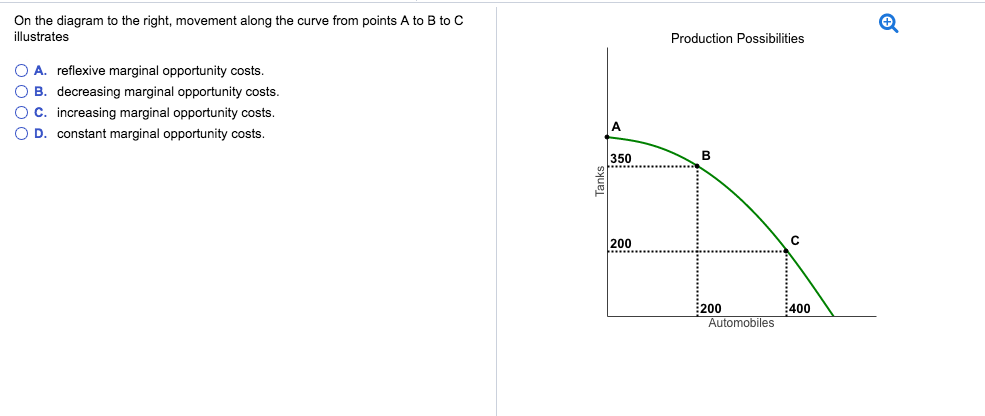
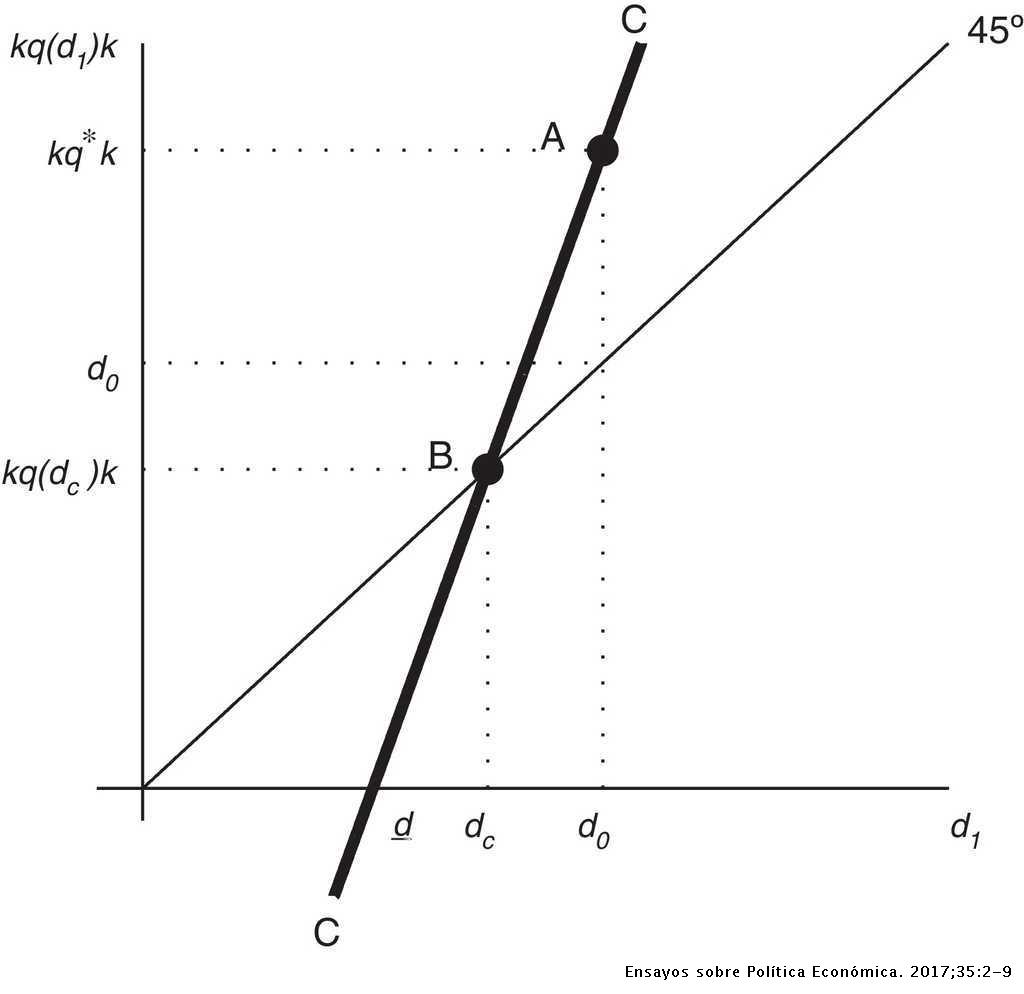
40 on the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates
Movement along a supply curve. The amount of commodity supplied changes with rise and fall of the price while other determinants of supply remain constant. This change, when shown in the graph, is known as movement along a supply curve. In simple words, movement along a supply curve represents the variation in quantity supplied of the commodity ... On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates A. reflexive marginal opportunity costs. B. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. C. increasing marginal opportunity costs. D. constant marginal opportunity costs.
