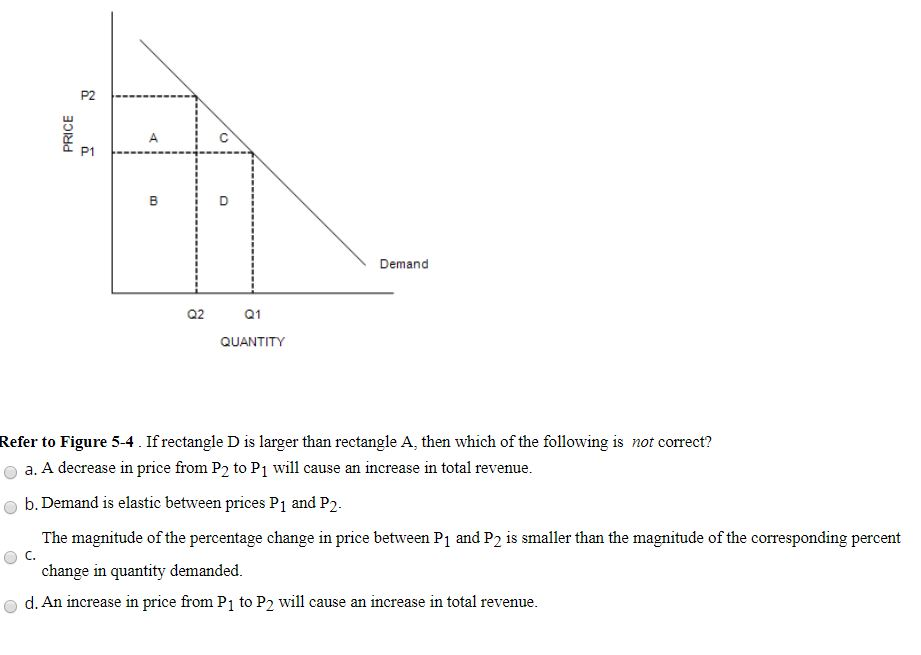
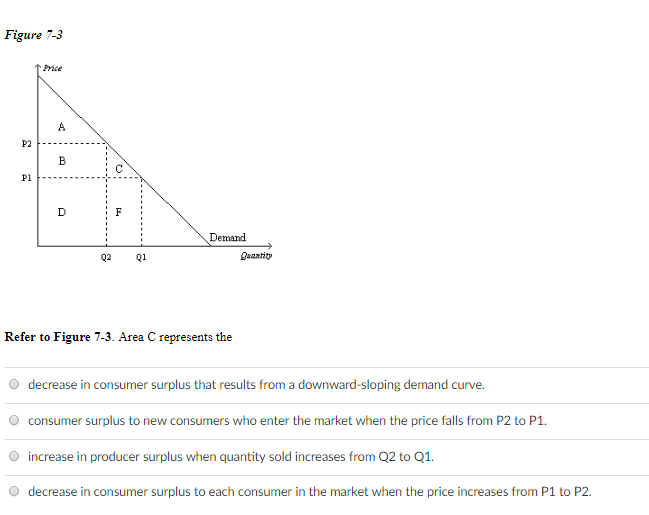
44 refer to the diagram. the decline in price from p1 to p2 will
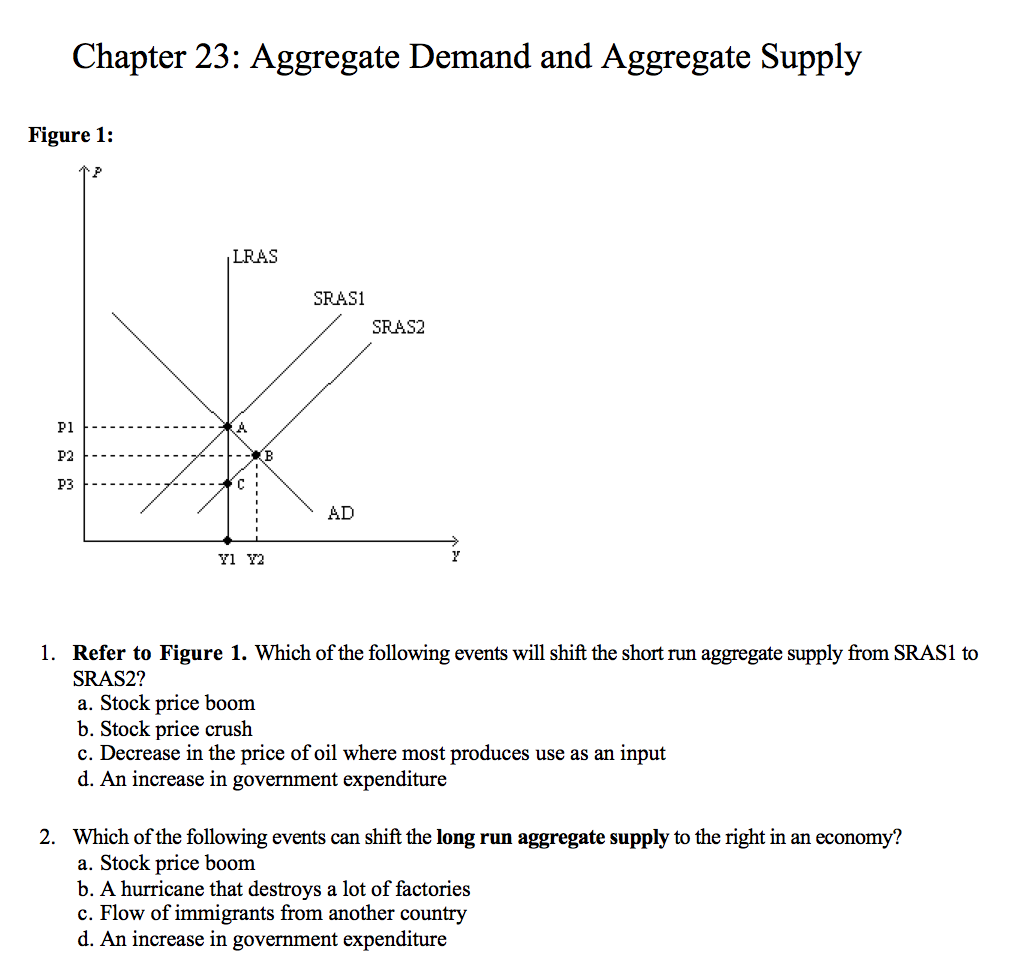
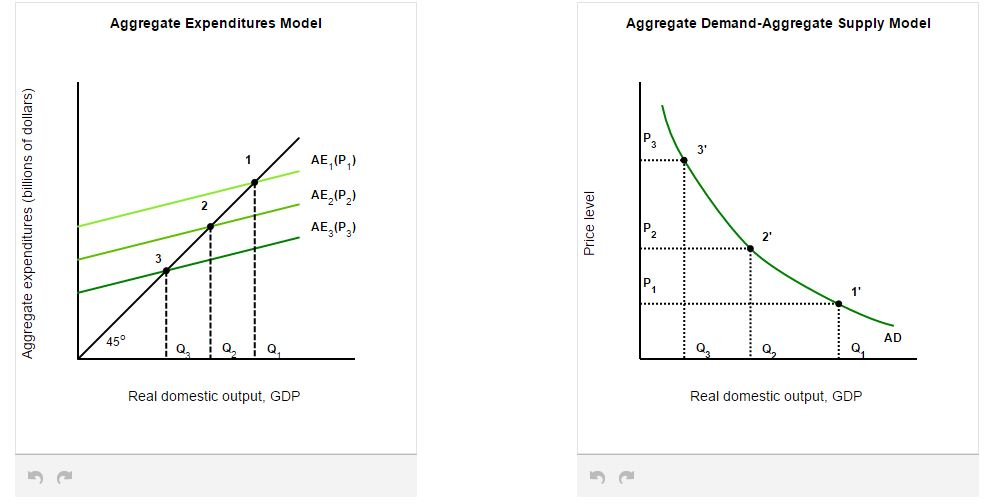
7. Refer to the above diagram. The initial aggregate demand curve is AD 1 and the initial aggregate supply curve is AS 1. If government offsets the decline in real output resulting from short-run cost-push inflation by increasing aggregate demand from AD 1 to AD 2: A) real output will rise above Q f. B) the price level will rise from P 1 to P 2. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A. increase total revenue by D B. increase total revenue by B + D C. decrease total revenue by A D. increase total revenue by D - A. D. increase total revenue by D - A. Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from $10 to $2, total revenue: A. rises from A + B to A + B + D + C and demand is elastic. B. falls from A + D to B ...
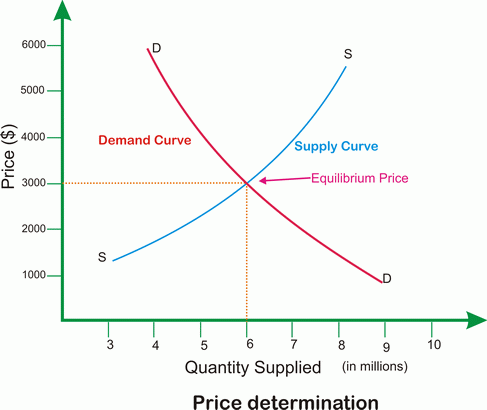
And price to fall from P2 to P1. Please refer Diagram 1 in attachment. 2. When unemployment decreases, it means that more people are working in the economy and hence their incomes are also higher. This means there is a higher purchasing power and also higher demand for products. Hence, The demand curve shifts from D1 to D2.
