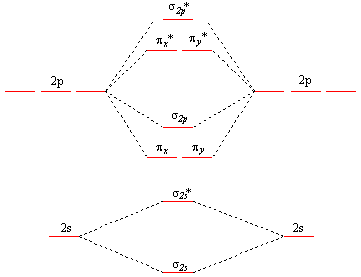
42 blank molecular orbital diagram
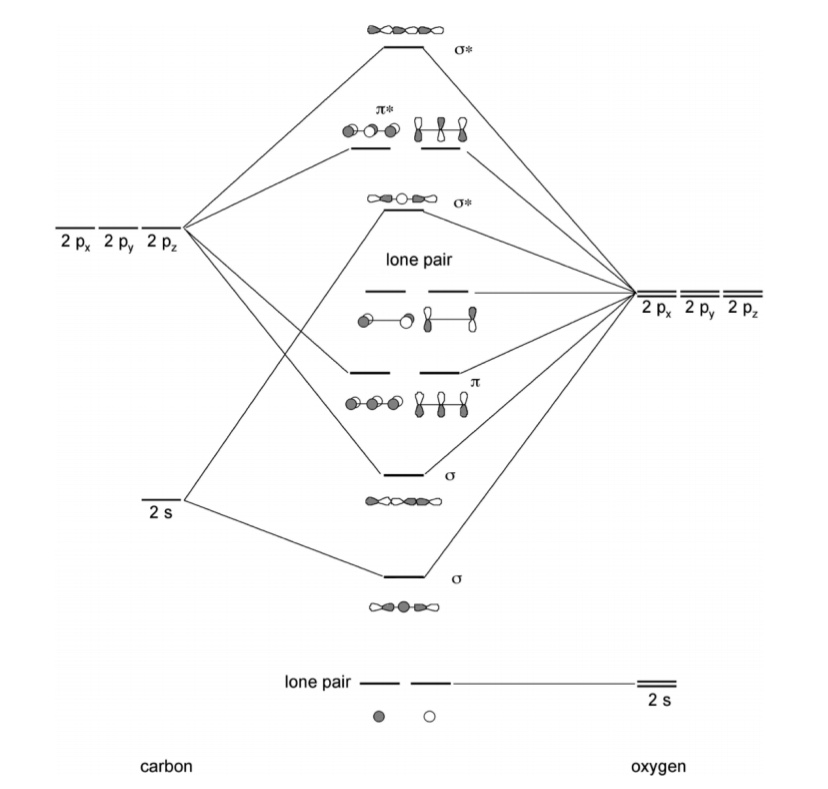
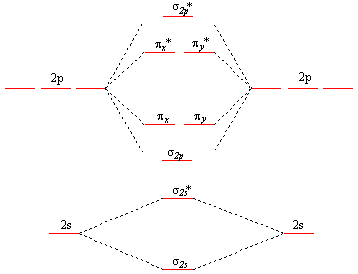
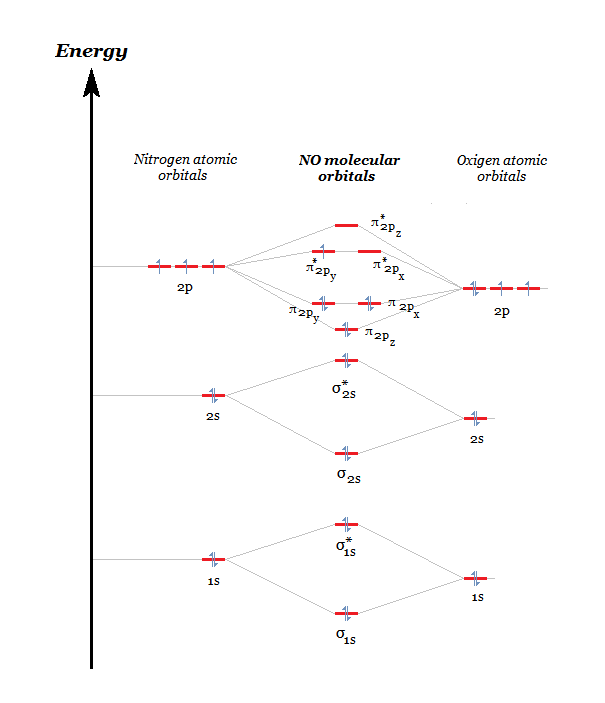
Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are similar (as in NO or CN *15. Use the appropriate molecular orbital energy diagram to. write the electron configuration for each of the following • Molecule orbital theory (Robert Mullikan). • Electrons are delocalised - Different to Lewis and hybridisation (these are not MO). • Energy level diagram represents this interaction. - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital.