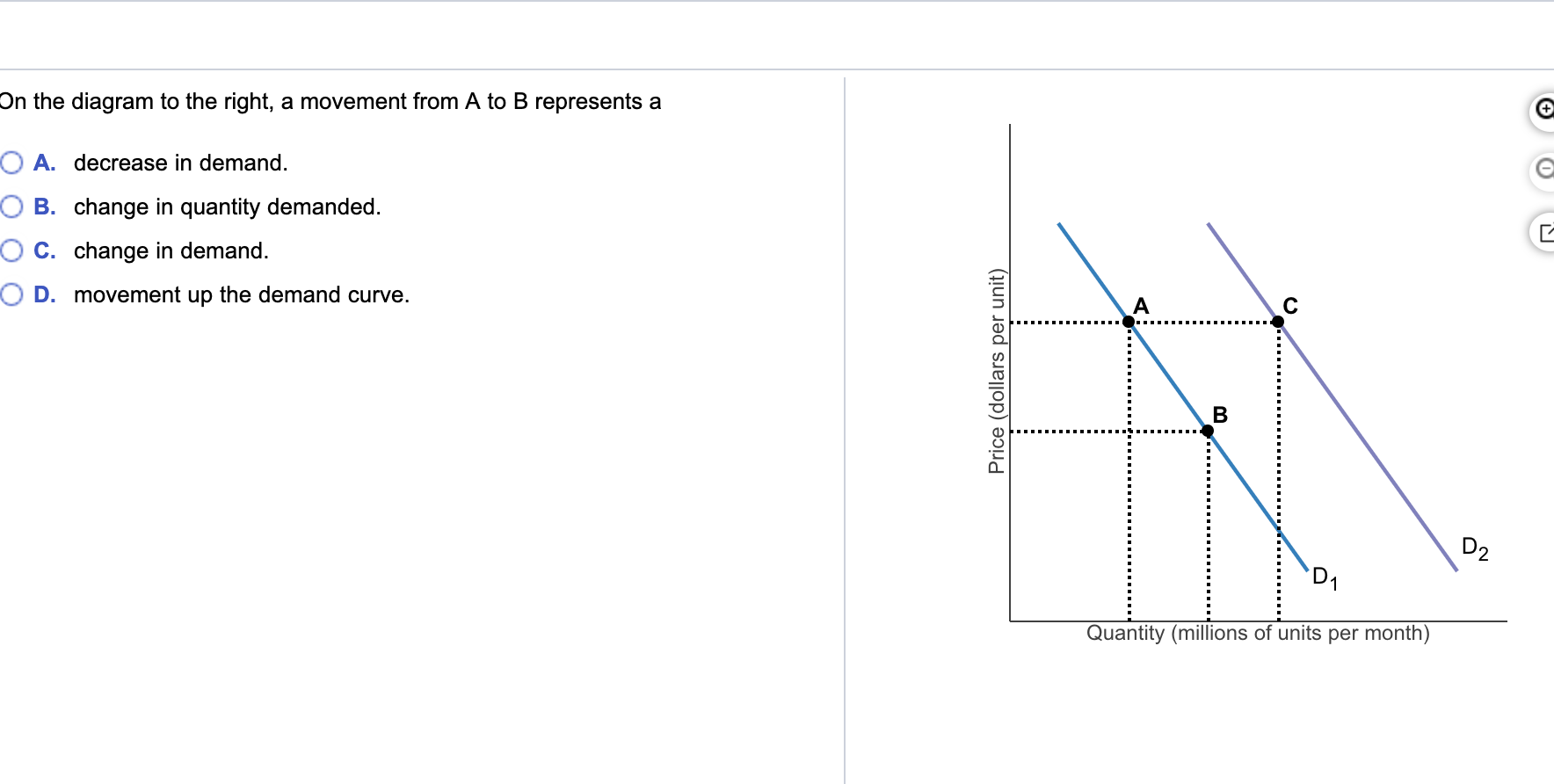
Movement along a demand curve can also be understood as the variation in quantity demanded of the commodity with the change in its price, ceteris paribus. There can be two types of movement in a demand curve - extension and contraction. Extension in a demand curve is caused when the demand for a commodity rises due to fall in price.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates ______. Image: increasing marginal opportunity costs. Rating: 5 · 1 review On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C ... a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that ... On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates. A. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. B. constant marginal opportunity costs.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates. A) right with a slope less than one. B) right with a slope greater than one. C) left with a slope less than one. D) left with a slope greater than one. 5. An increase in taxes shifts the IS curve, drawn with income along the horizontal axis and the interest rate along the vertical axis: A) downward and to the left. B) upward and to the right. moves left or right. both of the above. none of the above. Answer: Movement of the demand curve happens when all other factors affecting the quantity demanded, remain constant and only the price changes. Hence, the demand moves upward or downward along the same curve. Therefore, the correct answer is option A. b. technology improves c. input prices rise d. expectations change - you expect the price of your product to rise next month ANSWER: a. A change in price will cause a movement along the supply curve, or a decrease in quantity supplied. b. The supply curve will shift to the right. c. The supply curve will shift to the left. d. Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
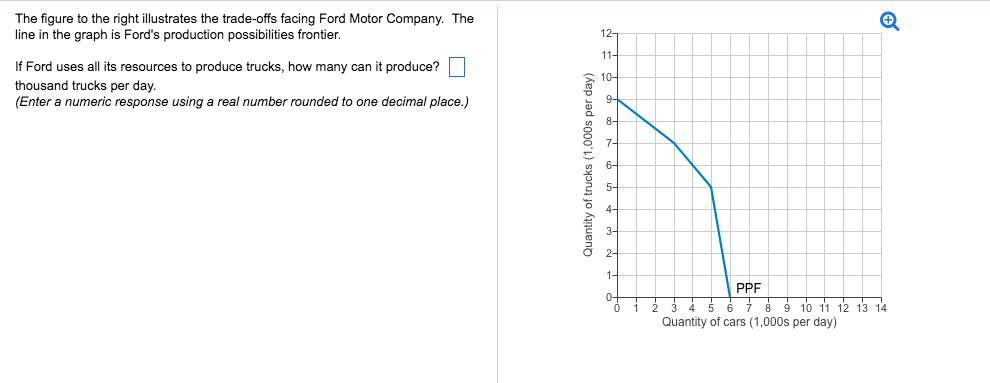
