41 the monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is
Your favorite homework help service - Achiever Essays No matter what kind of academic paper you need and how urgent you need it, you are welcome to choose your academic level and the type of your paper at an affordable price. We take care of all your paper needs and give a 24/7 customer care support system. Solved > 36) When a monopolistically competitive industry ... E) produce the output where average costs are minimized. The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. 38) Refer to Figure 11-3. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will A) produce Q2 at Price P1. B) produce Q1 at Price P2. C) produce Q1 at Price P1. D) produce Q2 at Price P2.
micro ch 3 Flashcards | Quizlet A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is $ 4.50, price is $ 4.75, marginal revenue is ...
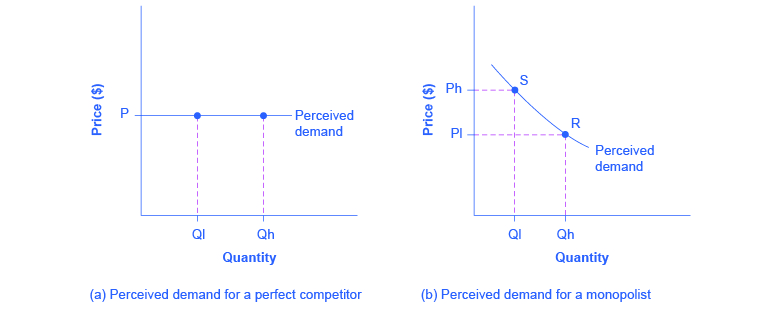
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is
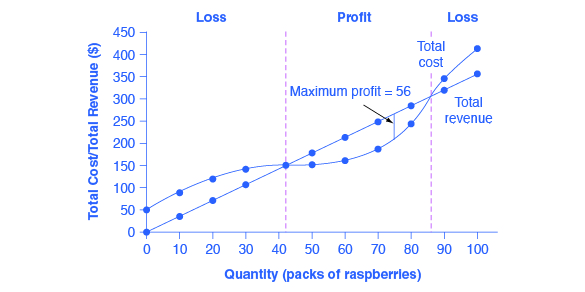
Final Part 2. Flashcards | Quizlet The demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive firm is. A) vertical. ... From the diagram above, what is the optimal quantity of output? Microeconomics exam 3 Flashcards - Questions and ... - Quizlet The greater the monopolistically competitive firm's success at product differentiation the lower is (are) the firm's price elasticity of demand. The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is Tutorial 11A.pdf - MONASH BUSINESS ECW 1101 INTRODUCTORY ... Monopolistically competitive firm in the short-run i. Profit-maximising output level = 10 units MR = MC ii. Profit-maximising price = $13 Corresponding demand curve iii. Total revenue = $13 x 10 units = $130 Price x Quantity iv. Total cost = $16 x 10 units = $160 Average total cost x Quantity v.
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is. Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help If a firm is in a competitive market and produces at Q2, its average costs will be AC2. A monopoly can increase output to Q1 and benefit from lower long-run average costs (AC1). In industries with high fixed costs, it can be more efficient to have a monopoly than several small firms. 2. Research and development PDF Mark Scheme (RESULTS) - Edexcel In a monopolistically competitive market each firm makes independent decisions about price and output, based on its product, its market and its costs of production • Monopoly market - pure monopoly where there is only one firm in the market - a sole supplier; OR a cartel, where firms collude as one firm OR where firms have Assisting students with assignments online - Success Essays Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. MIDTERM 2 ECON MICRO Flashcards | Quizlet If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a rate of output at which MC ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run ...