Molecular Orbital Theory: To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals. Have you ever thought about how sigma and pi bonds are formed? What is the difference between diamagnetic and paramagnetic behaviour?
Blank molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding. For heteroatomic dinuclear molecule, energy of BMO closely matches with those of more electronegative atom & energy of ABMO closely matches with those of less electronegative atom. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories If you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it. For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of...
Blank molecular orbital diagram. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram for short, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the Linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method (LCAO method) in particular.[1][2][3] A... Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. I'm trying to build a molecular orbital diagram for BF3 and I'm running into problems with irreducible representations on the F side. I found the following diagram for BF3 online but it doesn't generate the E' anti bonding and also doesn't generate enough molecular orbitals.
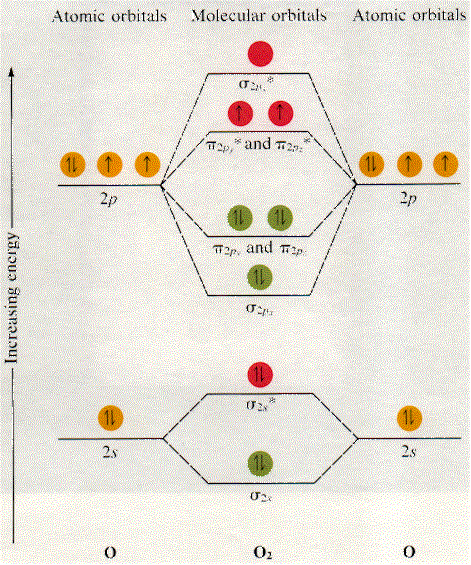
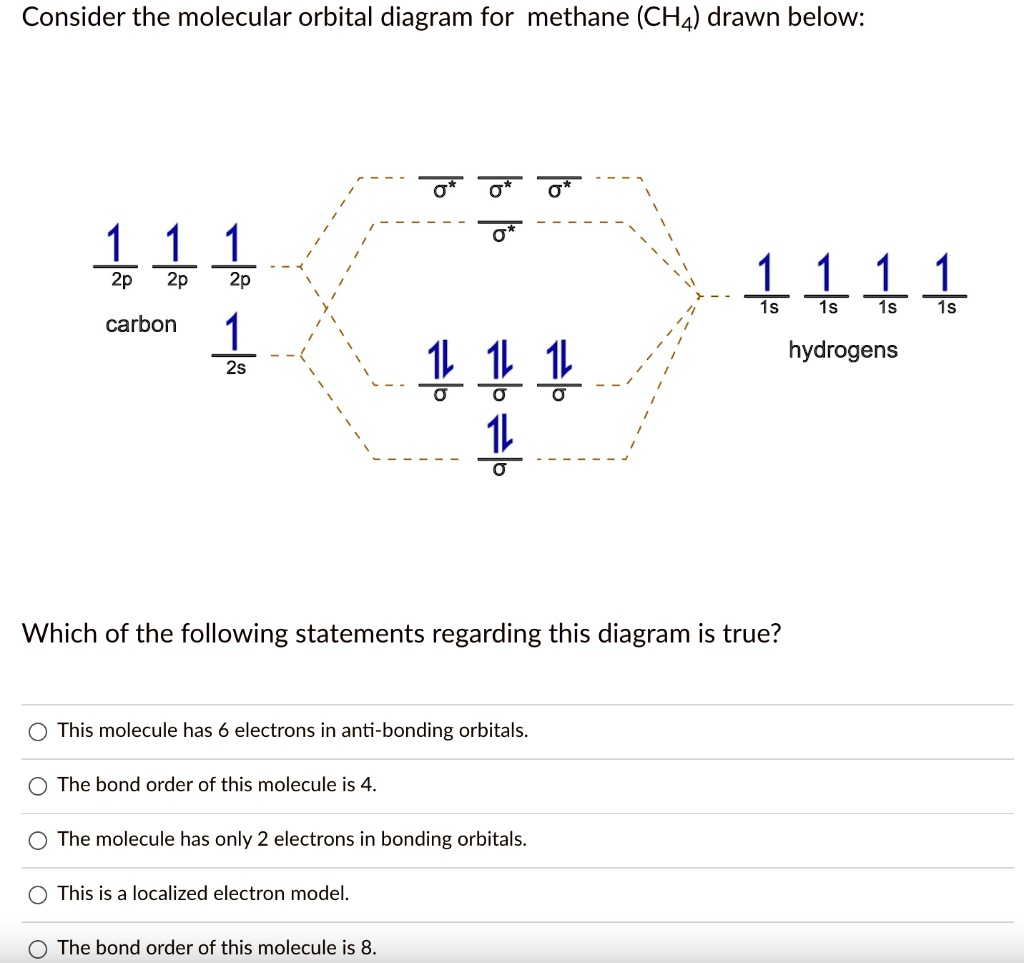
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. However, with more atoms, computers are required to calculate how the atomic orbitals combine. Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecules Geometry Molecular Orbital Atomic Orbitals. The majority of electron transitions in molecules occur in the _ region of the electromagnetic spectrum. -microwave -visible -X-ray -IR -UV. Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons. 1) If Nb > Na ,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than antibonding orbital, resulting in a net force of attraction.
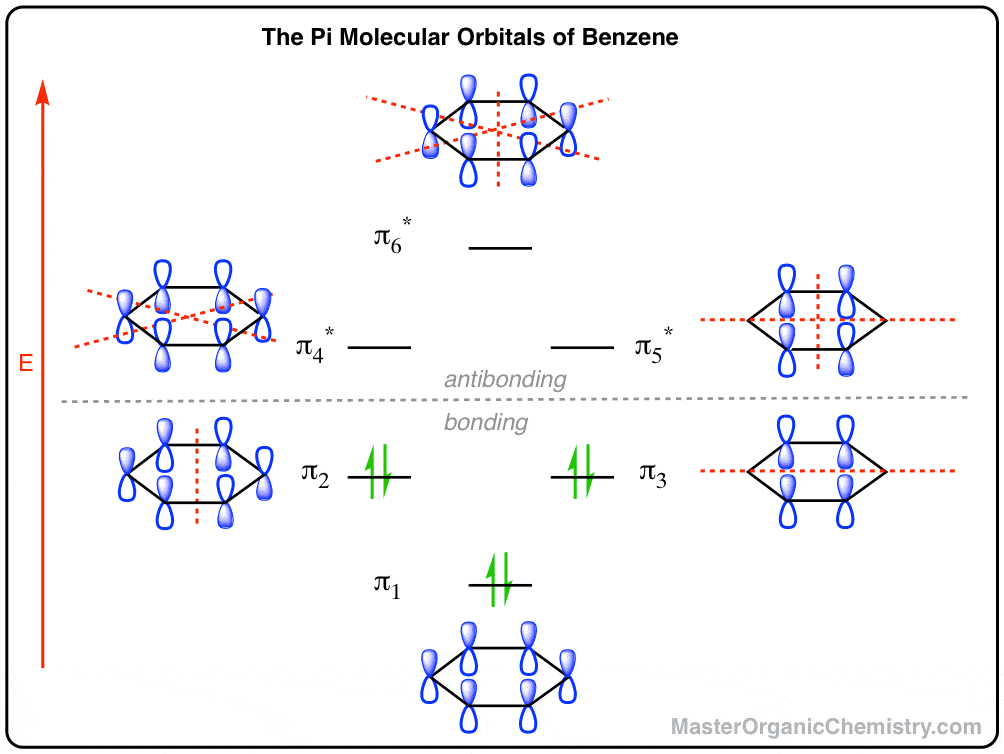
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the... IN THE APPLICATION of molecular orbital theory to calculations of chemical binding energies, we shall use s e v e r a l basic principles, some of which w e r e mentioned in Consider azulene, which has the following "molecular diagram": Clearly an electrophilic reagent would be expected to react a t. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row The Lowest-Energy Molecular Orbital (π1) Of The Butadiene Pi System Has Zero Nodes The Full Molecular Orbital Diagram For The Butadienyl System (n=4) A molecular orbital diagram without electrons is like an apartment building without people.