23 The diagram below represents a source of potential difference connected to two large, parallel metal plates separated by a distance of 4.0 × 10-3 meter. Which statement best describes the electric field strength between the plates? (1) It is zero at point B. (2) It is a maximum at point B. (3) It is a maximum at point C. For example, when an economy produces on the PPF curve, increasing the output of goods will have an opportunity cost of fewer services. Diagram of Production Possibility Frontier. Moving from Point A to B will lead to an increase in services (21-27). But, the opportunity cost is that output of goods falls from 22 to 18. In part (c) we show alternative combinations of r and Y which bring about commodity market equilibrium; that is to say ensure that I = S. The locus of points E, E, and E" is the IS curve in part (1) showing the complete set of combinations of Y and r levels that equilibrate the product market. The AD curve shifts to the right and there is movement upward along the SRAS curve. There will be no change in the LRAS curve. b. The price of commodities increases by 10% this year. This causes the SRAS curve to shift to the left. There will be a movement along the AD curve. There will be no change in LRAS. c. The price of oil falls.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates reflexive marginal opportunity costs. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. increasing marginal opportunity costs. constant marginal opportunity costs. Answer. Correct option (C). When we move from A to B, opportunity cost = (200 - 0) / (350 - 0) = 200 ... On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates A. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. B. constant marginal opportunity costs. C. increasing marginal opportunity costs. D. reflexive marginal opportunity costs On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates. A. reflexive marginal opportunity costs. B. On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates A. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. B. constant marginal opportunity costs. C. increasing marginal opportunity costs. D. reflexive marginal opportunity costs.
