40 o2 2 molecular orbital diagram
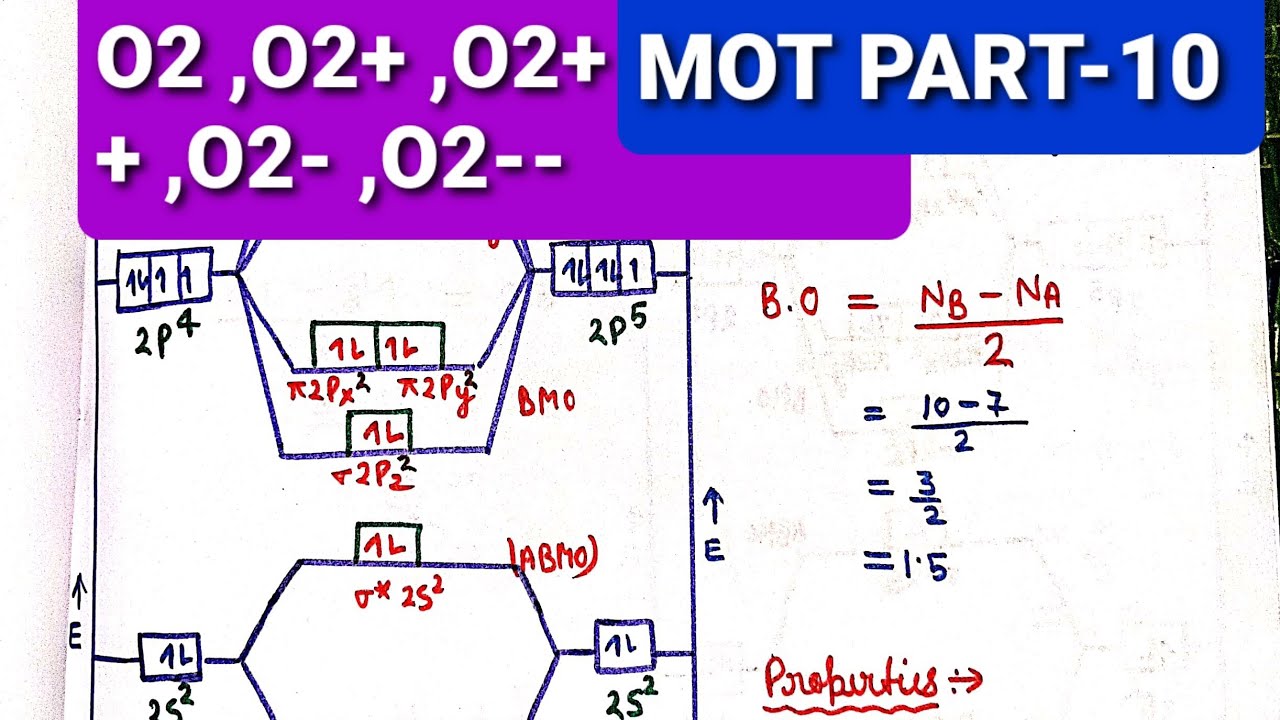
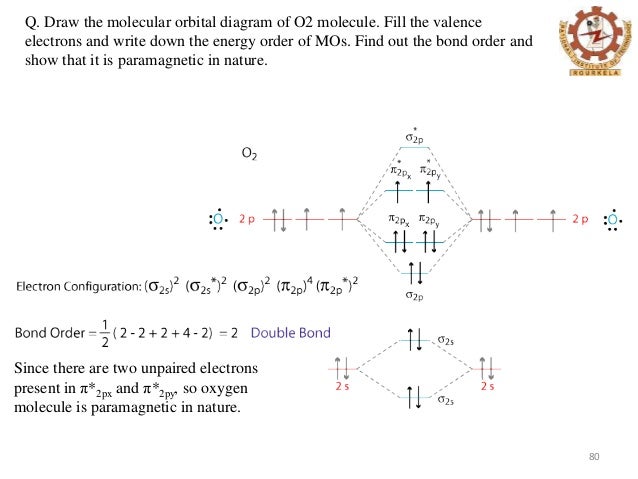
molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O-O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons. Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
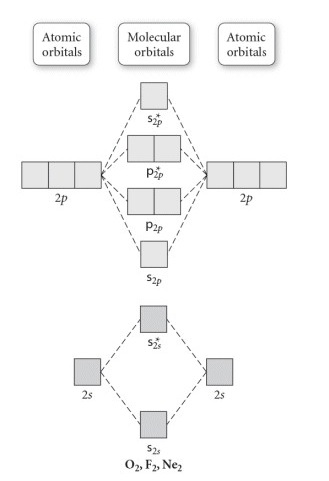
Oxygen's paramagnetism is explained by the presence of two unpaired electrons in the (π 2py, π 2pz)* molecular orbitals. Check Your Learning The main component of air is N 2. From the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.

