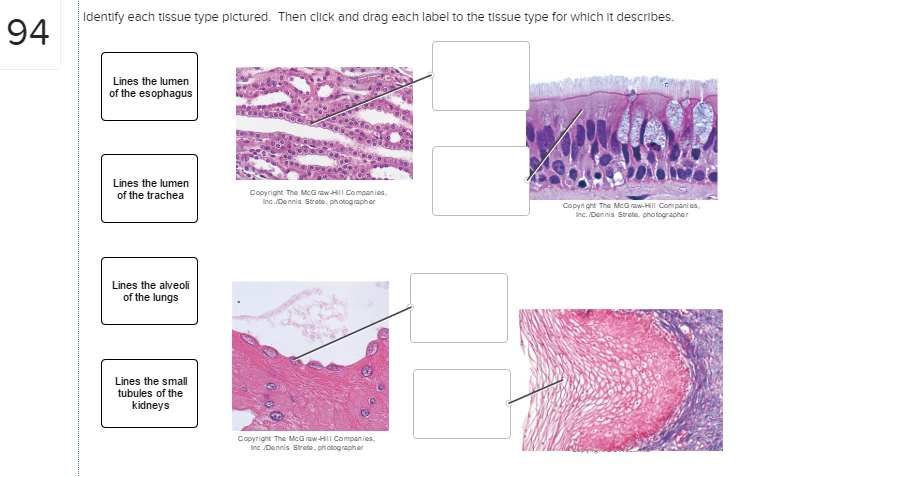
42 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
Alveolar sac - 2 or more alveoli sharing a common opening 2 types of alveolar epithelial cells Type I alveolar cells - form nearly continuous lining, more numerous than type II, main site of gas exchange Type II alveolar cells (septal cells) - free surfaces contain microvilli, secrete alveolar fluid (surfactant Feb 09, 2016 · Periodontal disease generally refers to inflammatory pathologic state of the gingiva and the supporting structures of the periodontium which include gingival, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, and cementum. They are commonly found in most human populations and result in significant morbidity, with exfoliation of the teeth in severe condition.
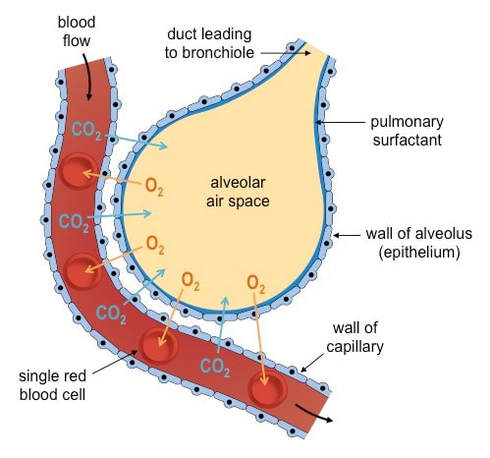
This diagram shows a diagram of an alveolar sac, showing how the organisation of the alveoli, and the network of blood capillaries that surround the alveoli (in red). The epithelium of the alveoli, contains two main types of cells:

On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
Jul 30, 2020 · Figure 1 is a diagram showing the main parts of the airway and lung. The airway consists of the oral and nasal cavities, which connect to the voice box (larynx), which connects to the windpipe (trachea). Note in the diagram that the windpipe splits into two air passages called bronchi, one going to each lung (right and left main bronchi). May 13, 2014 · Volume 509 Issue 7500, 15 May 2014. Many migrating birds rely on the Earth s magnetic field for their sense of direction, although what mechanism they use to detect this extraordinarily weak field ... B. Alveolar ducts The walls of alveolar ducts View Image are lined by alveoli and alveolar sacs (clusters of alveoli). C. Alveolus The walls of these structures are covered on both sides by squamous epithelium (too thin to see) of Type I cells lining adjacent alveolar lumens. Within the walls is an extensive capillary network.