Dec 19, 2021 · on the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates. asked Dec 16, 2020 in Other by manish56 Expert (60.4k points) 0 votes. 1 ...
b. Consumers will now demand more chocolate ice cream at any given price, represented by a rightward shift of the demand curve. As a result, both equilibrium price and quantity rise. c. The price of a substitute (vanilla ice cream) has fallen, leading consumers to substitute it for chocolate ice cream.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates. A. Constant marginal opportunity costs. B.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C ... Your neighbor's consumption point after trade is illustrated by point
B. Technology used in production C. The number of sellers D. The income of consumers When one of the four major factors changes, causing an increase in supply, the supply curve shifts _____. The graph to the right illustrates the supply of smartphones in a country.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curves from points A to B to C illustrates: What is absolute advantage? The ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors using the same amount of resources. What is comparative advantage? The ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than other producers.
Correct option (C). When we move from A to B, opportunity cost = (200 - 0) / (350 - 0) = …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates reflexive marginal opportunity costs. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. increasing marginal opportunity costs ...
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates A. reflexive marginal opportunity costs. B. constant marginal opportunity costs. C.. increasing marginal opportunity costs D. decreasing marginal opportunity costs.

Conceptual Marketing Corporation - æ¡è¿Žä¸åœ‹ã€‚ 移情,尊é‡ï¼Œå°Šåš´ã€‚ 從æ洲的角度 ...
C) downward shift in the AD curve and a movement down along the AE curve. D) leftward movement along both the AE and AD curves. Answer: A 13) A shift in the aggregate expenditure curve as a result of an increase in the price level results in a A) leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve. B) movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
3. On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates a. Constant marginal opportunity costs. b. Reflexive marginal opportunity costs. c. Increasing marginal opportunity costs. d. Decreasing marginal opportunity costs.
a) A leftward shift in the demand curve. b) A rightward shift in the demand curve. c) A movement up and to the left along a demand curve. d) A movement down and to the right along a demand curve. 11. The diagram below illustrates 3 possible demand curves for coconuts. Suppose that coconuts and pineapples are substitutes.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates-Increasing marginal opportunity costs (up to down). 4. A production possibilities frontier (PPF) is - A curve showing the maximum attainable combination of two products that may be produced with available resources and current technology.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates. answer. ... The diagram to the right illustrates the situation in the toilet paper market. Suppose the government wants to use a Pigovian tax to bring about the efficient level of production. What should the value of the tax be?
The right answer is option A, because a movement from B to C …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: On the diagram to the right, a movement from B to C represents a S1 OA. change in supply. B. decrease in supply. OC. change in quantity supplied.
Similar to the demand curve, a movement along the supply curve from point A to point B is called a change in the quantity supplied. Changes along the supply curve are caused by a change in the price of the good. As the price of the apples increases, producers are willing to supply more apples.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates: (i) reflexive marginal opportunity costs. (ii) decreasing marginal opportunity costs.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates. increasing marginal opportunity costs. Image: On the diagram to ... Rating: 5 · 4 reviews
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates. A. decreasing marginal opportunity costs. B. constant marginal opportunity costs.
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C ... a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that ...
On the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points A to B to C illustrates ______. Image: increasing marginal opportunity costs. Rating: 5 · 1 review





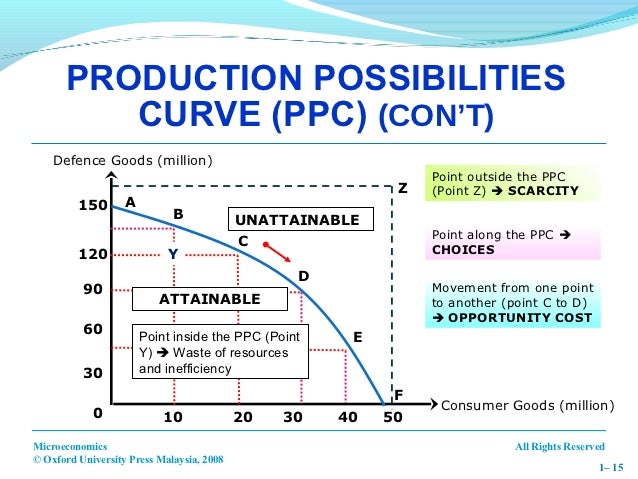


![Solved: 1. [5 Points] Based On The Aggregate Supply Relati ...](https://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2F0c9%2F0c94a09a-cc7e-4479-8ea2-647a2e79df2f%2FphptFBfOZ.png)

















0 Response to "40 on the diagram to the right, movement along the curve from points a to b to c illustrates"
Post a Comment