O2 2 molecular orbital diagram
The Molecular orbital diagram for O2 O 2 is like this: As you can see the oxygen molecule has two unpaired electrons in the lower π π * ant-bonding states. For O2+2 O 22 + basically remove the two unpaired electrons in the π π * anti-bonding states, as they are the most easily removed. 26.2K views View upvotes Related Answer Amara Sehrish Even rather simple molecular orbital (mo) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how mo diagrams are constructed, from n2, o2, f2, ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.draw the molecular orbital diagram for ne 2 and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable. O2. Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p *
O2 2 molecular orbital diagram. Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the ... We know that Oxygen has atomic number = 8. Thus, the electronic configuration for an atom of oxygen in the ground state can be given as - $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^4}$ One atom of oxygen has 8 electrons. Thus, two atoms will possess 16 electrons i.e. Oxygen molecules will have 16 electrons. The molecular orbital diagram of an Oxygen molecule is as - Remember: When two oxygen atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. They are flipped compare... Transcribed image text: Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O2-, O22-, and O2. Which has the highest bond order? Which would be paramagnetic, and which ...
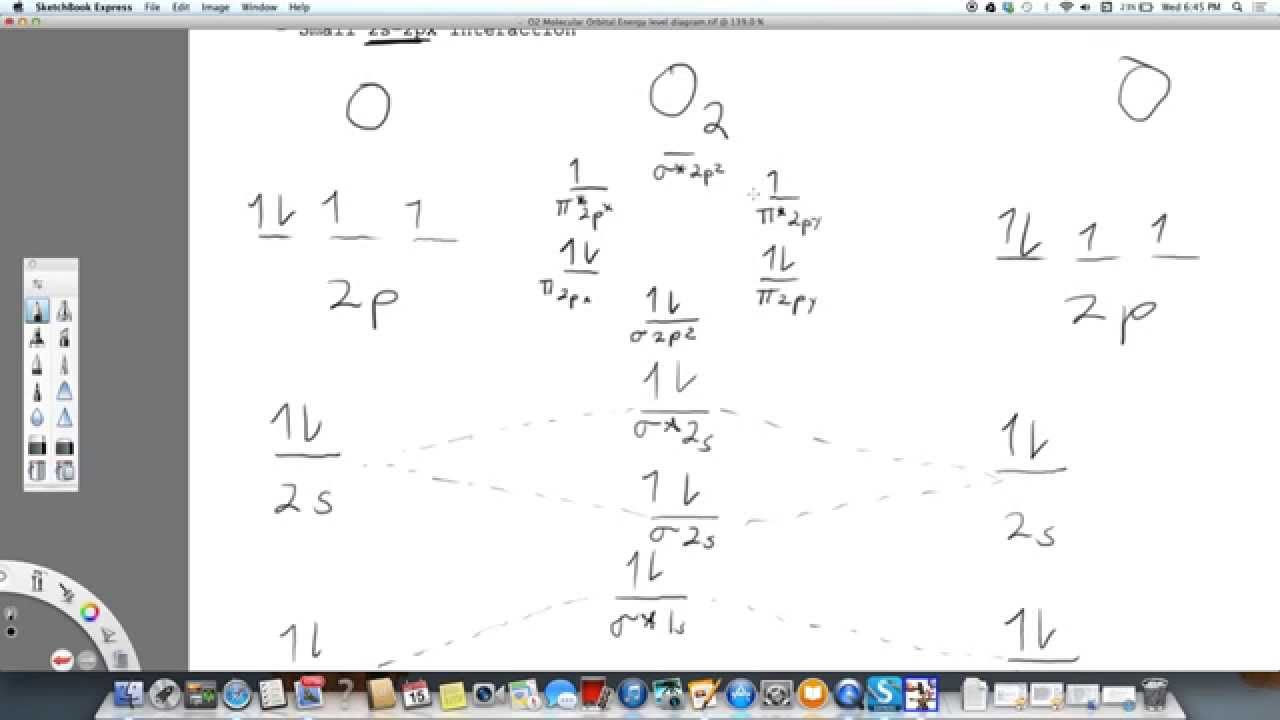
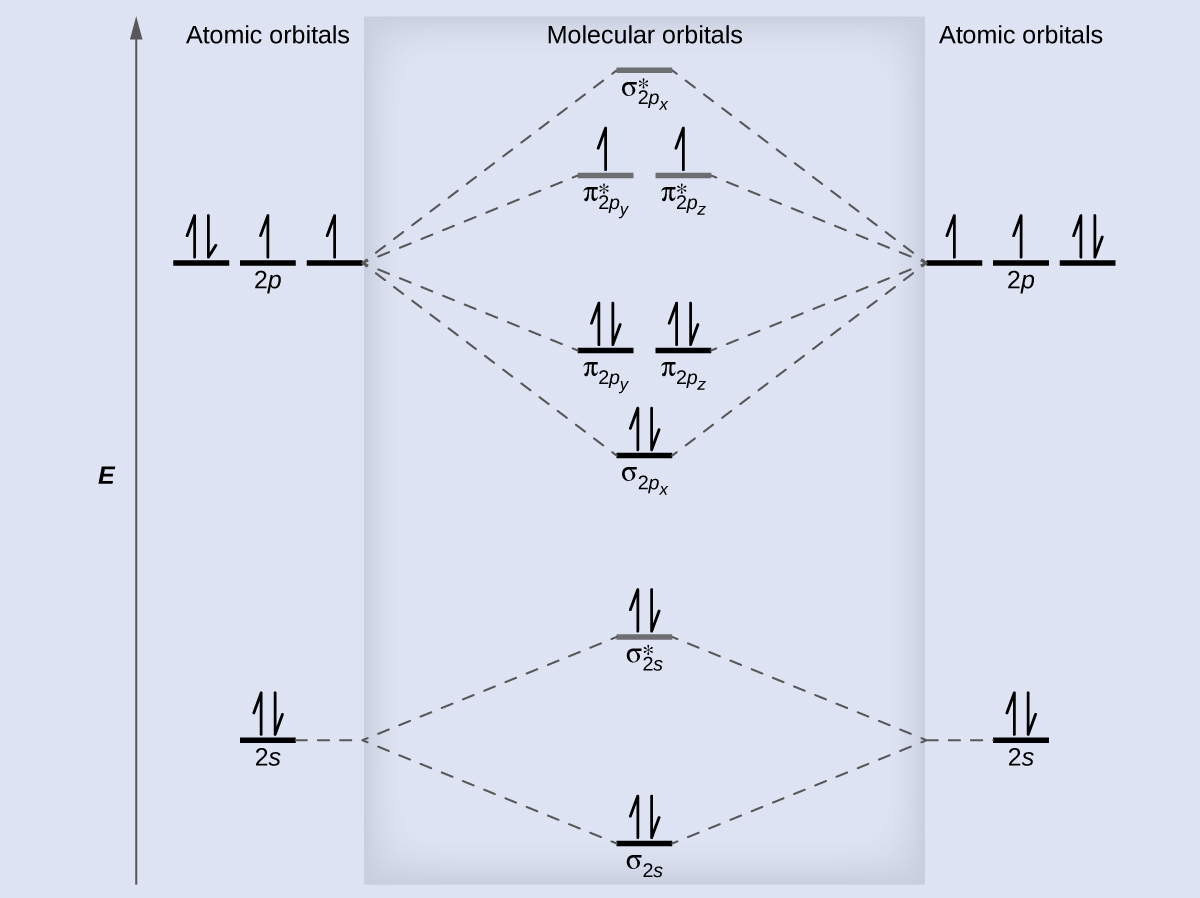
are combined. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2molecule would therefore ignore the 1selectrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2sand 2pvalence orbitals. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level The 2sorbitals on one atom combine with the 2sorbitals on another to form a 2sbonding and a 2s* O2 molecular orbital diagram oxygen has a similar setup to h 2 but now we consider 2s and 2p orbitals. This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals. molecular orbital diagram of O2+ Electronic configuration of O2+ In the case of O2- 17 electrons are present &3 electrons are present in antibonding orbitals. If number of electrons more in antibonding orbital the molecule become unstable. You'll need the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of O2. Begin with the atomic orbitals. Oxygen atom has 2s and 2p valence orbitals and 6 valence electrons: Each oxygen contributes 6, so we distribute 12 valence electrons into the molecule to get O2. Two 2s orbitals combine to give a σ2s bonding and σ* 2s antibonding MO.