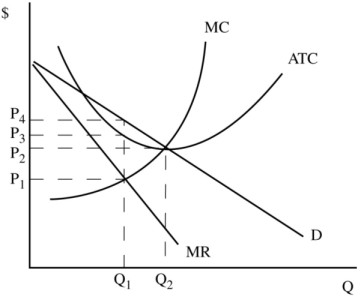
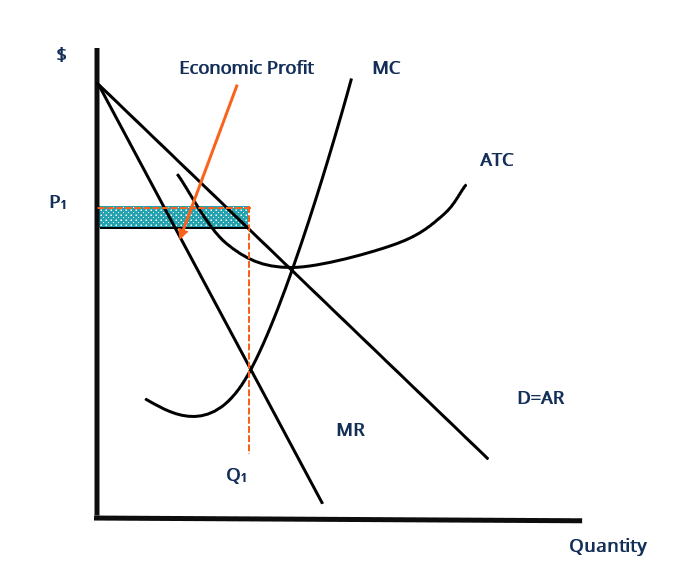
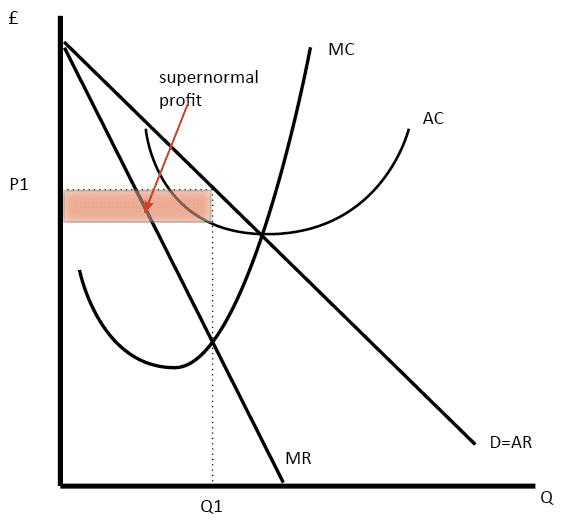
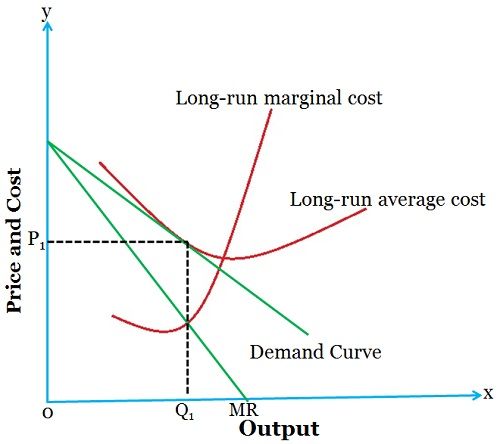
MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS STRATEGY - FlipHTML5 This is in contrast to competitive, monopolistically competitive,and monopolistic firms, all of which increase output when marginal costs decline. To see why firms competing in a Sweezy oligopoly may not increase outputwhen marginal cost declines, suppose marginal cost decreases from MC0 to MC1 inFigure 9-2. Role of Advertising in Monopolistic Competition and ... The new demand curve will correspond to higher levels of quantity demanded and the prices given by Q1 and P1 (Arnold 245). As such, the role of advertising in monopolistic competition is monumental. In monopolistic competition, the firm faces a comparatively elastic demand, and this limits the prices that can be charged on the product. 25.2 Price and Output for the Monopolistic Competitor - Quizlet The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A. not in long-run equilibrium. B. earning a positive economic profit. C. in long-run equilibrium. D. earning negative economic profits. Monopolistic Competition.docx - Monopolistic Competition ... (Irwin, 2006) Figure 1: Diagram of monopolistic competition short run In the short run, the monopolistic competition diagram is the same as the monopoly diagram. Where MR=MC, the firm maximizes profit. This is at output Q1 and price P1, resulting in an above-average profit.
Chapter 25 Flashcards | Quizlet The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A. not in long-run equilibrium. B. earning a positive economic profit. C. in long-run equilibrium. D. earning negative economic profits. Chapter 25 Homework Flashcards | Quizlet The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A.not in long-run equilibrium. B.in long-run equilibrium. C.earning a positive economic profit. D.earning negative economic profits. Economics Micros - Subjecto.com 7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A. 100. B. 160. C. 180. D. 210. B. 160. 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A. loss of $320. Pricing in Theory (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Hence the output of the firm under monopolistic competition must be smaller, and its average cost and price higher, than it would be under pure competition. Thus, from the point of view of the economy as a whole, competitive arrangement appears to be superior to that under monopolistic competition.
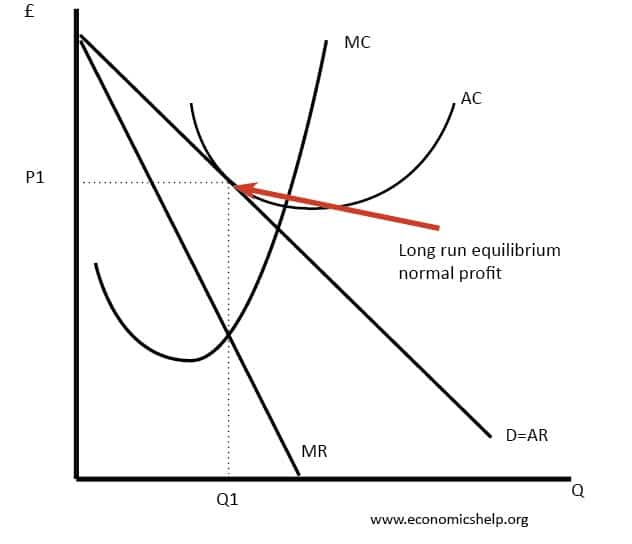
11 The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of ... The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is in long-run equilibrium 12 The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is earning positive economic profits. 25.3
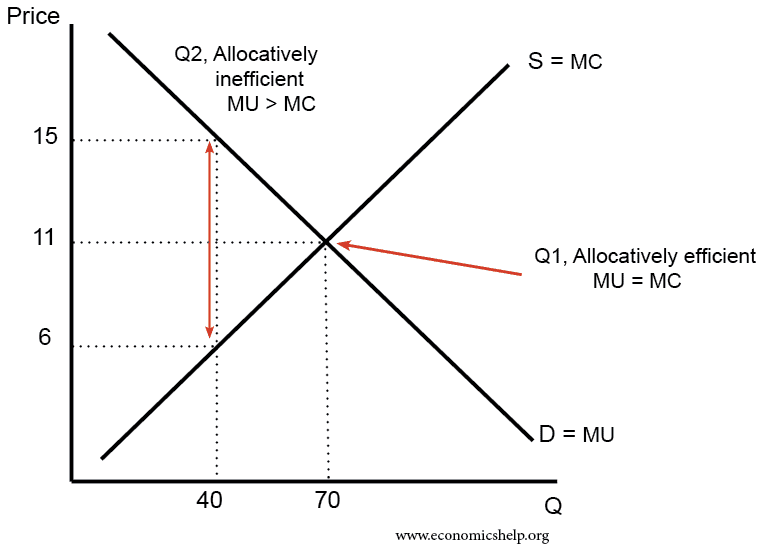
Monopolistic Competition [A Levels] As the diagram show, productive efficiency is at q1 and allocative efficiency level of output is q2. However, in a monopolistically competitive market, a firm is producing at profit maximising level q does not achieve any of the efficiency. Long Run In the long run too, a monopolistic competitive firm will not achieve any of the efficiencies.
Econ chapter 25 Flashcards | Quizlet The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is in long-run equilibrium. The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is earning positive economic profits. In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms make zero economic profits.
