42 pendulum free body diagram
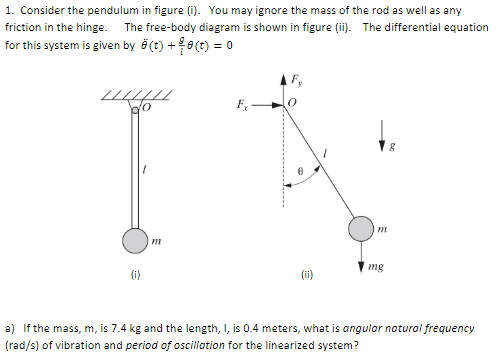
To begin, we first draw the free-body diagram where the forces acting on the pendulum are its weight and the reaction at the rotational joint. We also include a moment due to the friction in the joint (and the rotary potentiometer). The force diagram on the pendulum is shown in Figure 24.4. In particular, there is an unknown pivot force and the gravitational force acts at the center of mass of the rod. Figure 24.4 Free-body force diagram on rod The torque about the pivot point P is given by P τ=r P,cm ×mg. (24.3.2)
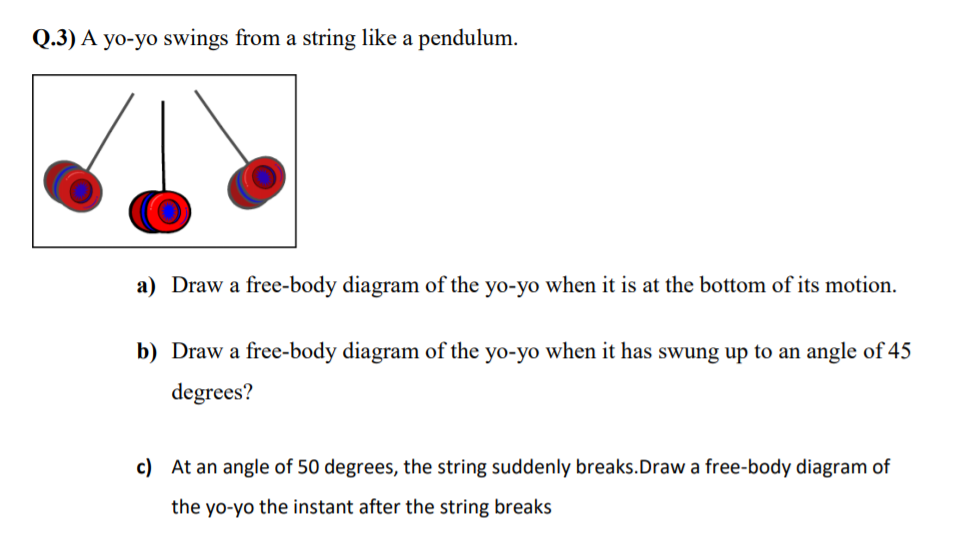
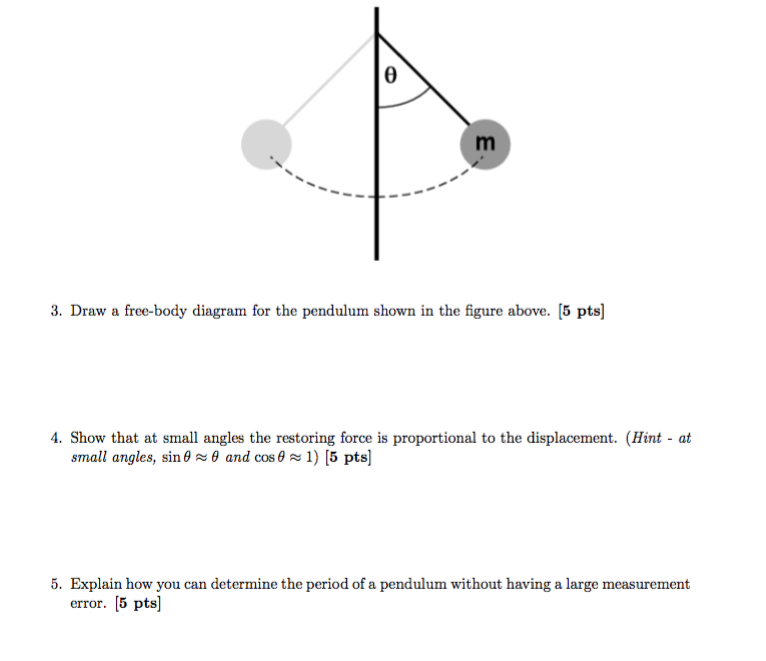
Physics questions and answers. Please help for questions 1, 2, and 3 (they are all together) Q1: Looking at the pendulum in Figure 6.1: list the forces that act on the hanging mass. Q2: For the pendulum in Figure 6.1, sketch a free-body diagram that shows all the forces that act on the mass, decomposed into their x- and y- components.