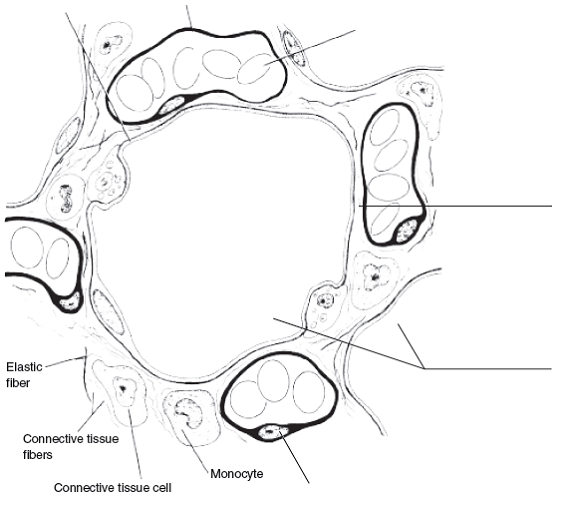
On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium. alveolar sac. middle lobe. terminal bronchiole. respiratory bronchioles. inferior lobe alveolar duct. alveolar duct alveoli ##### 13. On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the ##### respiratory membrane. Demonstrating Lung Inflation in a Sheep Pluck ##### 14. Lung, alveolus - 400X Here is a different alveolus. Now you can see the real difference between lung and adipose tissue. The outer edge of the empty space in adipose tissue consisted of the cell membrane and a very thin layer of cytoplasm. The alveolar wall or septum is made up of three tissue components: surface epithelium, supporting tissue, and an extensive network of continuous capillaries. Centrally it has capillaries surrounded by a vibrant network of elastin, reticular, and collagen fibers with a layer of squamous epithelial of two adjacent alveoli on either side. 28/05/2020 · Introduction. Coronaviruses are a diverse group of single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses with a wide range of vertebrate hosts (Cui et al., 2019).Four common coronavirus genera (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta) circulate among vertebrates and cause mild upper respiratory tract illnesses in humans and gastroenteritis in animals (Weiss and Navas-Martin, …
On the diagram below identify aveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, land red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. Elastic.4 pages Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Nov 18, 2020 · We uncovered two clusters of alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells (Fig. 1c), which produce surfactant that prevents alveolar collapse. These are intermingled throughout the alveolar epithelium (Fig. 1d ). 03/08/2020 · It occurs above or below the nodes and the base of leaves. {b) Lateral Meristem. It occurs on the sides, both in stem and root. ... Cuboidal epithelium (c) Alveolar tissue (d) Aerenchyma plant tissue. (CCE 2012) Answer: ... From the accompanying diagram (a) Identify the tissue (b) Infer the characteristic features of these cells. ...
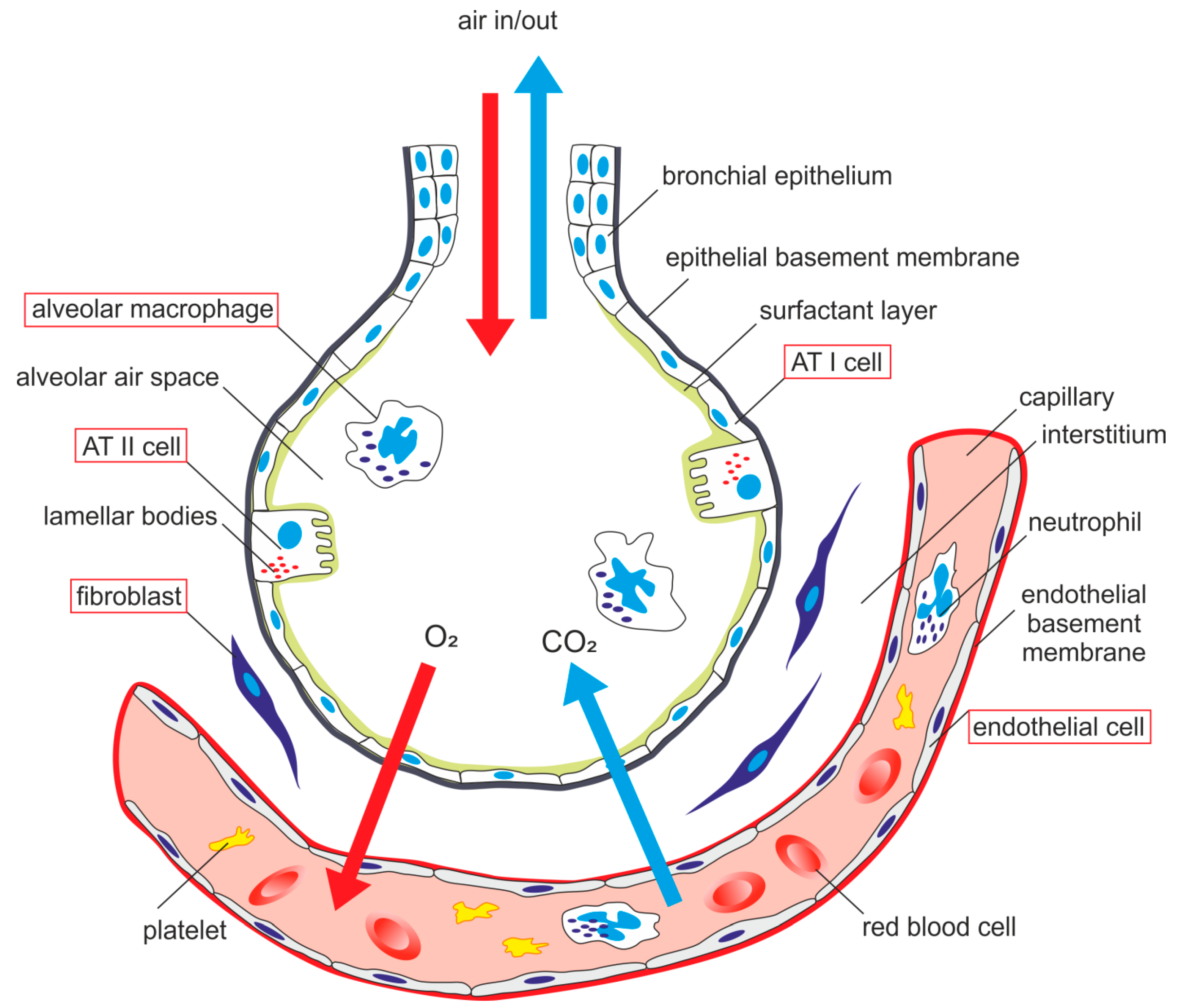
by N Kia'i · 2021 · Cited by 12 — Humidification requires serous and mucous secretions, and warming relies on the extensive capillary network that lays within the alveoli. The ... Be sure you know the types of cells found in the alveolus and how they can be distinguished on the basis of fine structure. Know the function of each cell type. Use TEMs to identify cell types and to aid in understanding the structure of the alveolar wall. #110 Lung Rabbit Orcein - Van Gieson - Paraffin section 6µm. alveolar epithelium The respiratory membrane is a composite structure consisting of three layers: (1) the endothelial cells lining an adjacent capillary (capillary endothelium) (2) the fused basal laminae that lie between the alveolar and endothelial cells(basement membrane - fused basal lamiae) - The epithelial lining of alveoli consists mainly of type I alveolar cells (also known as type I pneumocytes). - These are large, flat, squamous cells with few organelles and thin cytoplasm. - They cover about 93% of alveolar surface area. - Their primary purpose is air-blood gas exchange. - The junctions between these cells are narrow (1nm).
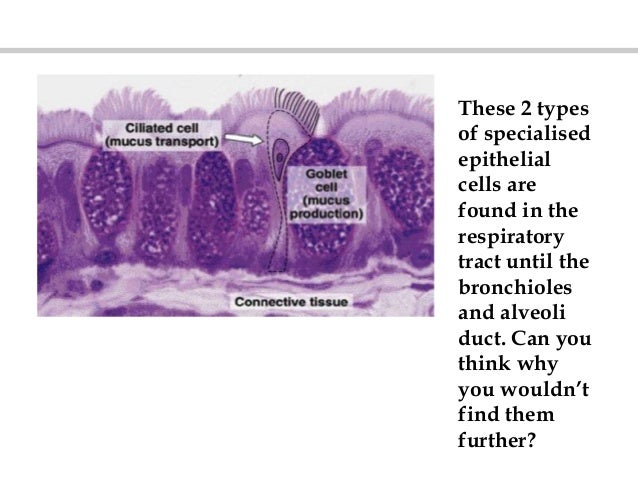
Ciliated columnar epithelium is composed of simple columnar epithelial cells with cilia on their apical surfaces. These epithelial cells are found in the lining of the fallopian tubes where the assist in the passage of the egg, and parts of the respiratory system, where the beating of the cilia helps remove particulate matter.
The epithelium here remains low cuboidal. Each respiratory bronchiole branches into between 2 and 11 alveolar ducts that still contain smooth muscle fibers in their walls. Along these walls, the alveolar ducts give rise to single alveoli and to numerous alveolar sacs, which are associated with 2 to 4 alveoli.
On the diagram below, identify the alveolar duet, respiratory bronchioles, terminal bronchiole ... The tracheal epithelium is ciliated and has goblet cells.
Bronchi, Bronchial Tree, & Lungs Bronchi and Bronchial Tree. In the mediastinum, at the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra, the trachea divides into the right and left primary bronchi.The bronchi branch into smaller and smaller passageways until they terminate in tiny air sacs called alveoli.. The cartilage and mucous membrane of the primary bronchi are similar to that in the trachea.
Put the following in order: 1. Alveolar Duct 2. Bronchiole 3. Tertiary Bronchus 4. Gas Exchange 5. Alveolar Sac 6. Nasopharynx 7. Secondary Bronchus 8. Trachea 9. Primary Bronchus 10. Nose 11. Resp...
The respiratory epithelium in trachea and bronchi is pseudostratified and primarily ... Alveolar epithelial cells (AEC) line the small, spongy sacs called ...Missing: diagram identify
Underneath the thin skin of the nose are its skeletal features. ... An olfactory epithelium used to detect odors is found deeper in the nasal cavity.
epithelial cells. Apical Basal Epithelial cells can also move protein and lipid from one side of the cell to the other by transcytosis. Transcytosis consist of endocytosis from on side of the cell, transport of the vesicles to the other side of the cell and then fusion of the vesicle with the cell membrane. Transcytosis allows cells to capture and
On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red bloo... A: Lungs provide the respiratory surface for the exchange of gases. Alveoli are very small sacs present...
the alveolar epithelium is a mosaic of type i alveolar epithelial cells which cover around 95% of the total alveolar surface with their thin squamous cell extensions interspersed with single cuboidal type ii alveolar epithelial cells which are easily recognized by their characteristic secretory organelles, the surfactant-storing lamellar bodies …
R.J. Mason, in Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine, 2006 The alveolar epithelium is composed of two types of epithelial cells, named alveolar type I and type II cells. Type I cells are large flat cells that comprise about 95% of the alveolar surface. Type II cells are small cuboidal cells with characteristic lamellar inclusions and apical microvilli and cover about 5% of the alveolar surface.
The diagram below shows the oxygen levels (paO: 2) in the alveoli and at ... Using only the letters A to G from the diagram, identify the following (letters may be used ... the epithelial cells covering the villi of a snake from each of Groups 1 and 2. microvilli 0.5 μm
The intraalveolar septa are the partition of two adjacent alveoli. They consists of two thin squamous epithelium layer. Mucosa layer of alveoli. Alveolar duct and alveolar sac lined by the patches of simple cuboidal epithelium. But alveolus is lined by simple squamous epithelium. These simple epithelium of alveoli contain the three major cells ...

(Fang Ruida) Davis. K Coronavirus pneumonia biomarkers and treatment(方瑞达) Davis。K å† çŠ¶åž‹ç—…æ¯’æ€§è‚ºç‚Žç”Ÿç‰©æ ‡å¿—ç‰©åŠæ²»ç–—防治
Alveolar epithelium- This primarily consists of two types of cells: a. Type 1 pneumocytes [ membranous pneumocytes]- flattened pavement type cells. ... This diagram illustrates the acinus which consists of the respiratory bronchioles (rb 1, 2, 3) the alveolar duct (ad) the alveolar sac (as) and the alveoli. (a) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 42446b12.
23/12/2021 · A comprehensive database of more than 35 histology quizzes online, test your knowledge with histology quiz questions. Our online histology trivia quizzes can be adapted to suit your requirements for taking some of the top histology quizzes.
Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
Ans. 1- Alveolar epithelium 2- Capil …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: iagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the brane respira Elastic fiber Connective tissue fibers Monocyte. Previous question Next question.
Solution for 14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane.…
14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillary blood? CIS 770 16.
07/12/2021 · Following histopathological examination of SARS-CoV-2-infected lung parenchyma, we found a spectrum of diffuse alveolar damage characterized by desquamation of the alveolar epithelium and mucous ...
Figure 13-2 is a diagram of the larynx and associated structures. On the figure, identify each of the structures listed below. Select a different- color for each and use it to color in the coding circles and the corresponding structures on the figure. Then answer the questions following the diagram.
In summary, the following things can be said about the alveolar shape and structure: Largely polyhedral shape. Open at one end, like a cup. Walls of the alveoli are composed of the pulmonary capillary sheet. Alveolar surfaces are covered in a thin (200nm) layer of surfactant which acts as the interface with the gas.
11/01/2017 · Tuberculosis is a public health problem worldwide, including in the United States—particularly among immunocompromised patients and other high-risk groups. Tuberculosis manifests in active and latent forms. Active disease can occur as primary tuberculosis, developing shortly after infection, or postprimary tuberculosis, developing after …
A bronchial tree (or respiratory tree) is the collective term used for these multiple-branched bronchi. The main function of the bronchi, like other conducting zone structures, is to provide a passageway for air to move into and out of each lung. In addition, the mucous membrane traps debris and pathogens.
The diagram given below is a simple epithelium. (MARCH-2015) a) Name the part marked as "P" in the figure. b) Write one function of a simple epithelium. Answer: a) Cell membrane (Out of syllabus) b) They are found in the walls of blood vessels and air sacs of lungs and are involved in a function diffusion. Question 21.
On the diagram below, identify the alveolar duct, respiratory bronchioles, terminal bronchiole, alveoli, and alveolar saci Examining Prepared Slides of Tracheal and Lung Tissue 14. The tracheal epithelium is ciliated and has goblet cells. What is the function of each of these modifications? cilia: goblet cells: 15.
01/12/2021 · 1. Introduction. Since its outbreak in January 2020, the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the highly contagious severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), has spread worldwide and become a serious public health problem [1,2].SARS-CoV-2 mainly infects the respiratory tract and lungs and leads to a new type of …
Types of Epithelial Tissue. There are three types of epithelial cells, which differ in their shape and function. Squamous- thin and flat cells Cuboidal- short cylindrical cells, which appear hexagonal in cross-section Columnar- long or column-like cylindrical cells, which have nucleus present at the base On the basis of the number of layers present, epithelial tissue is divided into the simple ...
Identify the tissue type and its function. Simple Squamous Epithelium •Diffusion and Filtration •Secretes lubricating substances in serosae. Identify the structure indicated. Skeletal Muscle. MultiplePeripherally Located Nuclei. Identify the structure indicated. Neuron Cell Body .
11/05/2021 · A schematic diagram of the alveolar lung-on-a-chip (Upper) and a photograph of an actual device are shown in Fig. 4A. The fabrication process of the chip is schemed in SI Appendix , Fig. S21 . The chip was composed of the 3D porous GelMA inverse opal scaffold (red part in the schematic) bonded to a PDMS chip.
Junqueira's Basic Histology Text and Atlas, 14th Edition
Epithelial tissues provide the body's first line of protection from physical, chemical, and biological wear and tear. The cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the body controlling permeability and allowing selective transfer of materials across a physical barrier. All substances that enter the body must cross an epithelium.
B. Alveolar ducts The walls of alveolar ducts View Image are lined by alveoli and alveolar sacs (clusters of alveoli). C. Alveolus The walls of these structures are covered on both sides by squamous epithelium (too thin to see) of Type I cells lining adjacent alveolar lumens. Within the walls is an extensive capillary network.
May 13, 2014 · Volume 509 Issue 7500, 15 May 2014. Many migrating birds rely on the Earth s magnetic field for their sense of direction, although what mechanism they use to detect this extraordinarily weak field ...
Jul 30, 2020 · Figure 1 is a diagram showing the main parts of the airway and lung. The airway consists of the oral and nasal cavities, which connect to the voice box (larynx), which connects to the windpipe (trachea). Note in the diagram that the windpipe splits into two air passages called bronchi, one going to each lung (right and left main bronchi).
























0 Response to "42 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium"
Post a Comment