Oct 28, 2014 — Ans: The stabilities of these can be best explained using Molecular orbital theory. ... Atomic orbitals of oxygen combine to form molecular ... The filling of molecular orbitals leaves 2 unpaired electrons in each of the π *(2p y) and π *(2p z) orbitals. Hence, the electronic configuration of the molecular orbitals accounts admirably for the paramagnetic properties of oxygen. This is among the greatest successes of the molecular orbital theory. Liquid O 2 is attracted towards the magnet. Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), ... Rating: 4.4 · 740 votes · Free · Android · Educational To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for (ce {O2}), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure (PageIndex {1}). We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
Aug 25, 2017 — O2^+2 means it loses 2 e-,there are 4 e- in p_orbitals.According to MOT(molecular orbital theory) 6 e- are in bonding molecular orbitals BMO and 2 e- are in ...3 answers · 7 votes: In O2 2+, there is 14 electrons. So, it’s MOT is comparable to N[code ]2[/code] & the MOT ...What is the electronic configuration O2^-2 molecule ...5 answersOct 6, 2015What is the molecular orbital diagram for O2- and ...5 answersMar 27, 2017Is O2 (2+) diamagnetic? - Quora1 answerDec 18, 2018What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2 ...6 answersMar 12, 2017More results from www.quora.com
Draw the complete molecular orbital diagram for O2 , O2 - , and O2 2- . Using these diagrams, determine for each molecule the number of unpaired electrons, if they are paramagnetic or diamagnetic, and the bond order. Question: Draw the complete molecular orbital diagram for O2 , O2 - , and O2 2- . Using these diagrams, determine for each ...
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of $ {N_2}$ or $ {O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond ...
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Show Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 7.7.12. Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as ...
As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [N b − N a ] / 2 = [1 0 − 6] / 2 = 2. Therefore there is a double bond present as O = O.
The double bond in C 2 consist of both Pi bonds because the four electrons are present in the two pi molecular orbitals. 10) N 2. ... Diagram for O2+ is wrong because 2p atomic orbital of 2nd O atom will have only 3 e-. Reply. Mrs Shilpi Nagpal says. September 26, 2018 at 11:06 am.
It is sigma2s(2)sigma2s*(2)sigma2p(2)pi2p(4)pi2p*(4)Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com
Now let's understand !! How to draw molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen molecule (O 2) ? Oxygen (O 2) molecule: Oxygen atom has electronic configuration 1s2, 2s2, 2p4 . Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each oxygen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px.
O2. Therefore, NF is predicted to be paramagnetic with a bond order of 2. The populations of the bonding (8 electrons) and antibonding (4 electrons) molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p *
Even rather simple molecular orbital (mo) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how mo diagrams are constructed, from n2, o2, f2, ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.draw the molecular orbital diagram for ne 2 and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable.
The Molecular orbital diagram for O2 O 2 is like this: As you can see the oxygen molecule has two unpaired electrons in the lower π π * ant-bonding states. For O2+2 O 22 + basically remove the two unpaired electrons in the π π * anti-bonding states, as they are the most easily removed. 26.2K views View upvotes Related Answer Amara Sehrish



.png)




















0 Response to "40 o2 2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment