because a process must act on input, shown by an incoming data flow, and produce output, represented by an outgoing data flow.
In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate ...

in a data flow diagram (dfd), a gray hole is a process that has _____.
Describes the expected number of occurrences for the data flow per unit of time. Volume and frequency. Each data flow represents a group of related data elements called a record or data structure. Record. The DFD ending point (s) for the data flow; the destination can be a process, a data store, or an entity. In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. a. no input b. at least one output and one input, but the output obviously is insufficient to generate the input shown c. no output d. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown ANSWER: data flow gray hole process data store. process. In a data flow diagram (DFD), systems analysts call an entity that receives data from the system a source. True False. ... In a data flow diagram (DFD), a black hole is a process that has _____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown
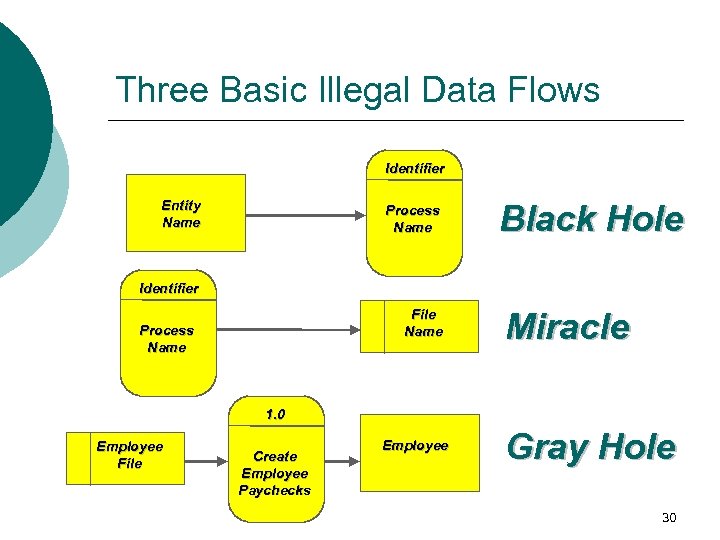
in a data flow diagram (dfd), a gray hole is a process that has _____.. _ In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has a. _ no output b. _ at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown c. _ no input d. A. In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. a. no output. b. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown. c. at least one output and one input, but the output obviously is insufficient to generate the input shown. d. no input. APPLY INSURANCE PREMIUM has no input and is called a spontaneous generation process CALCULATE GROSS PAY has no outputs and is called a black hole process CALCULATE GRADE has an input that is obviously unable to produce the output -- this is called a gray hole Incorrect combinations of data flow and process symbols. In a data flow diagram (DFD),a black hole is a process that has _____. A) no input. B) at least one output and one input,but the output obviously is insufficient to generate the input shown. C) no output. D) at least one input and one output,but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown. Categories. Questions.
Summary and next steps . Data flow diagrams can assist in Isolating the component parts of a business process, reducing the analytical complexity involved in determining the specifications that process support software would have to meet.; Shifting the focus of a process description to the data flows and processing steps that the process represents. _____ maintains consistency among data flow diagrams (DFDs) by ensuring that ... In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. • No output • No input • At least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown • At least one output and one input, but the obviously is insufficient to generate the input shown: Definition • At least one input and one output, but the input obviously is ... Data flow diagrams can be divided into logical and physical. The logical data flow diagram describes flow of data through a system to perform certain functionality of a business. In a data flow diagram (DFD), a spontaneous generation process is a process that has _____. a. no input b. at least one output and one input, but the output obviously ...
In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown Decision trees show the logic structure in a _____. Data Flow Diagram (DFD) provides a visual representation of the flow of information (i.e. data) within a system. By drawing a Data Flow Diagram, you can tell the information provided by and delivered to someone who takes part in system processes, the information needed to complete the processes and the information needed to be stored and accessed. 1.1 Draw, name and describe the four symbols used in a data flow diagram (DFD). You may use a table to present your answer. Name Draw Describe Process A process receives input data and produces output that has a different content, form, or both. Data Flow A data flow is a path for data to move from one part of the information system to another ... By showing processes as _____, an analyst can create data flow diagrams (DFDs) ... In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____.
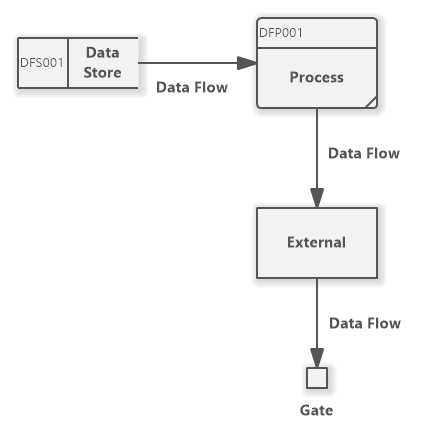
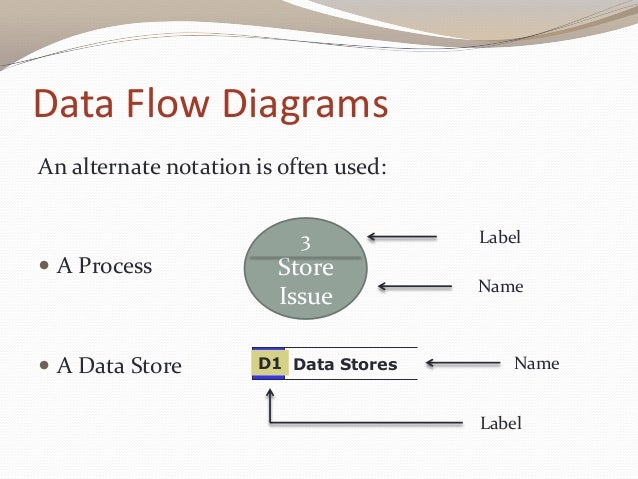
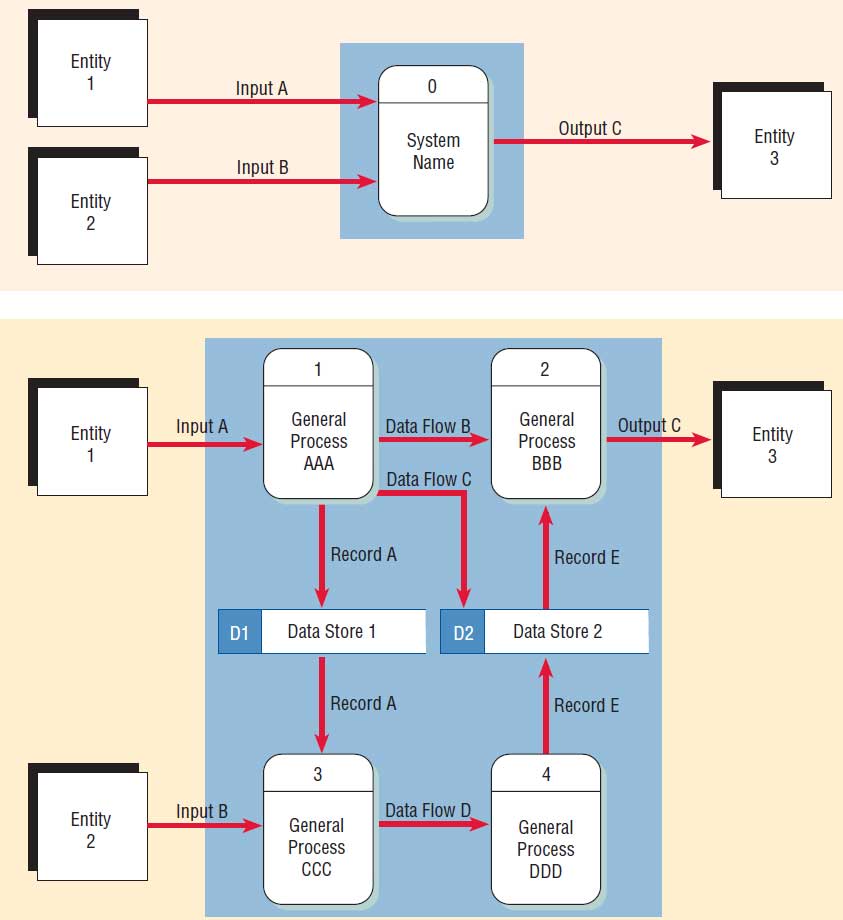
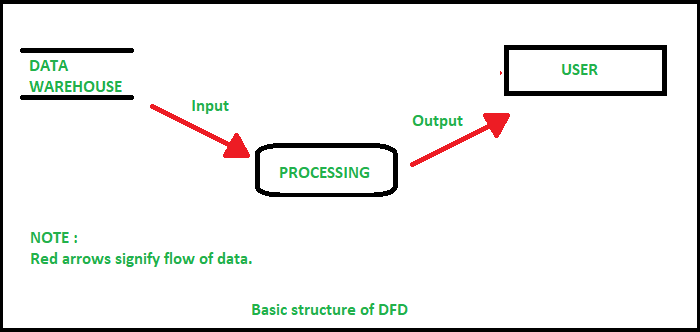
There are four basic symbols that are used to represent a data-flow diagram. Process. A process receives input data and produces output with a different content or form. Processes can be as simple as collecting input data and saving in the database, or it can be complex as producing a report containing monthly sales of all retail stores in the northwest region. Every process has a name that ...
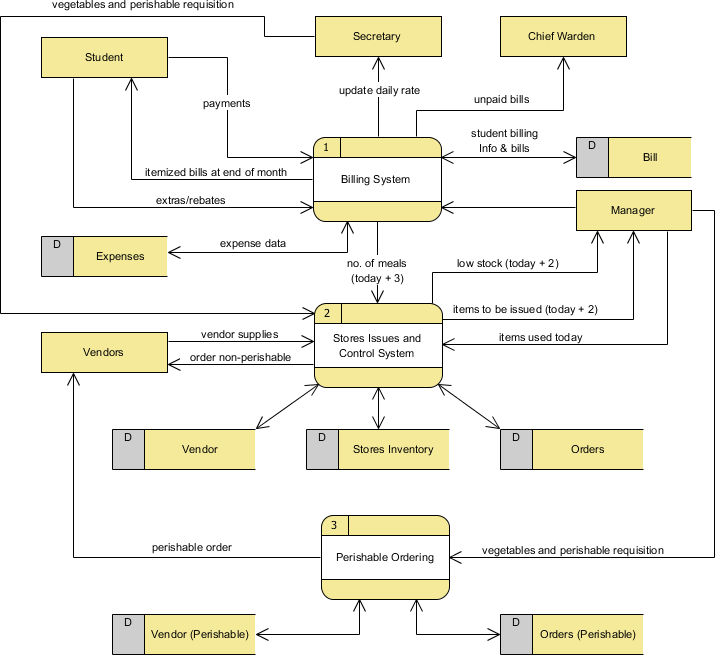
Three data flow and process combinations that you must avoid: ... • Gray hole. A gray hole is a process that has at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown. For example, a date of birth input is not sufficient to produce a final grade output in the CALCULATE GRADE process. Spontaneous generation, black holes, and gray holes are ...
Black hole - this is when a process has input, but produces no output. Gray hole.A gray hole is a process that has at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output. For example, Date is the input data but calculate grade the exit data. Correct Use of Data Stores: Correct use of external entities: Data Stores: Data stores cannot be used by ...
A black hole has input, but no output. A gray hole has at least one input and one output. 2. Step 1 is to draw a context diagram. A context diagram is a top-level view of an IS that shows the system's boundaries and scope. Step 2 is to draw a diagram 0 DFD to show the detail inside the black box. A diagram 0 DFD shows major internal processes ...
9. ____ is/are logically impossible in a DFD because a process must act on input, shown by an incoming data flow, and produce output, represented by an outgoing data flow. a. Spontaneous combustion b. Gray matter c. Black holes d. Black boxes
In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate ... Rating: 5 · 3 reviews
8.In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. a. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown. 9. In a data dictionary, _____ refers to whether the data element contains numeric, alphabetic, or character values. d.
What is Data Flow Diagram? Also known as DFD, Data flow diagrams are used to graphically represent the flow of data in a business information system. DFD describes the processes that are involved in a system to transfer data from the input to the file storage and reports generation. Data flow diagrams can be divided into logical and physical.
data store b. data flow c. process d. gray hole ANSWER: b 7. In data flow diagrams (DFDs), a process resembles a _____, where the inputs, outputs, and general functions of the process are known, but the underlying details are not shown. a. black box b. terminator c. business rule d. decision table ANSWER:
Diagramming mistakes: Black holes, grey holes, and miracles . A second class of DFD mistakes arise when the outputs from one processing step do not match its inputs. It is not hard to list situations in which this might occur: A processing step may have input flows but no output flows. This situation is sometimes called a black hole .
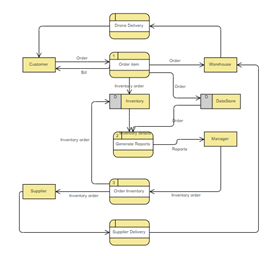
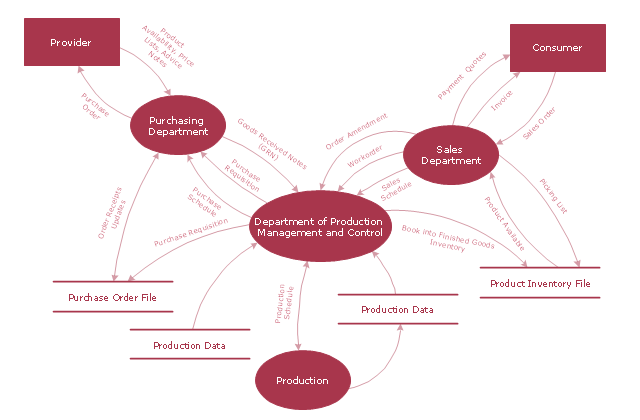
A Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is a traditional way to visualize the information flows within a system. A neat and clear DFD can depict a good amount of the system requirements graphically. It can be manual, automated, or a combination of both. It shows how information enters and leaves the system, what changes the information and where information ...
What is a Data Flow Diagram (DFD)? answer choices. A DFD is a graphical representation of how data flows through a business information system. A DFD is a flow chart that represent how data flows in a system. A DFD is is a way to structure an organization using different levels of authority and a vertical link, or chain of command, between ...
A data flow diagram (DFD) maps out the flow of information for any process or system. It uses defined symbols like rectangles, circles and arrows, plus short text labels, to show data inputs, outputs, storage points and the routes between each destination. Data flowcharts can range from simple, even hand-drawn process overviews, to in-depth ...
In data and process modeling, a(n) _____ shows what the system must do, regardless of how it will be implemented physically. a. organizational model b. physical model c. logical model d. relational model ANSWER: c 18. A data flow diagram (DFD) shows _____. a. how data is related b. what key fields are stored in the system c. how a system transforms input data into useful information d. what ...
In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown A data flow diagram (DFD) does not show the external entities that provide data to the system or receive output from the system.
In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. a. no output. b. at least one input and one output, but ...1 answer · 0 votes: Ans is - b. At least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown ------------------------------------------- ...
data flow gray hole process data store. process. In a data flow diagram (DFD), systems analysts call an entity that receives data from the system a source. True False. ... In a data flow diagram (DFD), a black hole is a process that has _____. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown
In a data flow diagram (DFD), a gray hole is a process that has _____. a. no input b. at least one output and one input, but the output obviously is insufficient to generate the input shown c. no output d. at least one input and one output, but the input obviously is insufficient to generate the output shown ANSWER:
Describes the expected number of occurrences for the data flow per unit of time. Volume and frequency. Each data flow represents a group of related data elements called a record or data structure. Record. The DFD ending point (s) for the data flow; the destination can be a process, a data store, or an entity.





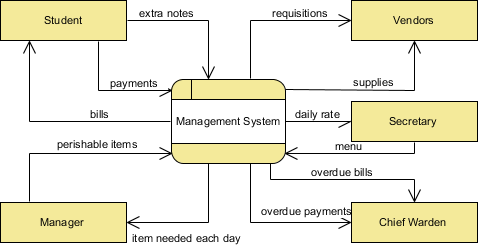


















0 Response to "43 in a data flow diagram (dfd), a gray hole is a process that has _____."
Post a Comment