41 atomic energy level diagram
1.1 Atomic structure. History of the atom • The model of the atom has changed as our observations of its behavior and properties have increased. • • That the electron shells can be converted into an energy level diagram showing the Principle Quantum Number, n. 4.1 Bohr's Atomic Model 4.2 Energy Levels 4.3 Energy Bands 4.4 Important Energy Bands in Solids 4.5 The separation between conduction band and valence band on the energy level diagram is (ii) Fig. 4.9 shows the energy level/band of silicon atom. The atomic number of silicon is 14 so that...
Atomic orbital energy levels.svg 503 × 304; 27 KB. AtomicOrbitals PeriodicTable EnergyLevels.tiff 496 × 323; 47 KB. Energy Level Diagram (dumb version).png 248 × 315; 3 KB.
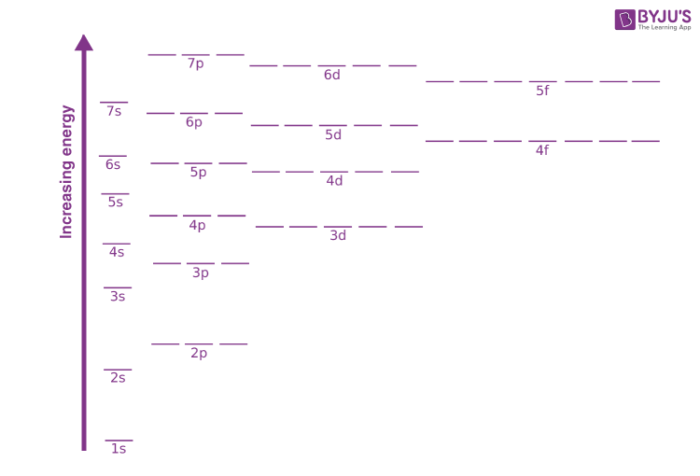
Atomic energy level diagram
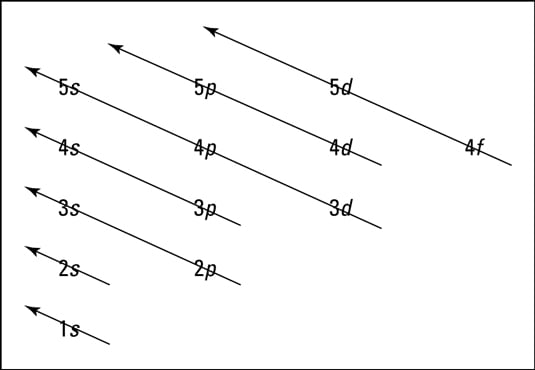
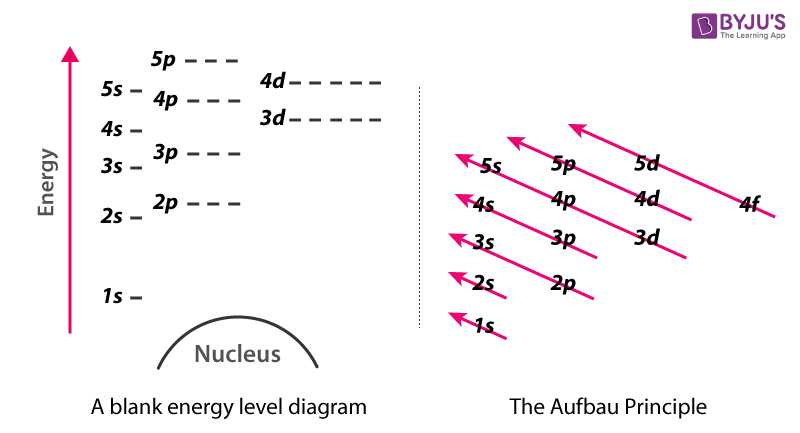
Orbits and energy levels. Unlike planets orbiting the Sun, electrons atomic orbitals. Electrons fill in shell and subshell levels in a semiregular process, as indicated by the arrows above. After filling the first shell level (with just an s subshell), electrons move into the second-level s subshell and then into... Figure 1. Generalized energy-level diagram for atomic orbitals in an atom with two or more electrons (not to scale). Electrons in successive atoms An atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus. Bibliographyon AtomicEnergyLevelsandSpectra July1979throughDecember1983 ArleneMusgrove and RomualdZalubas CenterforRadiationResearch NationalMeasurementLaboratory NationalBureauofStandards Gaithersburg,MD20899 Nationalbureau ofstandards UBRARY arc.-nb$ a'c I0o No963 /W U.S.DEPARTMENTOFCOMMERCE,MalcolmBaldrige,Secretary NATIONALBUREAUOFSTANDARDS,ErnestAmbler,Director ...