Pendulum free body diagram
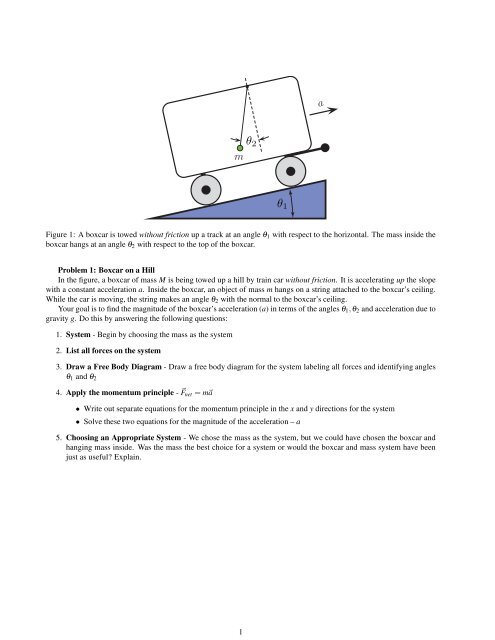
Next we draw the free body diagram for the pendulum. So we can write the net force as: F= Tcos θj− Tsin θi− mgj Using Newton's law F= maand the pendulum acceleration we found earlier, we have Tcos θj− Tsin θi− mgj= mR(θ''cos θi− θ'2sin θi+ θ''sin θj+ θ'2cos θj) Write the vector components of the above equation as separate equations. the pendulum, the following equation of motion is obtained P sin(µ)+N cos(µ)¡mgsin(µ) = ml˜µ+m˜ycos(µ) (4) where P is pointing towards the ground, relative to the cart free body diagram in Fig. 1, originating at the point where the cart and the pendulum connect. That same point on the pendulum free body diagram is pointing up. Pendulum Sim Activity; Related External Links. Simulink Intro Video; Simulink Modeling Video; Modeling Challenges Video; Contents. Train system; Free-body diagram and Newton's second law; Constructing the Simulink model; Running the model; Train system . In this example, we will consider a toy train consisting of an engine and a car. Assuming that the train only travels in …
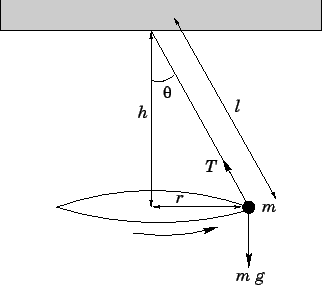
Pendulum free body diagram. moving projectile. After the capture, the pendulum swings to a maximum opening angle of µ. Using conservation of momentum and energy, the initial velocity v of the projectile can be determine based on the opening angle µ. The center of mass of the pendulum is labeled "cm". Figure 3.2: The free-body diagram for the ballistic pendulum. double pendulum problem lsu free body diagrams for the forces on each mass 2 newton's equations for the double pendulum we derive the same expressions for the first particle r. phys5 1f 10. 12 7 the simple pendulum step 1 - draw a free body diagram for the ball immediately after it is released the free body diagram is drawn in figure 12 18 ... u Free Body Diagram Figure 6.1: Mass Spring System. A cart of mass M slides on a horizon tal frictionless trac k, and is pulled b y horizon tal force u (t). On the cart an in v erted p endulum of mass m is attac hed via a frictionless hinge, as sho wn in Figure 28.1. The p endulum's cen ter of mass is lo cated at a distance l from its t w o ... 29.12.2021 · We apologize that the Science NetLinks website is unavailable. Unfortunately, the server and website became unstable and a security risk so the website needed to be taken down immediately. This page will be updated as we learn more and identify next steps. Please send any questions/concerns to snl@
Draw free-body diagrams that conform to the assumed displacement positions and their resultant reaction forces (i.e., tension or compression). c. Apply to the free body diagrams to obtain the governing equations of motion. The matrix statement of Eqs.(3.123) is The mass matrix is diagonal, and the stiffness matrix is symmetric. Check here to show the free-body diagram Purple is the true motion; orange is the comparison motion. This is a simulation of a simple pendulum (a ball attached to a massless rod). If the damping is set to zero, the pendulum moves without resistance. The larger the damping, the larger the resistive torque. Below are the free-body diagrams of the two elements of the inverted pendulum system. Summing the forces in the free-body diagram of the cart in the horizontal direction, you get the following equation of motion. (1) Note that you can also sum the forces in the vertical direction for the cart, but no useful information would be gained. A common actuator in control systems is the DC motor. It directly provides rotary motion and, coupled with wheels or drums and cables, can provide translational motion. The electric equivalent circuit of the armature and the free-body diagram of the rotor are shown in the following figure.