Solved Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Expert Answer Diagram monopolistic competition short run n the short run, the diagram for the monopolistic competition is the same as for a monopoly. The firm maximizes profit where MR=MC. This is at output Q1 and price P1, leading to supernormal profit Monopolist … View the full answer Previous question Next question
Monopolistic Competition - dineshbakshi.com As the diagram show, productive efficiency is at q1 and allocative efficiency level of output is q2. However, in a monopolistically competitive market, a firm is producing at profit maximising level q does not achieve any of the efficiency. Long Run. In the long run too, a monopolistic competitive firm will not achieve any of the efficiencies.
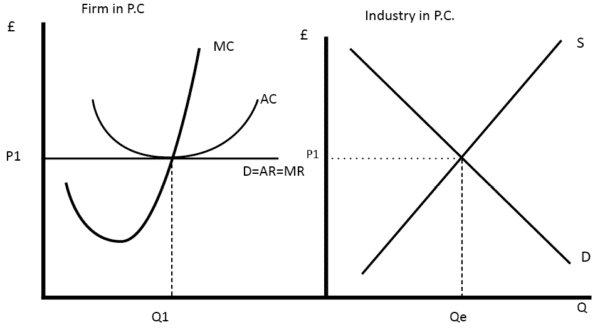
ECON FINAL Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's ...
Solved The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for ... Transcribed image text: The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. LRAC Dollars per unit MC E1 P1E P2 E2 | 1 Demand MR 0 Q1 Q2 Output FIGURE 11-3 Refer to Figure 11-3. If a decrease in industry demand led to an inward shift of each firm's demand curve, a typical firm would exit the industry and the industry would shut down. decrease costs in order ...
PDF Solution to Selected Questions: CHAPTER 12 MONOPOLISTIC ... In perfect competition, we know that profits are zero and price equals marginal cost. Here, T = $0 and P = MC = 5. Thus, when N approaches infinity, this market approaches a perfectly competitive one. 5. Two firms compete in selling identical widgets. They choose their output levels Q1 and Q2 simultaneously and face the demand curve P = 30 - Q
PDF Problem Set 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative ... Figure 13 - 14 illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm. 7) Refer to Figure 13 -14. Which of the following statements describes the firm depicted in the diagram? 7) A) The firm is making no economic profit and will exit the industry. B) The firm is in long - run equilibrium and is breaking even.
PDF Key Diagrams A2 Business Economics - tutor2u the level of output. If we make an assumption that these costs are sunk costs (i.e. they cannot be covered if the firm shuts down) then the loss per unit would be greater if the firm were to shut down, provided variable costs are covered. In the short run, the supply curve for a competitive firm is the marginal cost curve above average variable ...
Monopolistic Competition Long Run and Similar Products and ... Monopolistic Competition - definition, diagram and ... new . Diagram monopolistic competition short run. In the short run, the diagram for monopolistic competition is the same as for a monopoly. The firm maximises profit where MR=MC. This is at output Q1 and price P1, leading to supernormal profit. Monopolistic competition ...
On the graph above what is the profit maximizing level of ... A monopolistically competitive firm is producing an output level where average variable cost is R10.00, marginal cost is R5.00, marginal revenue is R6.00, and price is R12.00. In the short run, the firm should: A. decrease the level of output B. increase the level of output C. make no change in the level of output D. shut down
Economics - Homework 9 Flashcards | Quizlet A monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve because ... What is the amount of the firm's loss at its optimal output level?
Monopolistic_comp_with_monopoly.docx - Explain why a firm ... The monopolist and markets under monopolistic competition produce at higher than minimum average total cost (Q1 and Q2), and there is therefore also a productive inefficiency. It can be argued that monopolist will have a lower total cost due to its economies of scale. Economies of scale lead to falling average costs over a large range of output.
Monopolistic Competition - Managerial Economics In this example, MR and MC intersect at a quantity of 40, which is the profit-maximizing level of output for the firm. The profit maximizing price is $16. The volume of profits = Total Revenue - Total Cost =$60 . A firm under Monopolistic Competition like a firm under monopoly can have both profit and loss in the short run.
Tutorial 11A.pdf - MONASH BUSINESS ECW 1101 INTRODUCTORY ... Monopolistically competitive firm in the short-run i. Profit-maximising output level = 10 units MR = MC ii. Profit-maximising price = $13 Corresponding demand curve iii. Total revenue = $13 x 10 units = $130 Price x Quantity iv. Total cost = $16 x 10 units = $160 Average total cost x Quantity v.
Microeconomics exam 3 Flashcards - Questions and ... - Quizlet The greater the monopolistically competitive firm's success at product differentiation the lower is (are) the firm's price elasticity of demand. The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is
Final Part 2. Flashcards | Quizlet The demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive firm is. A) vertical. ... From the diagram above, what is the optimal quantity of output?



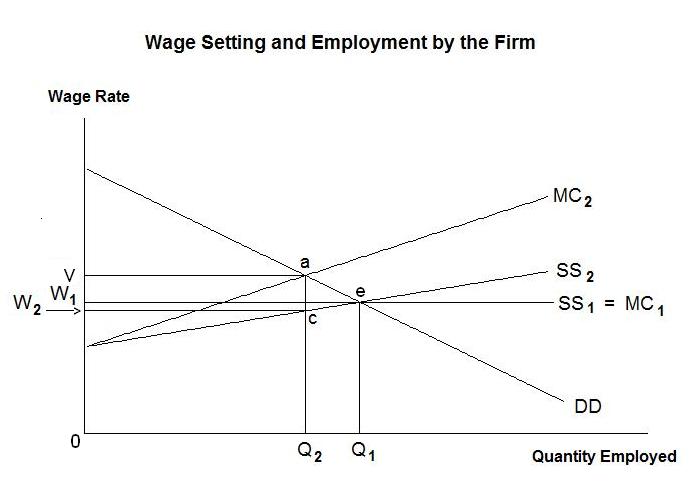



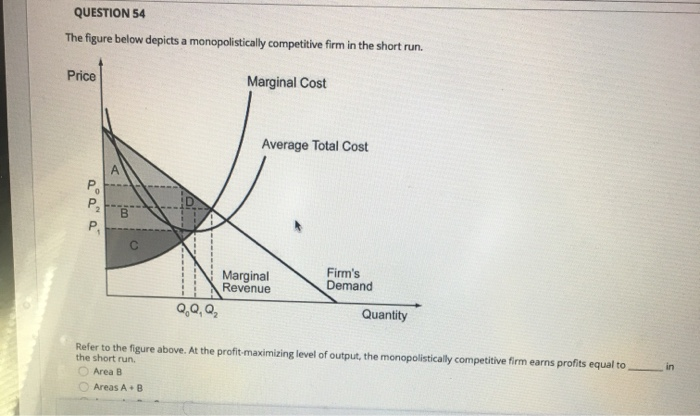


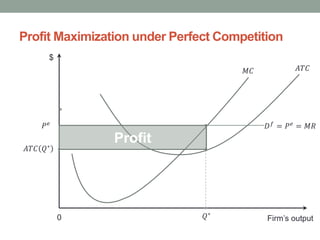



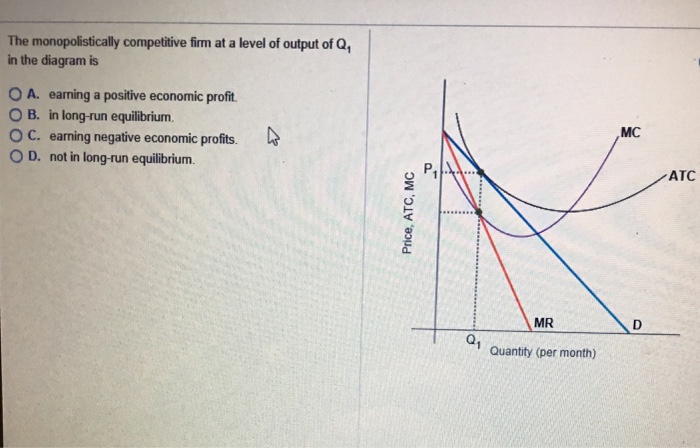



0 Response to "41 the monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is"
Post a Comment