Refer to the diagram. the decline in price from p1 to p2 will
Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from p1 to p2 will: increae total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist. C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. 171. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at: A. P1. B. P3. C. P2. D. P4. 172.
Refer to the diagram. the decline in price from p1 to p2 will. refer to the diagram. the decline in price from p1 to p2 will Price Demand Quantity Refer to the diagram. The decline in price from P, to P2 will A) increase total revenue by D. B) increase total revenue by B+D. C) decrease total revenue by A. D) increase total revenue by D . 1. l at tend to be 6 11. Two firms compete by choosing price. Their demand functions are Q1 = 20 - P1 + P2 and Q2 = 20 + P1 - P2 where P1 and P2 are the prices charged by each firm, respectively, and Q1 and Q2 are the resulting demands. Note that the demand for each good depends only on the difference refer to the diagram the decline in price from P1 to P2 well increase total revenue by B+ d if the price elasticity coefficient for a product is .68 and the seller wants to raise revenues by changing its price than the seller should cut the price of the product 37. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: A) selling the product at the highest possible price at which a positive quantity will be demanded. B) producing Q1 units and charging a price of P1.
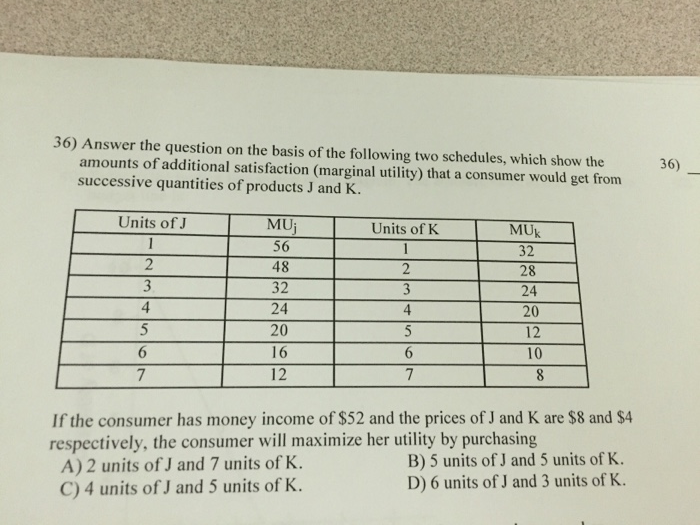
Transcribed image text: Price Demand Quantity Refer to the diagram. The decline in price from P, to P2 will A) increase total revenue by D. B) increase total revenue by B+D. C) decrease total revenue by A. D) increase total revenue by D . 1. l at tend to be 36) Answer the question on the basis of the following two schedules, which show the amounts of additional satisfaction (marginal utility ... Refer to the diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will Multiple Choice increase total revenue by D. increase total revenue by B + D. decrease total revenue by A. increase total revenue by D − A. Question: Refer to the diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will Multiple Choice increase total revenue by D. increase total revenue by ... Refer to the diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A) increase total revenue by D - A. B) decrease total revenue by A. C) increase total revenue by B + D. D) increase total revenue by D. A. The formula for cross elasticity of demand is percentage change in: A) quantity demanded of X/percentage change in price of Y. B) quantity demanded of X/percentage change in price of X. C ... Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): B + D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: increase total revenue by D - A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: ...
b. The price of commodities increases by 10% this year. This causes the SRAS curve to shift to the left. There will be a movement along the AD curve. There will be no change in LRAS. c. The price of oil falls. SRAS shifts to the right and results in a downward movement along the AD curve. There is no change in the LRAS. d. If the price of elasticity of demand for a product is 2.5 then a price it from $2 to $1.80 will ... In which of the following instances will total revenue decline ... Refer to the above diagram. In P1 P2 price range demand is Relatively elastic. 10 in quantity demanded due to a change in price is . large. An . inelastic. demand is one in which the change in quantity demanded due to a change in price is . small. The formula used here for computing elasticity . of demand is: (Q1 - Q2) / (Q1 + Q2) (P1 - P2) / (P1 + P2) If the formula creates an . absolute value. greater than 1, the ... 35) Refer to the diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: A) nothing concerning price elasticity of demand. B) that consumer purchases are relatively insensitive to price changes. C) that demand is inelastic with respect to price. D) that demand is elastic with respect to price.
