42 can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure?
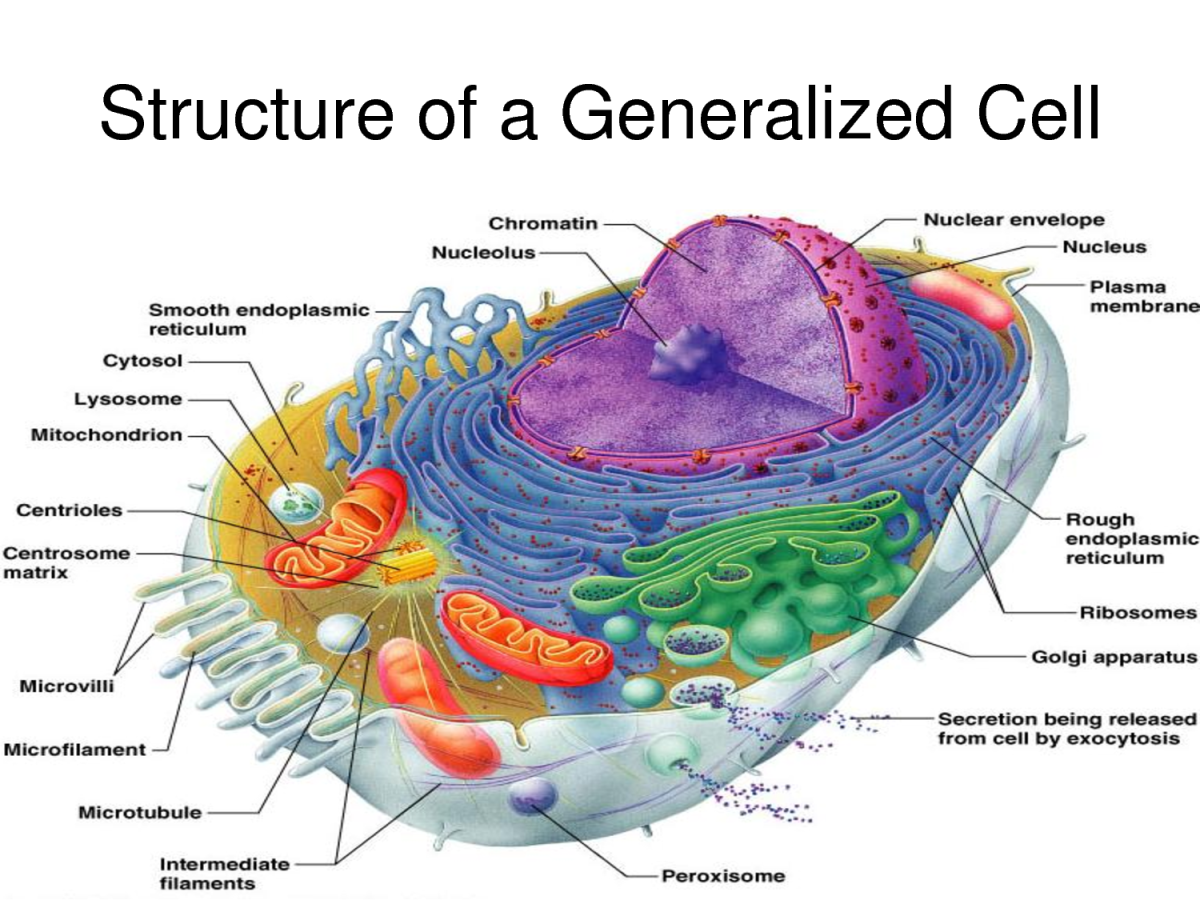
A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles. We are aware that all life stems from a single cell, and that the cell is the most basic unit of all living organisms. The cell being the smallest unit of life, is akin to a tiny room which houses several organs. Here, let's study the plant cell in detail... Learners should draw label lines to indicate the cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus and vacuole. The cells have a regular shape and each cell has a cell wall. Note: As an extension activity learners can also do wet mount preparations of cheek cells. Methylene Blue can be used to stain the cheek cells. Examining animal cells under the microscope Aim
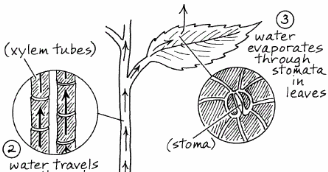
Play this game to review Plant Anatomy. Terrestrial plants have stomata on the surface of their leaves. A single stomata is surrounded by two guard cells that change shape in response to environmental factors and open or close the stoma. Which of the following best explains how the structure of the leaf is used in processes that occur in plants?
Can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure?