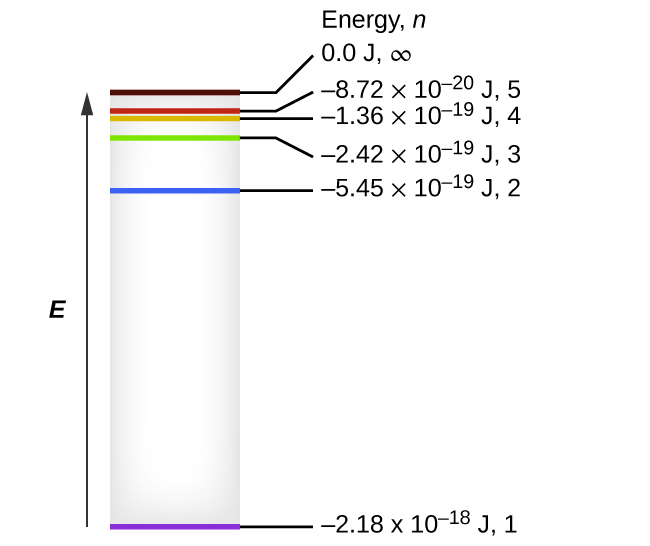
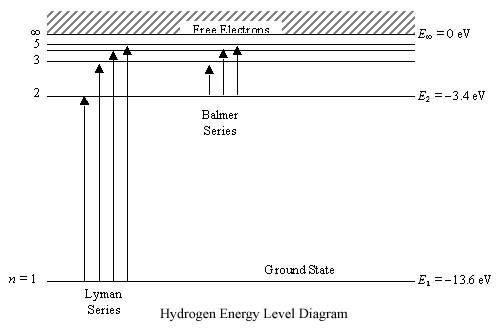
Atomic energy level diagram. Energy-level diagram of uranium, 31-34 Energy levels,of atoms, 30, 31 Engstrom s investigations, 144, 225, 226, 296... [Pg.345]. Step 2 Use matching valence-shell atomic orbitals to build bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals and draw the resulting molecular orbital energy-level diagram (Figs. Orthohelium and Parahelium Energy Levels. In the helium energy level diagram, one electron is presumed to be in the ground state of a helium atom, the 1s state. An electron in an upper state can have spin antiparallel to the ground state electron (S=0, singlet state, parahelium) or parallel to the... 3. Draw two electrons in the first energy level and label them with their charge. 4. Draw three electrons in the second energy level and label them with their charge. 5. What element is represented by the diagram? _____ Part B: Atomic Calculations 6. Label the information provided in the periodic table. 7. What does the atomic number represent?8 Part of a series of articles about. Quantum mechanics. Schrödinger equation. Introduction. Glossary. History. v. t. e. A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels.
About Atomic Energy Levels. In steady-state conditions, the electrons move around the nucleus in allowed stable orbits. Each orbit corresponds to a discrete energy level for the atom. Energy level diagram of some of the excited states of the 12C nucleus. The angular momentum (J), parity (P), and isospin (T) quantum numbers of the states are indicated on the left using the notation J P. P and n respectively at the top of the diagram indicate the separation energies for a proton and a neutron. Atomic energy level diagram for the hypothetical one-electron atom of Prob. 84. (a) We first determine the energy hν of the photon emitted Schematic diagram of the Rutherford-Bohr atomic model with one orbital electron of mass m e and a finite nucleus of mass M. Both the orbital electron... What is energy level diagram? In chemistry, an electron shell, or energy level, may be imagined as an orbit with electrons around the nucleus of an atom. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the “K shell” followed by the “L shell” then the “M shell” and so on away from the nucleus. The shells can be denoted by alphabets (K, L, M, …) or quantum numbers ( n = 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on).
Energy Level Diagrams. Atomic energy transformations can be represented using an energy level diagram. --> think of a ball on a staircase: gain of energy = move up step/s, loss of energy = move down step/s, ΔE = change of energy (energy required/difference in energy). occupy certain energy levels in the atom. An extremely useful way of displaying the structure of an atom is with an energy-level diagram, such as that shown for hydrogen in Figure a. The lowest energy level, called the ground state, corresponds to the n =1 Bohr orbit. Higher energy levels, called excited states, correspond to successively larger Bohr orbits. The energy associated with a certain energy level increases with the increase of its distance from the The hydrogen atom contains only one electron in 1s hydrogen energy levels with electronic For s-block elements, the electron enters the ns-orbitals and progressively filled with atomic number. Category: Atomic energy level diagram Show details. Atomic Energy Levels (video) - Khan Academy. 2 hours ago We like representing these Just Now Energy level diagrams are a means of analyzing the energies electrons can accept and release as they transition from one accepted orbital...
Atomic Energy Levels. October 26, 2020February 24, 2012 by Electrical4U. Atoms constitute the building blocks of all materials in existence. This is because, each of them possess a dedicated amount of energy which is expressed in terms of an integral multiple of the equation Where h is the...
In describing the energy levels of atoms and nuclei it is very convenient to be able to nd the allowed values of (l, m) given the values of (l1, l2) for two 4.3.2 Atomic periodic structure. We calculated the energy levels for the Hydrogen atom. This will give us spectroscopy information about the excited...
The atom is electrically neutral in its ordinary state because the number of negative electrons that revolve around the nucleus is equal to the number of positive protons in the nucleus, to express an atom of any element, we use two terms, which are mass number & atomic number.
Energy Level Diagrams Atomic Number Atomic # represents the number of protons (p+) in the nucleus of an atom. For a neutral atom the # protons = # electrons. (total positive charge equals the total negative charge). The atomic number is the top right number on the periodic table for each atom. Example: Carbon has atomic # 6 which means C has
The atomic structure of atoms and molecules is commonly represented in an energy level diagram and is strongly related to emission (and absorption) spectra. The electronic energy levels of atoms and diatomic molecules have their spectroscopic notation
Atomic Energy level diagram. Thread starter hoangan_lyk12. Start date Oct 27, 2010. Related Threads on Atomic Energy level diagram.
Energy Level Diagrams. • Note similarity in patterns of lines, for monovalent ions but not wavelengths. • The spectrum of an ion is significantly different Energy Level Diagrams for lower states of Na, Mg, Al. Ionic spectra versus atomic spectra. • Spectra of excited atoms differ from those of excited ions of...
Atomic Energy Level Diagrams. Energy level diagrams can be useful for visualizing the complex level structure of multi-electron atoms. Forms of such diagrams are called Grotrian diagrams or term diagrams in various parts of the literature. While the energy level diagram of hydrogenwith its single electron is straightforward, things become much more complicated with multi-electron atomsbecause of the interactions of the electrons with each other.
Atomic Physics. Helium and two-electron atoms Part 1. The helium atom. Work together - …… 1. Draw an energy level diagram showing all helium excited states. Label the energy levels… according to. (a) Configurations.
Energy level diagrams are a means of analyzing the energies electrons can accept and release as they transition from one accepted orbital to another. These energies differences correspond to the wavelengths of light in the discreet spectral lines emitted by an atom as it goes through de-excitation or by the wavelengths absorbed in an absorption spectrum.
This chapter describes atomic energy levels, electron states in the atom, fine structure of atomic levels, and the Mendeleev periodic system. In the non-relativistic approximation, the stationary states of the atom are determined by Schrodinger's equation for the system of electrons, which move in the...
4 Bohr's model for the hydrogen atom 4.1 The four postulates 4.2 Derivation of the allowed orbital radii 4.3 Derivation of the electron's orbital peed 4.4 Derivation of the kinetic, potential and total energies of an electron 4.5 The energy level diagram for atomic hydrogen; unbound states and ionization 4.6...
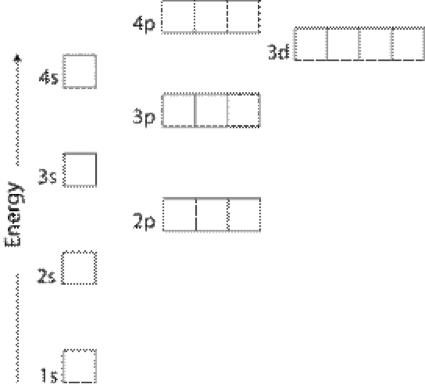
Electron configuration of carbon(C) atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
More on Atomic Energy levels. If atoms are left undisturbed, they usually drop to the lowest available energy level and stay there, in their "ground state." Occasionally, however, they may also be pushed up to some higher energy ("become excited") e.g. by a collision with a fast atom or electron, one...
We like representing these energy levels with an energy level diagram. The energy level diagram gives us a way to show what energy the electron has without having to draw an atom with a bunch of circles all the time. Let's say our pretend atom has electron energy levels of zero eV, four eV, six eV, and seven eV.
Description. Atomic Energy Levels and Grotrian Diagrams, Volume I: Hydrogen I - Phosphorus XV presents diagrams of various elements that show their energy level and electronic transitions. The book covers the first 15 elements according to their atomic number. The text will be of great use to researchers and practitioners of fields such as astrophysics that requires pictorial representation of the energy levels and electronic transitions of elements.
NIST Atomic Spectra Database Levels Form. Best viewed with the latest versions of Web browsers and JavaScript enabled. This form provides access to NIST critically evaluated data on atomic energy levels. Spectrum: e.g., Fe I or Mg Li-like or Z=59 II or 198Hg I.
The representation of relative energy levels of various atomic orbital is made in the terms of energy level diagrams. Multiple electron system : The energy levels of such system not only depend upon the nuclear charge but also upon the another electron present in them.
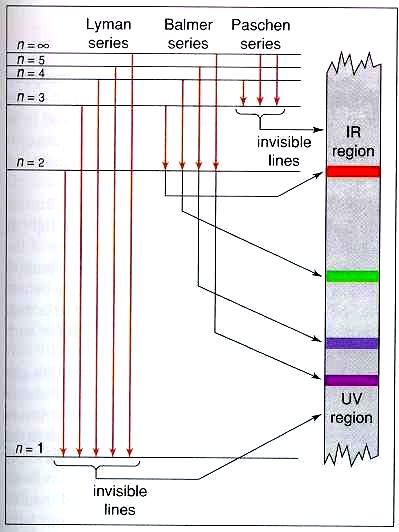
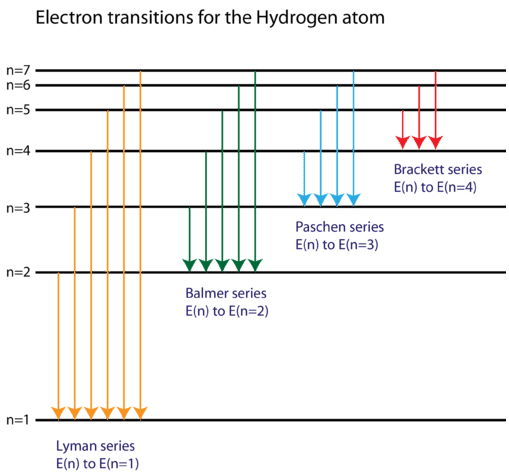
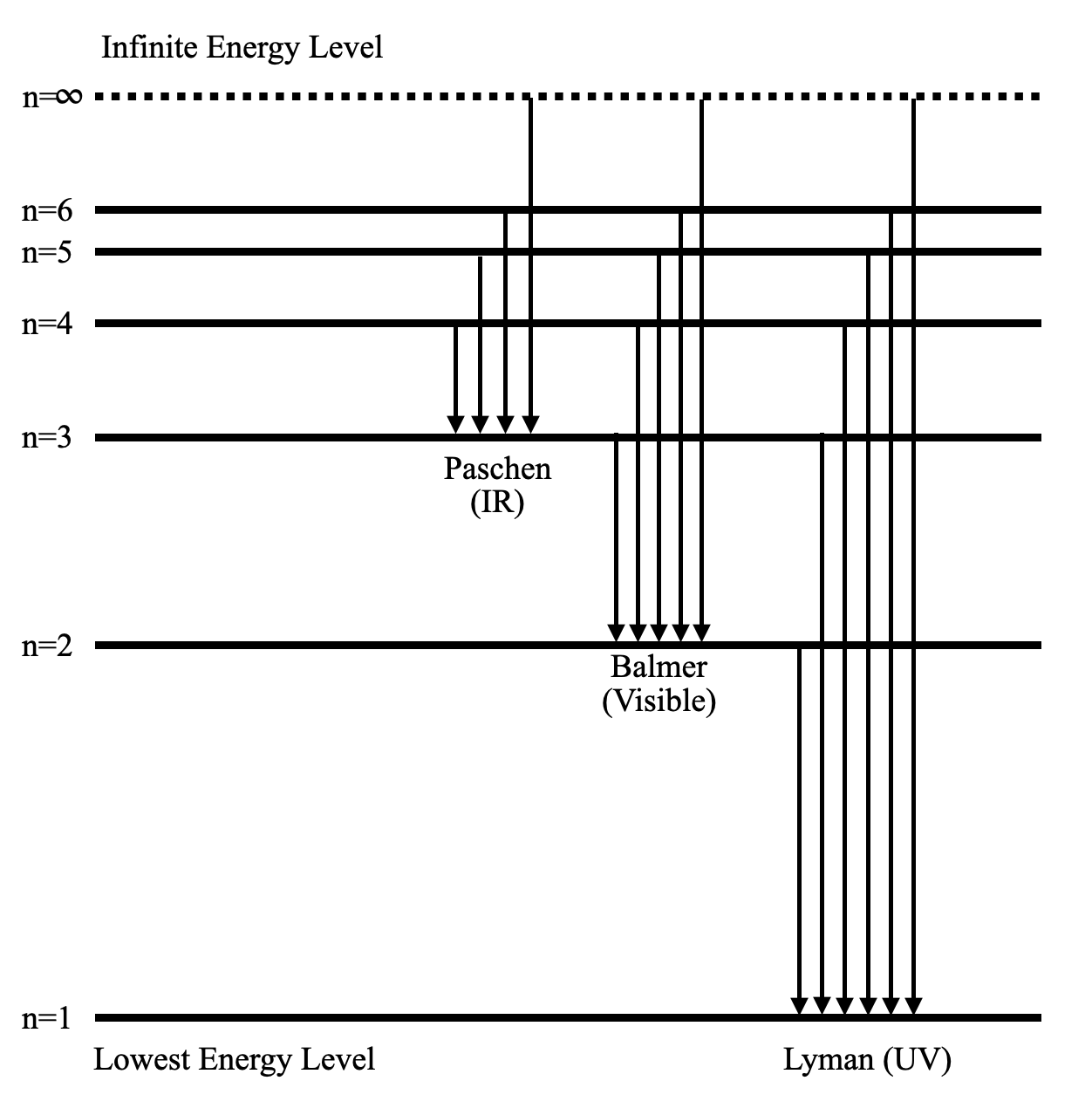
Energy-level diagrams are used for many systems, including molecules and nuclei. A theory of the atom or any other system must predict its energies Figure 7. Energy-level diagram for hydrogen showing the Lyman, Balmer, and Paschen series of transitions. The orbital energies are calculated...
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ1s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ1s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals.
This page introduces the atomic hydrogen emission spectrum, showing how it arises from electron movements between energy levels within the atom. The next few diagrams are in two parts - with the energy levels at the top and the spectrum at the bottom. If an electron fell from the 6-level, the...
We propose some random horizontal lines and ask you to do some physics.If you're unbelievably confused, please see the earlier parts of this playlist...
Bibliographyon AtomicEnergyLevelsandSpectra July1979throughDecember1983 ArleneMusgrove and RomualdZalubas CenterforRadiationResearch NationalMeasurementLaboratory NationalBureauofStandards Gaithersburg,MD20899 Nationalbureau ofstandards UBRARY arc.-nb$ a'c I0o No963 /W U.S.DEPARTMENTOFCOMMERCE,MalcolmBaldrige,Secretary NATIONALBUREAUOFSTANDARDS,ErnestAmbler,Director ...
Figure 1. Generalized energy-level diagram for atomic orbitals in an atom with two or more electrons (not to scale). Electrons in successive atoms An atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus.
Orbits and energy levels. Unlike planets orbiting the Sun, electrons atomic orbitals. Electrons fill in shell and subshell levels in a semiregular process, as indicated by the arrows above. After filling the first shell level (with just an s subshell), electrons move into the second-level s subshell and then into...















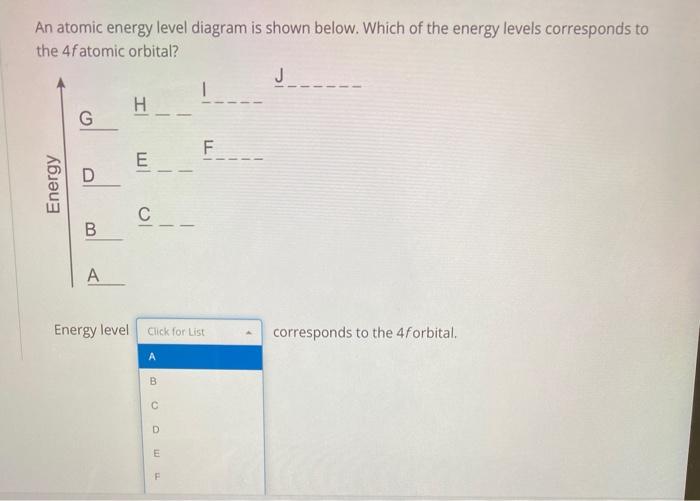

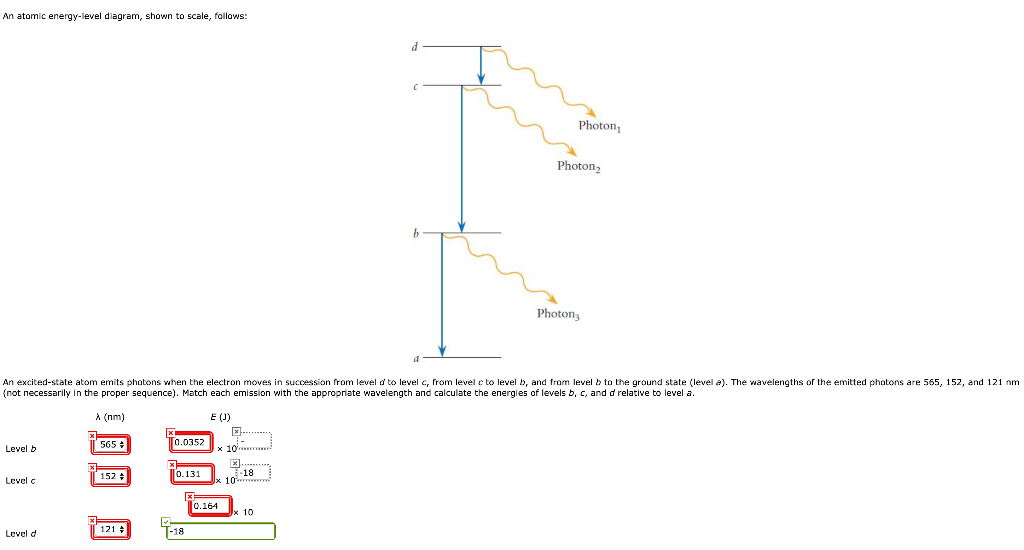
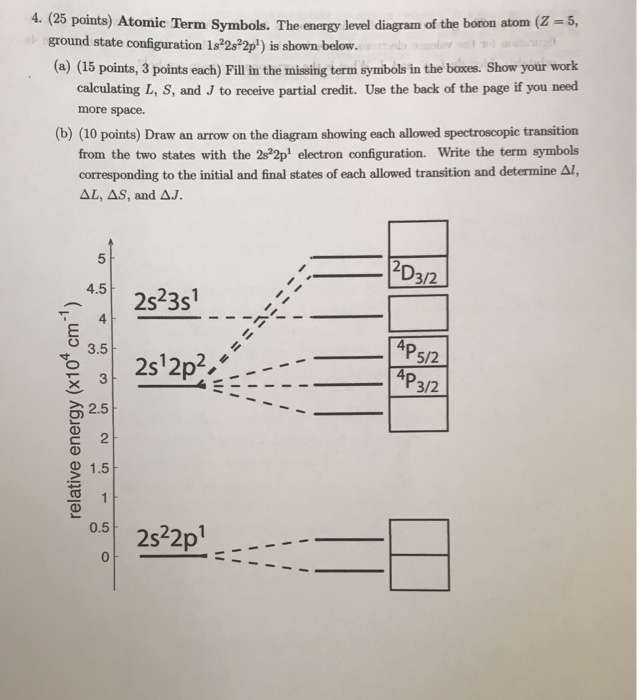


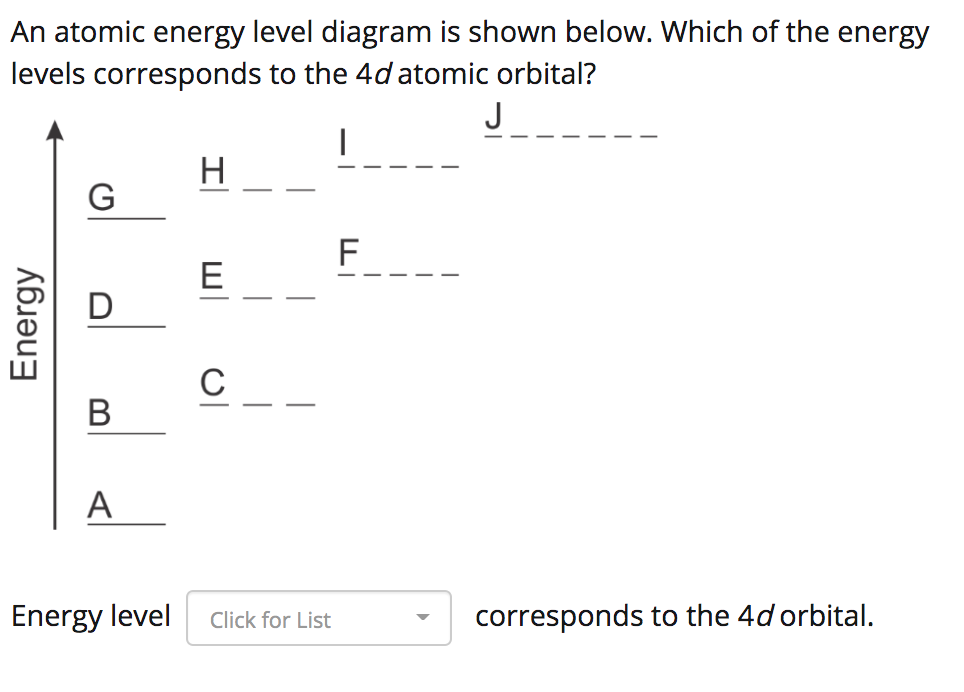


0 Response to "41 atomic energy level diagram"
Post a Comment