Assume that nominal wages initially are set based on the price level P2 and that the economy initially is operating at its full-employment level of output Qf. In the long run, an increase in the price level from P2 to P3 will . move the economy from b to d. Refer to the diagram. If the price level rises above P1 because of an increase in aggregate demand, the. economy will move up along curve ...
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be: ... a 10 percent decline in the price of bacon will: ... Refer to the diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): B + D. The ...
Elasticity 1. In which of the following instances will total revenue decline? A. price rises and supply is elastic B. price falls and demand is elastic C. price rises and demand is inelastic D. price rises and demand is elastic. 2. The demand for a necessity whose cost is a small portion of one's total income is: A. perfectly price inelastic.
Refer to the above diagram. Total revenue at price P1 is indicated by area(s): B. A+B. Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram.
The decline in price from P1 to P2will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A. 8. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: A. that consumer purchases are relatively insensitive to price changes.
Refer to the above diagram. Total revenue at price P1 is indicated by area(s): A+B. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: increase total revenue by D - A. Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from $10 to $2, total revenue: falls from A + B to B + C and demand is inelastic. The price elasticity of supply measures how: responsive the quantity supplied of X is ...
Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say:
Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A) increase total revenue by D. C) decrease total revenue by A. B) increase total revenue by B + D. D) increase total revenue by D - A. Answer: D. Type: G Topic: 2 E: 360 MI: 116 72. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: A) that consumer purchases are relatively insensitive to price changes. B ...
The decline in price from p1 to p2 will. The decline in price from p1 to p2 will increase total revenue by d a a is square lost when price goes down but d goes right and adds refer to the above diagram. If the price level rises above p 1 because of an increase in aggregate demand.
Picture Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic. Refer to the diagram. In the P 3 P 4 price range, demand is: of unit elasticity. relatively inelastic. relatively elastic. perfectly elastic. P1 P2 P4 Q3...
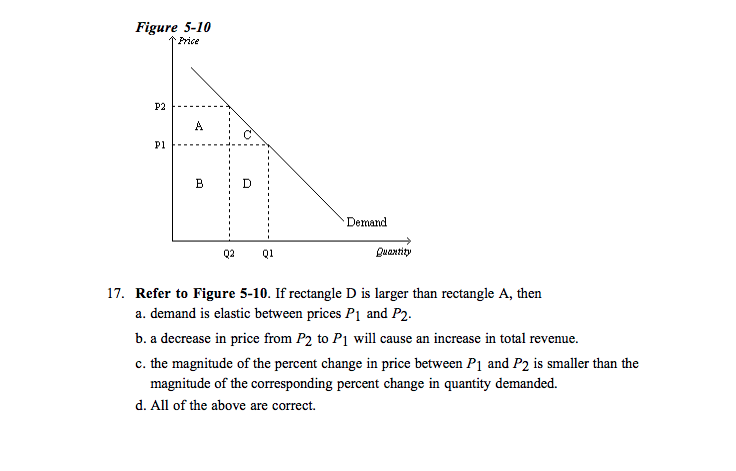
Long-run average costs decline continuously through the range of demand. What do economies of scale, the ownership of essential raw materials, and patents have in common? They are all barriers to entry. The nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand curve: Is the industry demand curve. In the accompanying diagram, if price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: Increase by C − A. In ...
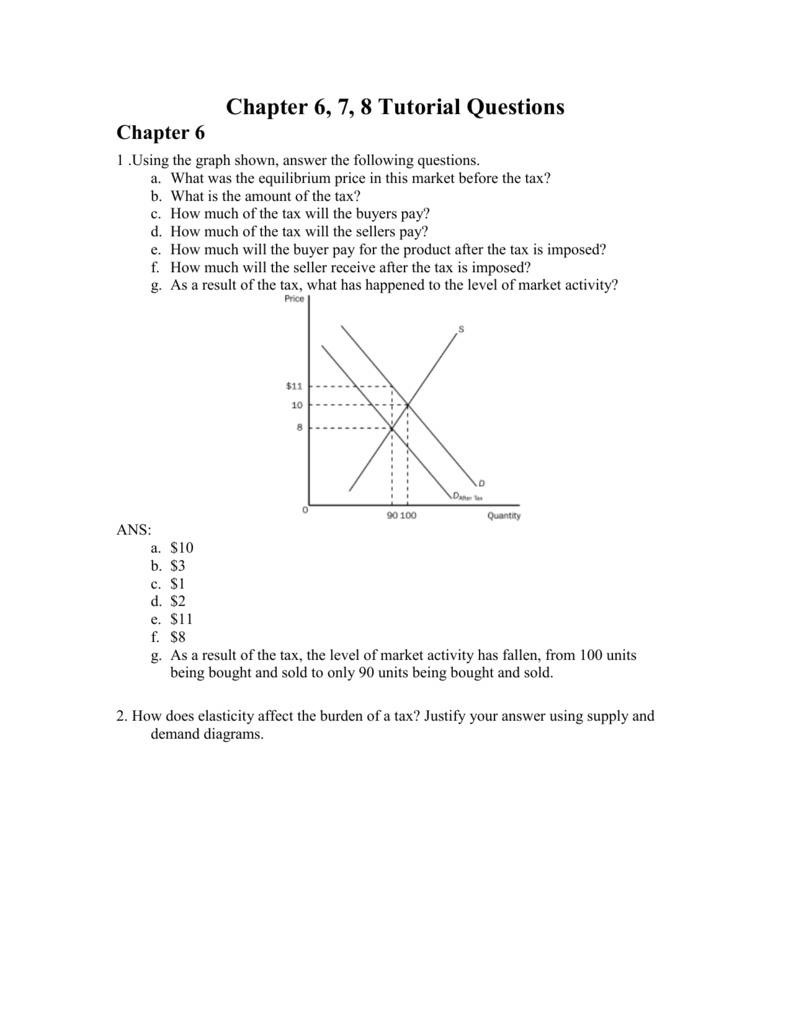
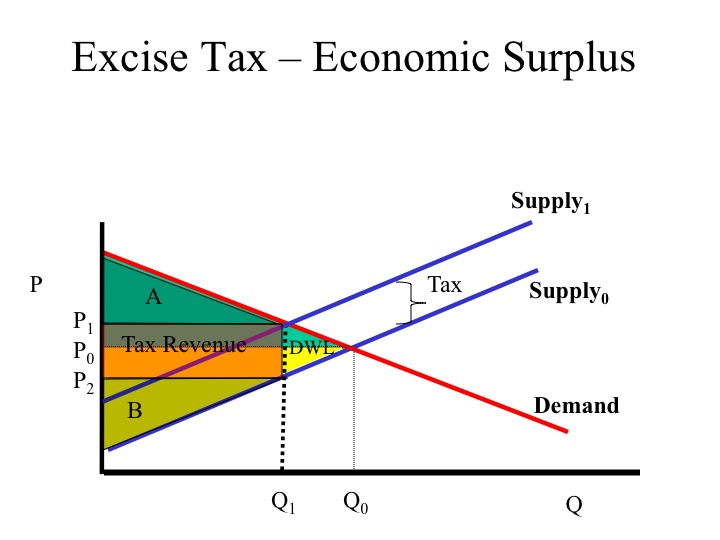
The equilibrium price is P1 and the equilibrium quantity is Q1. If the tax is imposed on car buyers, the demand curve shifts down by the amount of the tax ($1000) to D2. The downward shift in the demand curve leads to a decline in the equilibrium price to P2 (the amount received by sellers from buyers) and a decline in the equilibrium quantity ...
1.Refer to the diagram above. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: a. b. d. a. the demand curves facing existing firms would shift to the right. b. the demand curves facing existing firms would shift to the left.
24. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A.
Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A.
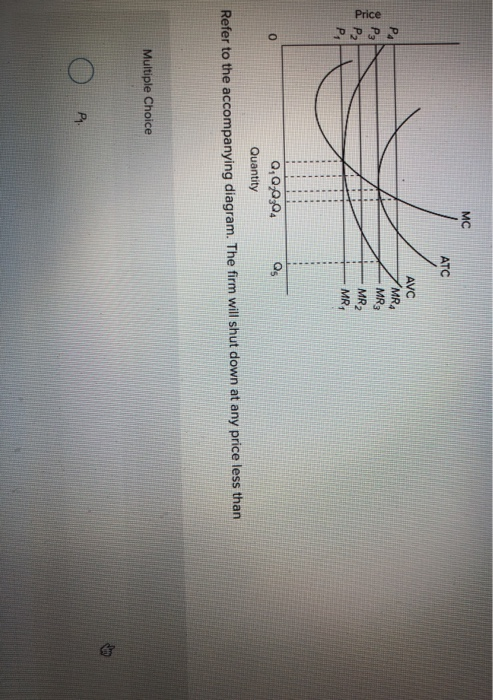
C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. 171. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at: A. P1. B. P3. C. P2. D. P4. 172.
Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.
Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from p1 to p2 will: increae total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say:

























0 Response to "44 refer to the diagram. the decline in price from p1 to p2 will"
Post a Comment