Can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure? Part A Drag each label to its appropriate place in the diagram. a. leaf b. blade c. petiole d. node e. cotyledon f. stem g. root h. internode DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes. Label the two lower nodes (the first and second nodes) on the plant diagram. petiole - a leaf stalk; it attaches the leaf to the plant. root - a root is a plant structure that obtains food and water from the soil, stores energy, and provides support for the plant. Most roots grow underground. root cap - a
Can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure?. The pistil has 3 parts. 1) The stigma is the sticky tip where pollen grains stick. 2) The ovary is at the base of the pistil and contains the ovules. 3) The style is the thin stalk that connects the stigma down to the ovary. When fertilized, the ovules become the plants seeds. The ovary becomes the plant's fruit. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (21 ratings) Not a plant Charophyte algae ( due to its movement) Non vascular plant (Bryophytes are an informal group consisting of divisions of non-vascular land …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Can you identify the plant group to which each of these ... Figure: Diagram of Plant cell wall. Source: Wikipedia Definition of plant cell wall. It is the rigid outer cover of the plant cell with a major role of protecting the plant cell, giving it, its shape. Structure of plant cell wall. It is a specialized matrix that covers the surface of the plant cell. Can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure? a. leaf b. blade c. petiole d. node e. cotyledon f. stem g. root h. internode. A major role of root hairs is to _____. increase the root surface area for absorption.
2 The use of plant fibres to replace oil-based products is increasing. The tensile strength of plant fibres can be changed by treating the fibres with chemicals. A student investigated the effect of treating banana fibres with a solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The student used some of the banana fibres as a control group. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of plant cell. 1. A plant cell (Fig. 291) is more or less a polyhedral structure limited on the outside by a rigid limiting membrane called cell wall. 2. Inside, it contains the protoplast. The contents of each living cell is known by the name protoplast. 3. Learning through Art: Plant Parts Can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure? Part A Drag each label to its appropriate place in the diagram. Building Vocabulary: Plant Growth 3 of 9 Can you place each word in the appropriate sentence? Part A Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences. 1. The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base. Answer link.
Different Parts of a Plant Cell. Plant cells are classified into three types, based on the structure and function, viz. parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. The parenchyma cells are living, thin-walled and undergo repeated cell division for growth of the plant. They are mostly present in the leaf epidermis, stem pith, root and fruit pulp. 1.23 Incoming and outgoing messages 1 SEQUENCE DIAGRAM note right : You can also put notes! Alice --> Bob : ok @enduml 1.23 Incoming and outgoing messages You can use incoming or outgoing arrows if you want to focus on a part of the diagram. Use square brackets to denote the left "[" or the right "]" side of the diagram. @startuml [-> A ... Identify basic common structures of plants. While individual plant species are unique, all share a common structure: a plant body consisting of stems, roots, and leaves. They all transport water, minerals, and sugars produced through photosynthesis through the plant body in a similar manner. All plant species also respond to environmental ... Broadly, plants have two organ systems: A) the root system and B) the shoot system. A typical diagram of a plant body consists of three parts: 1) roots, 2) stems, and 3) leaves, each having specialized functions.Apart from these basic parts, a flowering plant also contains 4) flowers and 5) fruits.. The root system covers the underground parts of a plant, which include the roots, tubers, and ...
plant Anat Figure 2. A herbaceous plant. The vegetative plant body consists of roots, stems, and leaves. The buds are located in the axils of the leaves and at the shoot tip. The roots also grow from meristem tissues in the root tip. Label the diagram based on your observations of a living plant and the structures named in Exercise 1 Discussion .
Make sure the veins are facing up, that means the leaf must be upside-down. Place the white paper over the leaf. Use the crayon on its side to gently colour on the paper over the leaf to trace the leaf. Label the leaf with the name of the plant it came from. Repeat this process with all the leaves.