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
Figure 19.14 Molecular orbital diagram for an octahedral complex of a first series transition metal (only a interactions are considered in this simplified Figure B A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for ferrocene. The subscripts g and u refer to the parity of the orbitals g (German gerade, even)...
Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules This energy diagram for the molecular orbitals is shown in Fig.1 However, experimental evidence for oxygen and heavier diatomic molecules have...
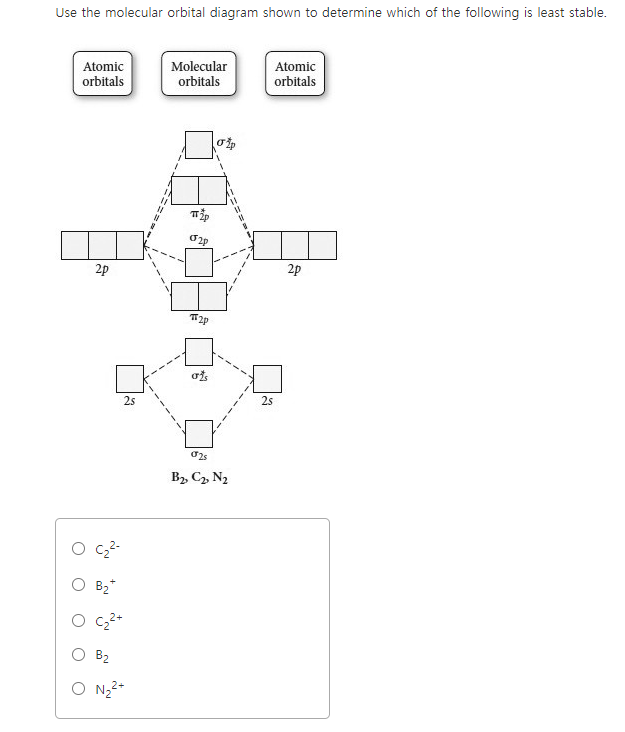
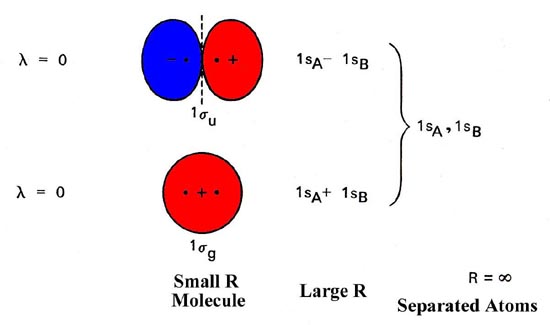
A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H2+.
Molecular orbital theory is more powerful than valence-bond theory because the orbitals reflect the geometry of the molecule to which they are applied. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms.