body diagram Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM The term "compound" is used to distinguish the present rigid-body pendulum from the "simple" pendulum of Section 3.4b, which consisted of a particle at the end of a massless string. Derive the general differential equation of motion for the pendulum of figure 5.16a and determine its ... Begin by drawing the free body diagram for the upper mass and writing an expression for the net force acting on it. Define these variables: T = tension in the rod; m = mass of pendulum; g = gravitational constant; The forces on the upper pendulum mass are the tension in the upper rod T 1 , the tension in the lower rod T 2, and gravity −m 1 g. We write separate equations for the … - Pendulum angle label - Draw free body diagram 1. Let's start by the ground We will start by drawing the floor. We draw the components in a brown tone (brown!80!red) and add the dots using patterns TikZ library, which includes crosshatch dots option. Hence, the ground can be drawn in two steps: A pendulum is a body suspended from a fixed support so that it swings freely back and forth under the influence of gravity. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's …
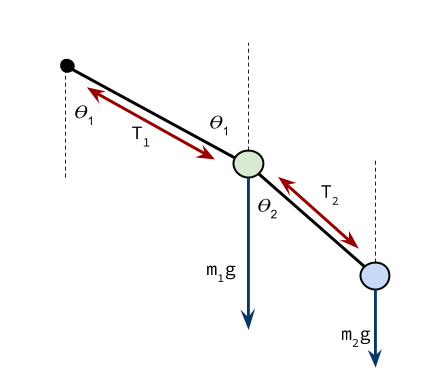
Single and Double plane pendulum Gabriela Gonz´alez 1 Introduction We will write down equations of motion for a single and a double plane pendulum, following Newton's equations, and using Lagrange's equations. Figure 1: A simple plane pendulum (left) and a double pendulum (right). Also shown are free body diagrams for the forces on each mass.
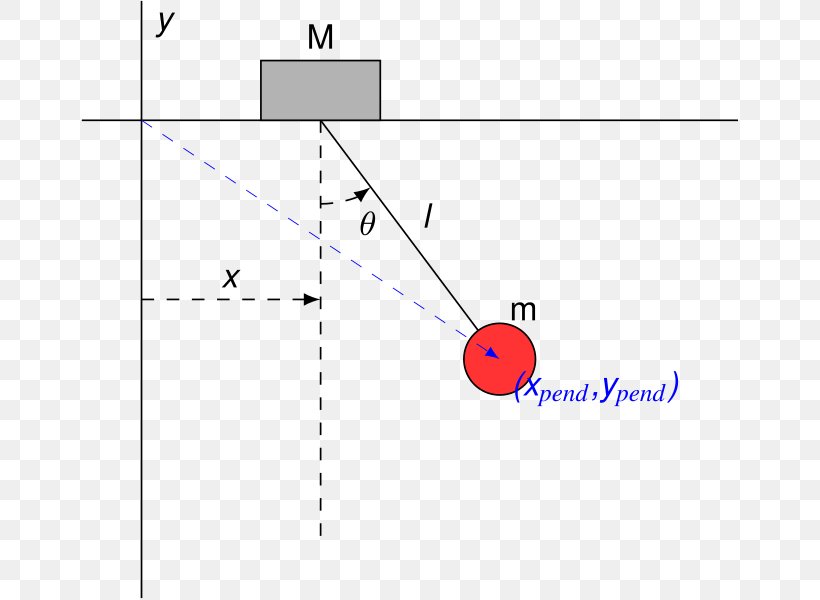
... cart mounted motor driven inverted pendulum free body diagram is shown in Fig. 1 [1-4, 16-18, 20-23]. For this nonlinear system, the equations of the dynamics are developed following the...
(iv) The diagram below shows a free conductor AB is kept in a magnetic field and is carrying current from A to B. (To avoid confusion complete path of the circuit is not shown) The direction of the force experienced by the conductor will be: (a) Up (b) Down (c) Towards N (d) Towards S [1]
Free body diagram of pendulum Thread starter-EquinoX-Start date Nov 30, 2008; Nov 30, 2008 #1 -EquinoX-564 1. Homework Statement I am asked to draw a free body diagram of a pendulum and a bob with it's maximum amplitude of 30 degrees. Below is my attempt, I just forgot to say that theta is equal to
Known for his satirical wit and sardonic view of human nature, Ambrose Bierce earned the nickname "Bitter Bierce." His mocking cynicism is on full display in The Devil's Dictionary, a work that originally appeared under the title The Cynic’s Word Book.This humorous and often strikingly insightful book is always worth a casual visit as he takes his turn handing out striking …
Find the equation of motion of this pendulum by taking the time rate of change of the angular momentum computed with respect to the pivot. ... Be sure to include a free body diagram. Pendulum with Torsional Spring - Solution: The free body diagram depicting the torques on the body is shown below. Note the directions of the unit
The diagram at the right shows the pendulum bob at a position to the right of its equilibrium position and midway to the point of maximum displacement. A coordinate axis system is sketched on the diagram and the force of gravity is resolved into two components that lie along these axes.
20.04.2015 · Join for free. Public Full-text 1. Content uploaded by Suman Debnath. Author content. All content in this area was uploaded by Suman Debnath on Apr 20, 2015 . Content may be subject to copyright ...
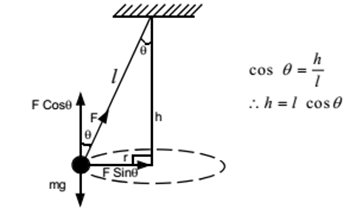
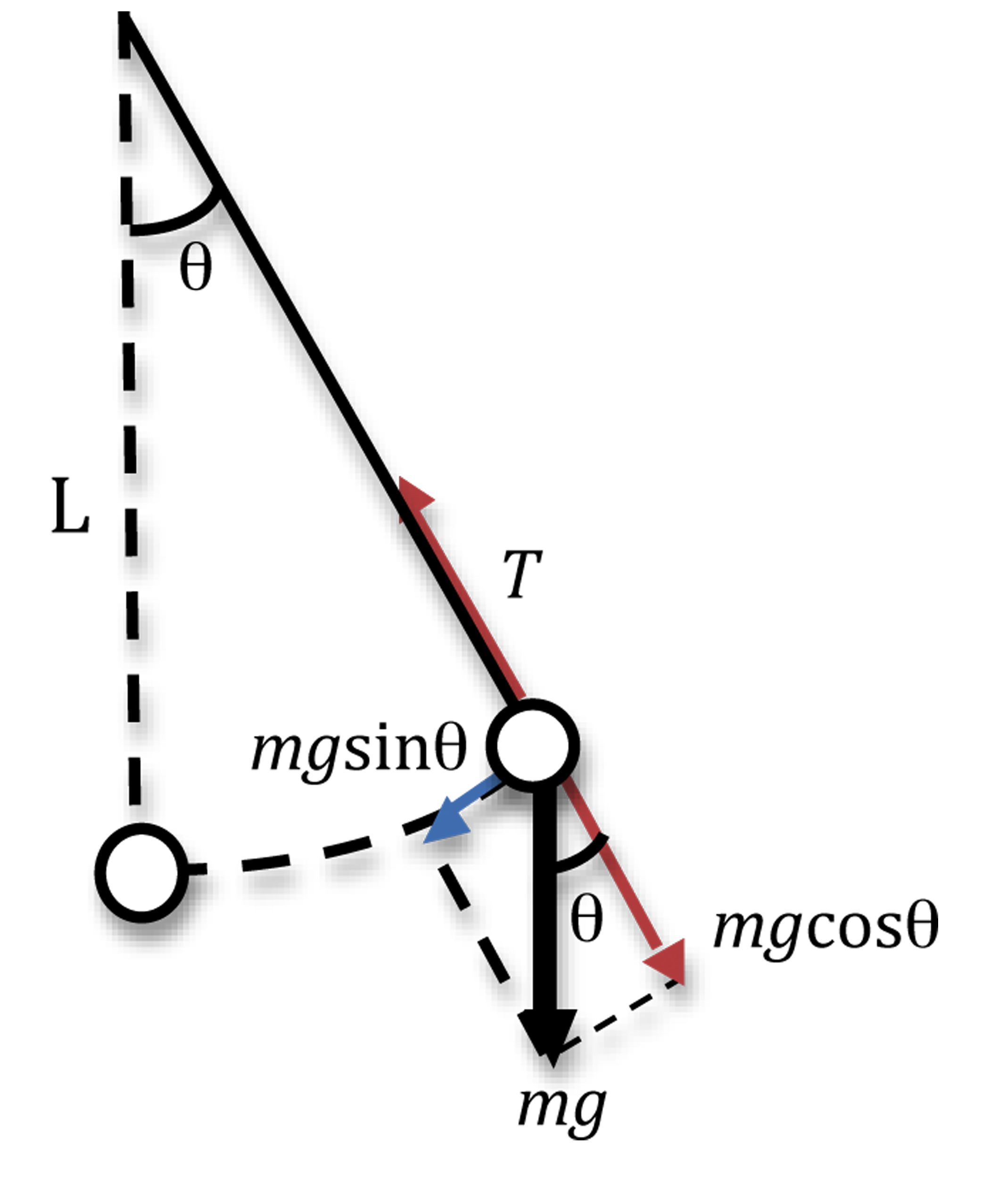
free body diagram in Fig. 6 below. Free Body Diagram Fig. 6 The free body diagram of the pendulum bob shows the gravitational force mg, the tension force T and the centripetal acceleration ac. The components of the gravitational force are also shown. Applying Newton's second law along the direction of tension force on gets T mg θ mgCos(θ)
The rope is pulling on this ball. And so, we could say the force of the tension, so it might look something like this, the force, force of the tension. Now just with that, we have constructed a free body diagram, and we can immediately answer their question, what are the forces that are acting on the ball, which arrows show it.
Answer to Solved 1. Draw a free body diagram of a pendulum while in
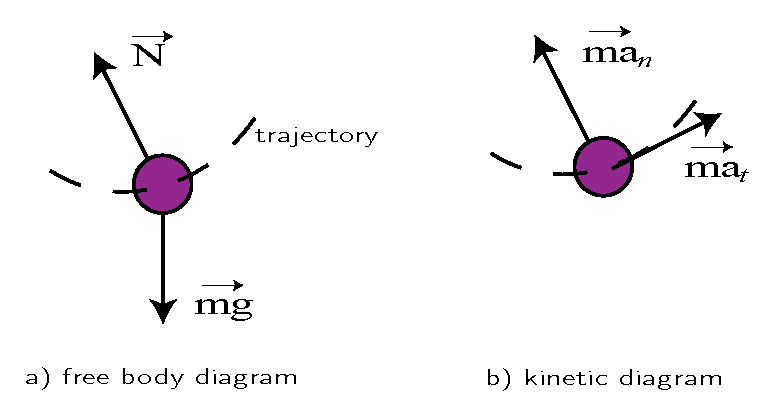
The second is tension in the string which changes in both size and direction as the pendulum swings. When it swings through the bottom of its arc, the pendulum has maximum speed and requires the maximum force to hold it in its circular path. The forces at the bottom are shown here in a free-body diagram.
Dr. Massa and the great Orbax discuss the conical pendulum, drawing free body diagrams and centripetal acceleration.
immediately after it is released. The free-body diagram is drawn in Figure 12.18). There is a downward force of gravity, and a force of tension.2 pages
of the inverted pendulum-cart system. In (1), F a is the force exerted on the cart by the motor. (M+ m) x+ mL p = F a (1) mL p x + 4mL2 p 3 mgL p = 0 (2) One way of doing this is by considering the free-body diagrams of the cart and the pendulum separately and writing their respective equations of motion.
Double Pendulum • The disk shown in the figure rolls without slipping on a horizontal plane. Attached to the disk through a frictionless hinge is a massless pendulum of length L that carries another disk. The disk at the bottom of the pendulum cannot rotation relative to the pendulum arm. • Draw free-body diagrams and
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force acting on the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, …
4.1.1 Pendulum phenomenological model 10 4.2.1 Free body diagram of the Inverted Pendulum system 12 5.1.1.1 Block diagram for optimal configuration 23 5.4.1 Schematic diagram of the State feedback controller (using LQR) in Simulink 26 6.1.1 Schematic diagram of the a feedback control system 29
-Rigid Body Kinematics x y z = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 X Y Z i j k = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 I J K . Derivation of Equations of Motion -Rigid Body Kinematics Free Body Diagram After substitutions and evaluation: Derivation of Equations of Motion-Lagrange Equations ... Spring Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation ...
Pendulum Sim Activity; Related External Links. Simulink Intro Video; Simulink Modeling Video; Modeling Challenges Video; Contents. Train system; Free-body diagram and Newton's second law; Constructing the Simulink model; Running the model; Train system . In this example, we will consider a toy train consisting of an engine and a car. Assuming that the train only travels in …
the pendulum, the following equation of motion is obtained P sin(µ)+N cos(µ)¡mgsin(µ) = ml˜µ+m˜ycos(µ) (4) where P is pointing towards the ground, relative to the cart free body diagram in Fig. 1, originating at the point where the cart and the pendulum connect. That same point on the pendulum free body diagram is pointing up.
Next we draw the free body diagram for the pendulum. So we can write the net force as: F= Tcos θj− Tsin θi− mgj Using Newton's law F= maand the pendulum acceleration we found earlier, we have Tcos θj− Tsin θi− mgj= mR(θ''cos θi− θ'2sin θi+ θ''sin θj+ θ'2cos θj) Write the vector components of the above equation as separate equations.










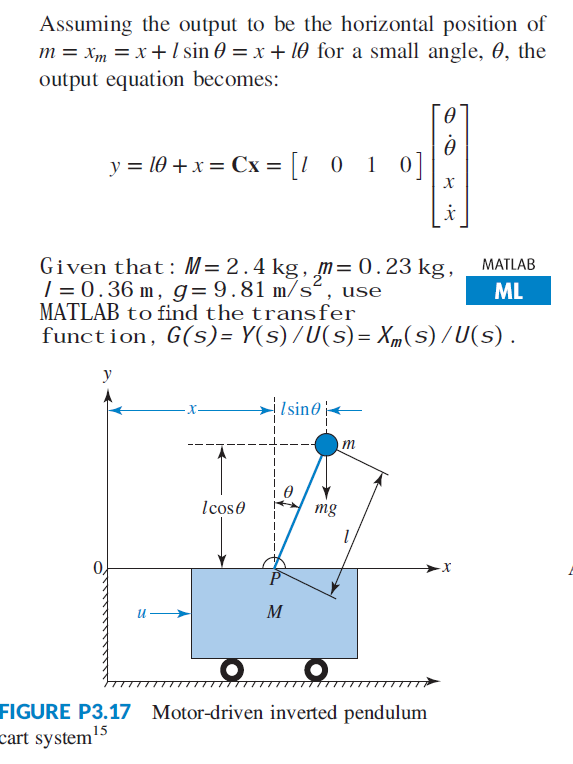
![Solved] Figure P3.17 shows a free-body diagram of an inverted ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/images/question_images/1610/5/9/8/2625fffc7761c8491610598263454.jpg)






0 Response to "42 pendulum free body diagram"
Post a Comment