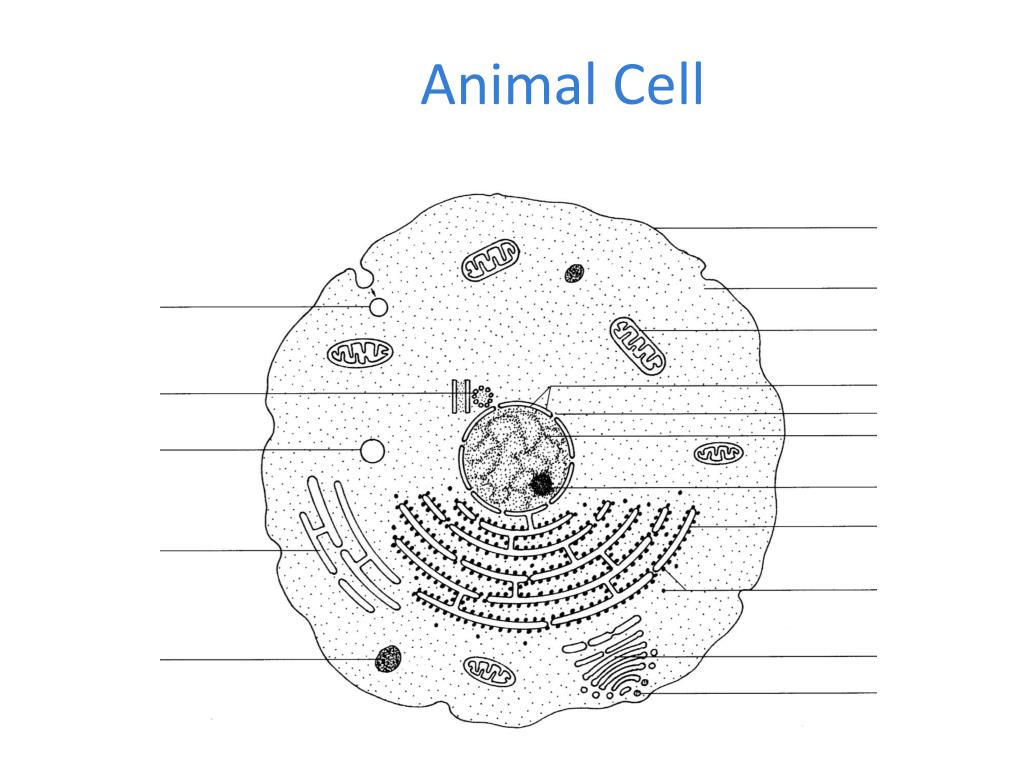
Cells differ in size, shape and structure and therefore carry out specialised functions. Link this to tissues. The differences between plant and animal cells can be linked to Grade 9. Cell theory (ESG4T) The cell theory developed in 1839 by microbiologists Schleiden and Schwann describes the properties of cells.
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the plant cell which is the fundamental unit of all living organisms in terms of structure and function. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of plant cell. History of Discovery: Robert Hooke in 1665 first discovered plant cell. The term 'cell' was […]
diagram and information below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a germinating bean seed that has been split open. A)ribosomes B)nuclei C)mitochondria D)vacuoles When water is available and growth begins, the plant embryo inside the seed secretes enzymes to digest the starch stored in the seed. The enzymes in cells of the
The lower epidermis produces a waxy cuticle too in some plant species. The lower epidermis contains pores called stomata that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to move in and out of the plant respectively. '''Stomata''': Tiny pores (small holes) surrounded by a pair of sausage shaped guard cells. These cells can change shape in order to close the ...
A few plant cells help in the transport of water and nutrients from the roots and leaves to different parts of the plants. Also read: Golgi Apparatus. To more about a plant cell, its definition, structure, diagram, types and functions, keep visiting BYJU'S Biology website or download BYJU'S app for further reference.
A plant has two organ systems: 1) the shoot system, and 2) the root system. The shoot system is above ground and includes the organs such as leaves, buds, stems, flowers (if the plant has any), and fruits (if the plant has any). The root system includes those parts of the plant below ground, such as the roots, tubers, and rhizomes.
Structures Unique to Plant Cells. Cell Wall: A wall on the outside of the membrane, which, in combination with the vacuole (as described below), helps the plant cell maintain its shape and rigidity.; Plastids: Used in photosynthesis to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into food.The most well-known plastids are chloroplasts, which contain the chlorophyll that gives many plants their ...
The diagrams show a cheek cell from a human and a leaf cell from a plant. (a) The two cells have a number of parts in common. (i) On the cheek cell, label three of these parts which both cells have. (3) (ii) In the table, write the names of the three parts you have labelled above and describe the main function of each part. Part Function
Label the two lower nodes (the first and second nodes) on the plant diagram. petiole - a leaf stalk; it attaches the leaf to the plant. root - a root is a plant structure that obtains food and water from the soil, stores energy, and provides support for the plant. Most roots grow underground. root cap - a
DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure? Part A Drag each label to its appropriate place in the diagram. a. leaf b. blade c. petiole d. node e. cotyledon f. stem g. root h. internode




























0 Response to "42 can you correctly place the labels on this diagram of basic plant structure?"
Post a Comment