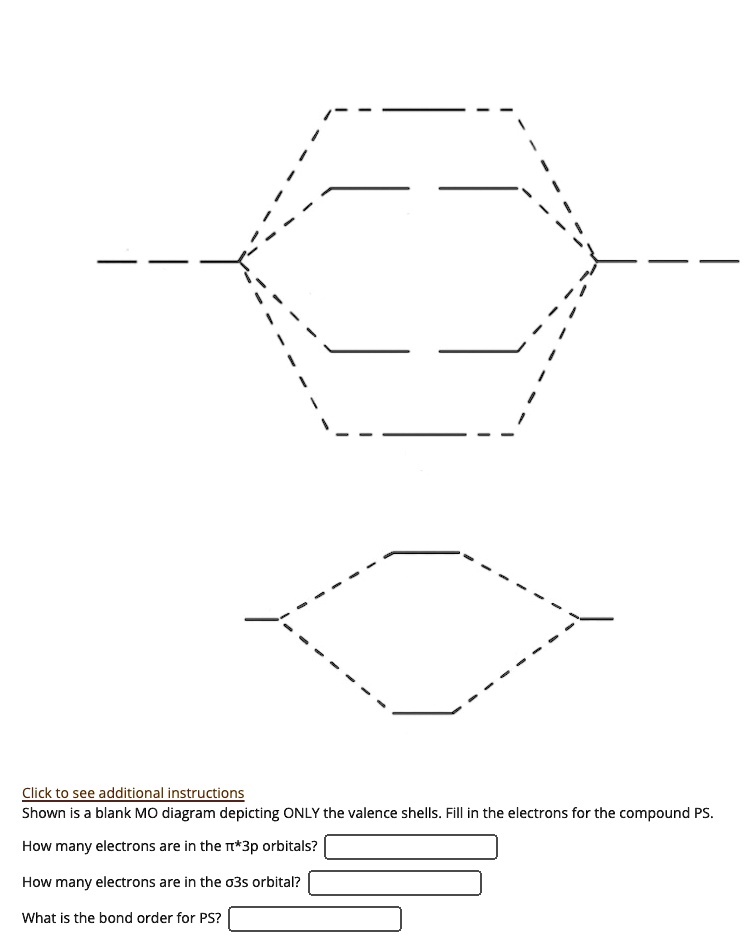
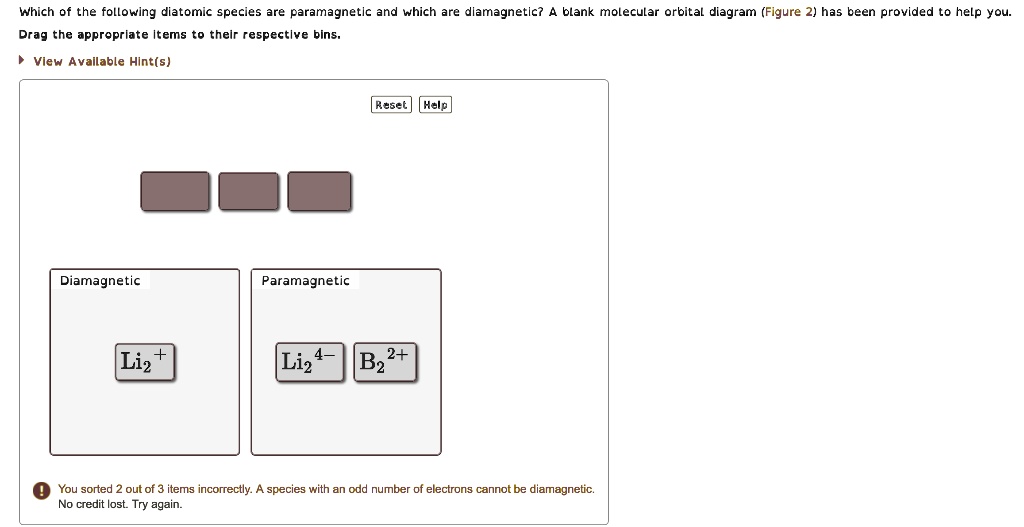
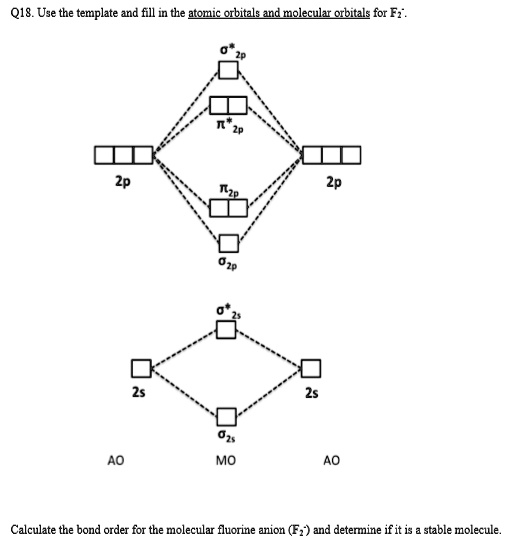
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part A 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in LaTeX by means of the package MOdiagram. For information about the more traditional molecular structure...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of...
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories If you can understand the foundation and skeleton of the diagram specific to that molecule, then it will be easier and faster for you to draw it.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding. For heteroatomic dinuclear molecule, energy of BMO closely matches with those of more electronegative atom & energy of ABMO closely matches with those of less electronegative atom.
















0 Response to "42 blank molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment