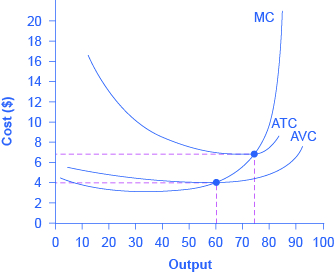
44 the mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of
Question : 81. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of : 1321325. 81. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: A. demand. B. conservation of matter and energy. conservation of matter and energy. drawn for metals reacting with sulfur, chlorine, etc., but the oxide form of the diagram is most common). The oxygen partial pressure is taken as 1 atmosphere, and all of the reactions are normalized to consume one mole of O2. The majority of the lines slope upwards, because both the metal and the oxide are present as
(d) the minimum point of MC curve. 349. When LAC curve is _____ it will be tangent to rising portions of the SAC curves (a) sloping downward (b) sloping upwards (c) constant (d) none of the above. 350. When the LAC curve slopes upward, the firm is experiencing _____ (a) economies of scale (b) external economies (c) diseconomies (d) none of ...
The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: 11eacf22_e8e2_b2ff_aab5_4793d8a674df_TB6686_00 A)demand. B)conservation of matter and energy. C)diminishing marginal utility. D)diminishing returns. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of A demand B from CECN 204 at Ryerson University. Short-run and Long-run Supply Curves (Explained With Diagram) In the Fig. 24.1, we have given the supply curve of an individual seller or a firm. But the market price is not determined by the supply of an individual seller. Rather, it is determined by the aggregate supply, i.e., the supply offered by all the sellers (or firms) put together.
The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. Decreasing MC means to shift the MC curve downwards in the firms diagram, such that MC intersects MR at a greater quantity such that the firm has to charge a lower price and produce a larger quantity. ... Therefore the supply curve is only an upwards-sloping part of the marginal cost curve. ... Understanding the law of supply. 2. Supply curve ... The marginal cost to society of reducing pollution rises with increases in pollution abatement because of the law of: diminishing returns. The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of: diminishing returns. Suppose that Susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. Economists would expect: Total revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is a straight line sloping up. The slope is equal to the price of the good. Total cost also slopes up, but with some curvature. At higher levels of output, total cost begins to slope upward more steeply because of diminishing marginal returns. 27. The aggregate supply curve (short-run) slopes upward and to the right because: A) changes in wages and other resource prices completely offset changes in the price level. B) the price level is flexible upward but inflexible downward. C) supply creates its own demand. D) wages and other resource prices adjust only slowly to changes in the
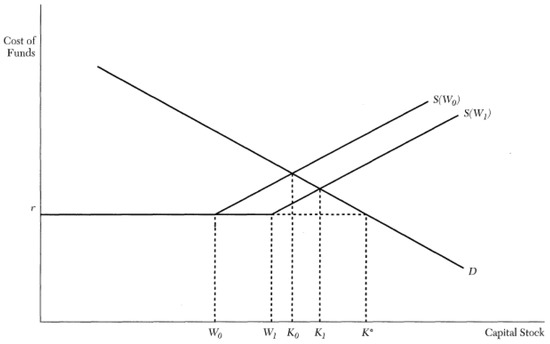
If the demand curve reflects consumers' full willingness to pay, and the supply curve ... The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. Structural Analysis by R C Hibbeler 8th edition when more complex cost and revenue curves are required (remember that this is A2!) Diagrams included in this revision document 1. The law of diminishing returns 2. Fixed and variable costs in the short run 3. Changes in variable costs and the effect on the profit maximising price, output and profit 4. The long run minimum efficient scale 5. The supply curve slopes upward because the volume suppliers in an industry are willing to produce increases as the price the market pays increases. Under typical circumstances, the revenue and profit derived by a supplier increases as the market price rises.
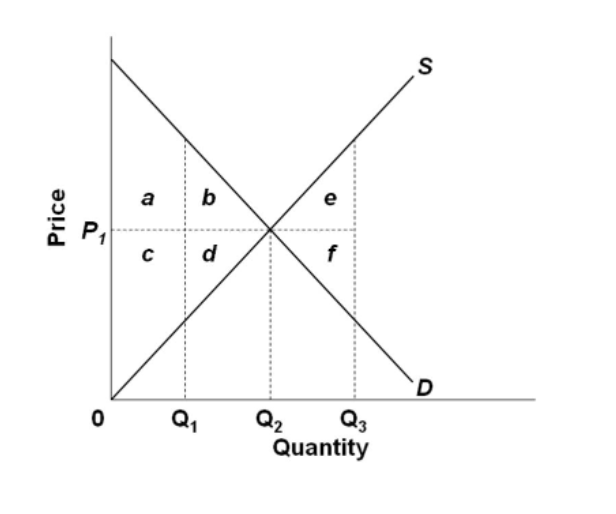
The average total cost curve is upward-sloping. B) ... There are diseconomies of scale. In Figure 8.1, diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market. ... A law established by the government to protect new industries. B) Along this curve: d P d Q = d d Q ( C ( Q) Q) − k Q 2. Thus d P / d Q is the difference of two terms, the first of which is the slope of the AC curve; we showed in Leibniz 7.3.1 (using the quotient rule) that this is ( MC − AC) / Q. Also, we know from the equation of the isoprofit curve that k / Q = P − AC. Since slope is defined as the change in the variable on the y-axis divided by the change in the variable on the x-axis, the slope of the supply curve equals the change in price divided by the change in quantity. Between the two points labeled above, the slope is (6-4)/(6-3), or 2/3. Note that the slope is positive, as the curve slopes up and right. (a) See the graph. Over the 0 to 4 range of output, the TVC and TC curves slope upward at a decreasing rate because of increasing marginal returns. The slopes of the curves then in crease at an increasing rate as diminishing marginal returns occur. (b) See the graph. AFC (= TFC/Q) falls continuously since a fixed amount of capital cost is
In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy, productively efficient firms optimize their production process by minimizing cost consistent with each possible level of production, and the result is a cost curve. Profit-maximizing firms use cost curves to decide output quantities.
The AFC curve slopes continuously downward because the total fixed cost is the same regardless of output. of the law of diminishing marginal returns. marginal cost does not change with the output level. variable costs change as output increases. The MC curve eventually slopes upward because most of the costs are fixed costs. marginal returns.
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. ... show demand curves reflecting the prices Alvin and Elmer are willing to pay for a public good, rather than do without it. If the marginal cost of the optimal quantity of this public good is $10, the optimal quantity must ... the optimal project size is the one for which MB = MC.
The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of: diminishing returns. The MB curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of: diminishing marginal utility. (Consider This) Suppose that Susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. Economists would expect:
The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of diminishing returns 2. Then there is a range in which it shows diminishing returns to scale sloping upwards. Market Supply And Market Demand Consider this suppose that susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. When supply is represented visually ...
Isoprofit curves can be upward-sloping when at high profit levels. Every price-quantity combination lies on an isoprofit curve. Isoprofit curves slope downward when the price is above the unit cost. An isoprofit curve joins all combinations of price and output for which the firm’s profit is the same.
The law of diminishing marginal returns explains quizlet. The law of diminishing marginal returns explains quizlet The law of diminishing marginal returns explains quizlet ...
Supply curves must reflect all costs of production, and demand curves must ... The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of:. Rating: 4,8 · 4 reviews
(a) See the graph. Over the 0 to 4 range of output, the TVC and TC curves slope upward at a decreasing rate because of increasing marginal returns. The slopes of the curves then increase at an increasing rate as diminishing marginal returns occur.' (b) See the graph.
The firm's marginal cost curve slopes upward in the short run because of the law of diminishing marginal returns. The short-run is a period where a...
Microeconomics Questions and Answers. Get help with your Microeconomics homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Microeconomics questions that are explained in a way that's easy for you to ...
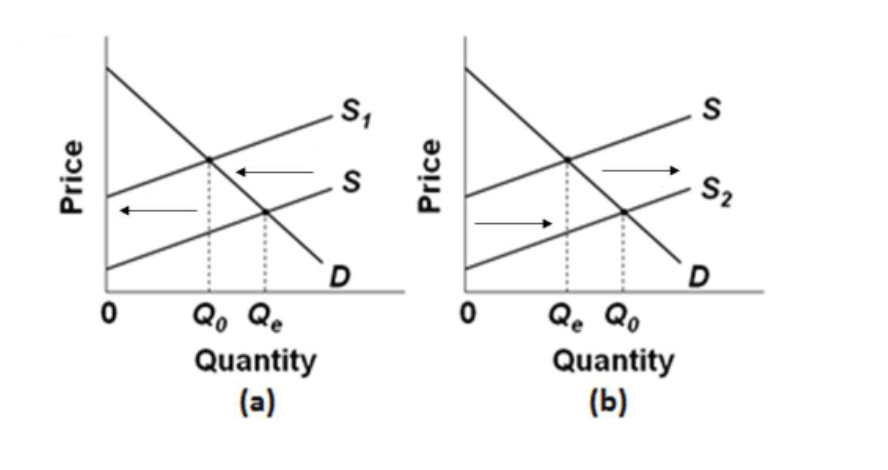
a.marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount. ... Refer to the diagram in which S is the market supply curve and S1 is a supply curve ...
Which one of the following might shift the marginal benefit curve from MB1 to MB2? The MB curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of: Home
If the demand curve reflects consumers' full willingness to pay, and the supply ... The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of.
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: asked Aug 12, 2018 in Economics by Get_Bizzy. A. demand. B. conservation of matter and energy. C. diminishing marginal utility. D. diminishing returns. principles-of-economics; 0 Answers. 0 votes. answered Aug 12, 2018 by X5452 ...
By representing both good X and good Y in a single diagram in this way, the intersection of the two offer curves depicts equilibrium in both markets simultaneously, something that is possible (indeed necessary) because of Walras' Law. Offer curves need not be upward sloping throughout.
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. A)demand. B)conservation of matter and energy. C)diminishing marginal utility. D)diminishing returns. Correct Answer: Explore answers and other related questions. 10+ million students use Quizplus to study and prepare for their homework, quizzes and exams through 20m+ questions in ...
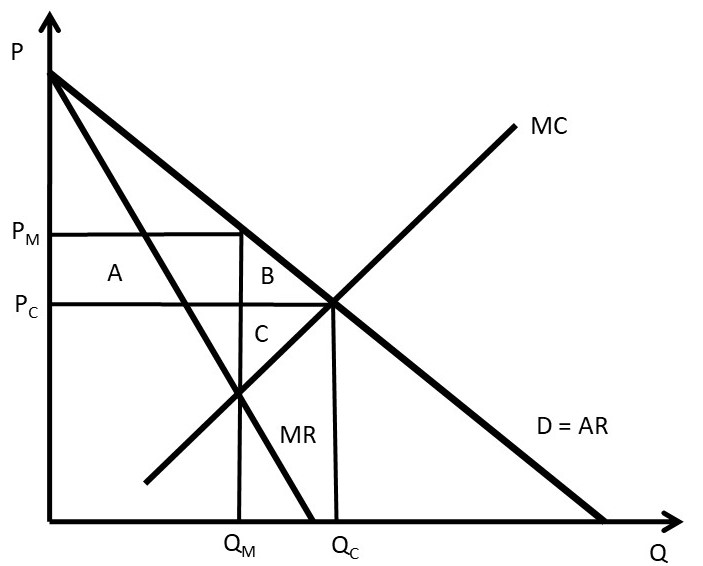
The marginal cost of a firm is important in economic theory because it will maximize profits up to the point where the marginal cost (MC) equals the marginal revenue (MR). As well, a firm's supply curve is effectively the part of the MC curve above average variable costs (from point B upwards, on the diagram below).
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: 11ea82e6_0566_bf46_9299_49abc54aca85_TB2474_00_TB2474_00 A) demand. B) conservation of matter and energy. C) diminishing marginal utility. D) diminishing returns.
The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of: diminishing returns. The MB curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of: diminishing marginal utility. (Consider This) Suppose that Susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. Economists would expect: those enjoying the art to "free ...
Both curves also have the same slope. ... Figure 2 shows a top-down view of the free-body diagram of the forces exerted on the pin at a particular moment in time. From a top-down perspective, ... The force increases because it is part of a Newton's third law pair of …
Supply curves must reflect all costs of production, and demand curves must ... The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of:. Rating: 4,4 · 9 reviews
summing vertically the individual demand curves for the public good. ... The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of.
Society's marginal cost of pollution abatement curve slopes upward because of the law of diminishing marginal utility. False.
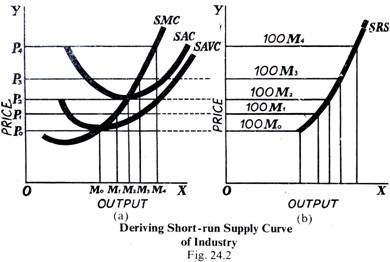
The LRS curve of an increasing cost industry will slope upward towards right, i.e., the law of supply will work in this case. However, in the case of decreasing cost and constant cost industries the LRS curve will be a downward sloping curve and a horizontal straight line, respectively. In these cases, we shall get exceptions to the law of supply.
Supply curves are traditionally represented as upward-sloping because of the law of diminishing marginal returns. This need not be the case, however, as described below. Special cases of a supply curve. As described above, the general form of a supply curve is upward sloping. There are cases, however, when supply curves do not slope upwards.
The MC curve slopes upward due to. asked Aug 18, 2019 in Economics by kntmeng. A. increasing returns to scale. B. diminishing returns. C. constant returns to scale. D. decreasing returns to scale. microeconomics; 0 Answers. 0 votes. answered Aug 18, 2019 by ...
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. A) demand. B) conservation of matter and energy. C) diminishing marginal utility. D) diminishing returns. Categories.
100% (1 rating) The correct answer is THE LOW OF DIMINISHING RETURNS. The marginal c …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: MB MEB 0 Amount of Pollution Abatement e MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of demand conservation of mattor land energy diminishing marginal ubilit Sa. Previous question Next question.
Is an Upward-Sloping Demand Curve Possible? In economics, the law of demand tells us that, all else being equal, the quantity demanded of a good decreases as the price of that good increases. In other words, the law of demand tells us that price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions and, as a result, demand curves slope downward. Must this always be the case, or is it possible for ...
Answer (1 of 11): The simple answer is diminishing marginal returns. Assuming costs are on the vertical axis and quantity is on the horizontal axis, marginal cost curves are usually positive, reflecting higher costs, after the initial period of down sloping caused by increasing efficiency. Onc...
The mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Consider this suppose that susie creates a work of art and displays it in a public place. The mb curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of.
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: <demand. <conservation of matter and energy. <diminishing marginal utility. <diminishing returns. diminishing returns. The MB curves in the diagram slope downward because of the law of: <conservation of matter and energy. <diminishing returns. diminishing <marginal utility.
This upward slope represents increasing marginal costs with an increase in production. When prices are low, quantity is low, but as price and profits increase, supply increases, as well, creating an upward curve. Supply curves can also be flat or even vertical. If the marginal cost stays the same, a flat curve results.
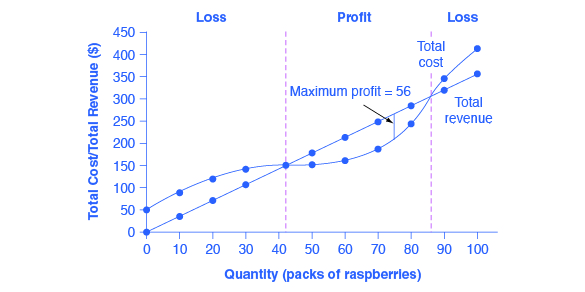
Total Cost and Total Revenue at the Raspberry Farm. Total revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is a straight line sloping up. The slope is equal to the price of the good. Total cost also slopes up, but with some curvature. At higher levels of output, total cost begins to slope upward more steeply because of diminishing marginal returns.
The MC curves in the above diagram slope upward because of the law of: A. demand. B. ... The MB curves in the above diagram slope downward because of the law of: A. conservation of matter and energy. B. diminishing returns. C. diminishing marginal utility. D. increasing cost.
Short-run and Long-run Supply Curves (Explained With Diagram) In the Fig. 24.1, we have given the supply curve of an individual seller or a firm. But the market price is not determined by the supply of an individual seller. Rather, it is determined by the aggregate supply, i.e., the supply offered by all the sellers (or firms) put together.
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of A demand B from CECN 204 at Ryerson University.
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of: 11eacf22_e8e2_b2ff_aab5_4793d8a674df_TB6686_00 A)demand. B)conservation of matter and energy. C)diminishing marginal utility. D)diminishing returns.
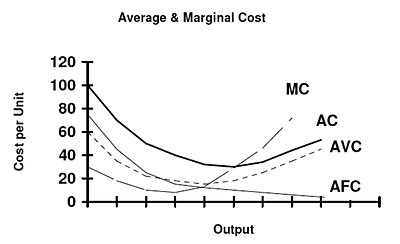
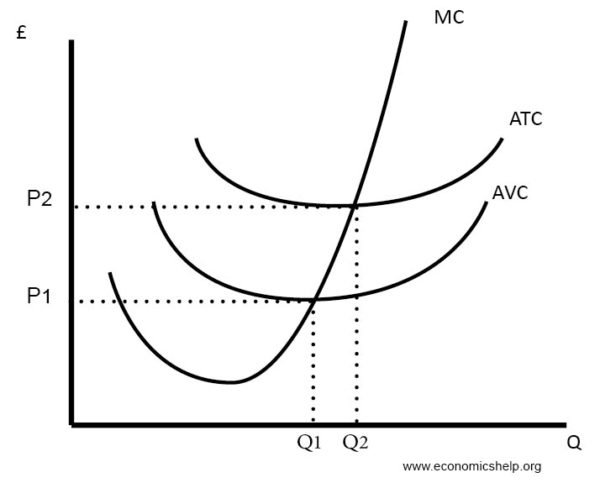








/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)














0 Response to "44 the mc curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of"
Post a Comment