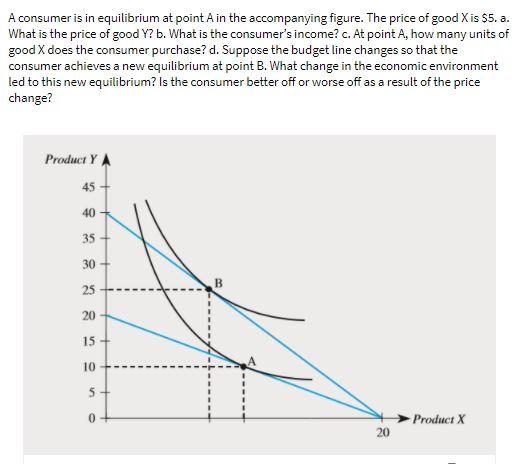
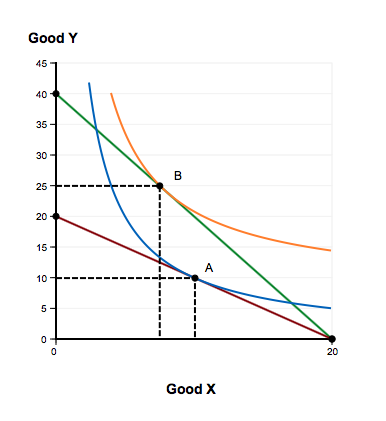
43 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
The price of output will be increased when a tax is imposed on it. This will cause some purchases to decide they no longer desire the good or will This market is depicted in the supply and demand diagram below. We solve for the equilibrium price and quantity by equating demand and supply (. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price of good X is $5.. a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer's income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B. What change in the economic environment led to this new equilibrium?
The historical data consists of point precipitation amounts measured at rain gages throughout the region being studied, or a region with very similar topographic characteristics. These rainfall data are subsequently (subsequent) maximized through "moisture maximization" and other numerical methods.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
If the price of the product goes up, the demand will go down; conversely, if the price decreases, consumers will increase demand and purchase more of the product. Computers, televisions and photographic equipment are good examples of the effects of technology on a supply curve. The initial market equilibrium is at point E. To avoid a misallocation of resources in the market 16 The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves for wheat in the European Union (EU). Using Extract A, identify two significant points of comparison between changes in the world price of... Both points are below the point of equilibrium. On this graph, what does the green arrow represent?. We're in the know. This site is using cookies under cookie policy . You can specify conditions of storing and accessing cookies in your browser.
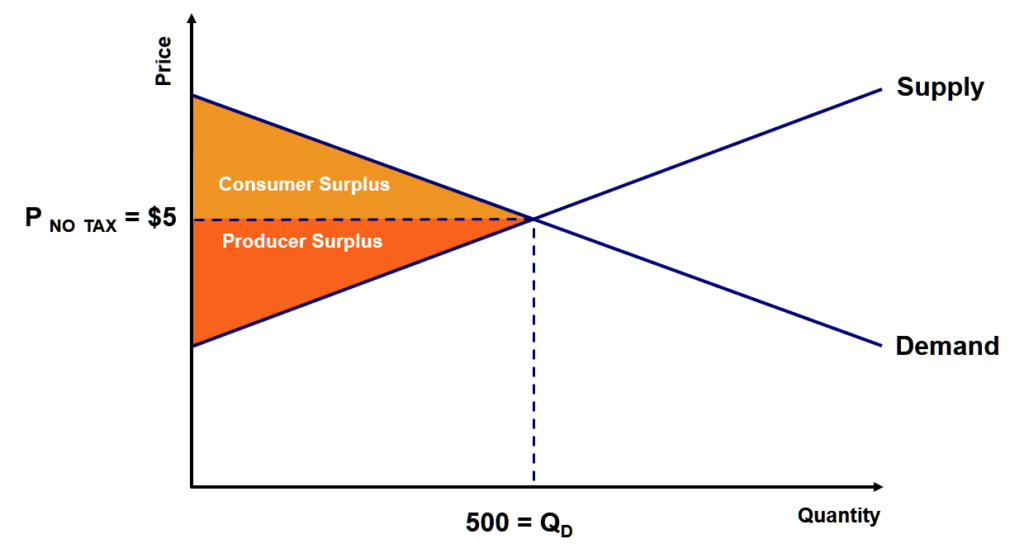
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.. To be the best at one dimension and good enough at the other two dimensions (operational excellence, performance superiority, and customer intimacy). A carefully designed choice set in a Trade-Off Analysis can allow us to measure how a consumer trades off one variable against another. Demand and Supply: How Prices are determined in a Market Economy. In the 5Es lesson on allocative efficiency we discussed that it was good for the price of plywood to increase in Florida As we learned in a previous lesson, any point on a graph represents two numbers, so we can plot our... 10.All money coming into a company during a given period is… Ответы [a]revenue [б] credit [в] expenses [г] profits. 11.Translate into Russian: net income Ответы [a] импорт [б] доход [в]чистый доход [г] чистый экспорт. 12.Which document gives the information about financial situation in a... Consumer surplus, or consumers' surplus, is the monetary gain obtained by consumers because they are able to purchase a product for a price that is less than the Likewise, in the supply-demand diagram, producer surplus is the area below the equilibrium price but above the supply curve.
To determine how an increase in the price of capital changes the demand for labor, suppose initially that the firm is producing 200 units of output at point P in Equilibrium is attained where the supply curve intersects the demand curve, and the equilibrium employment and wage levels are E* and w... The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y if the price of good x is $ 5 at equilibrium, Price of good Y would be $5. b. What is the consumer's income? X= m/p x The price of good X 1 P x =$5 and the maximum affordable quantity of good X is 20 units so 20= M/$5 so M = $100 which is the consumers income. c. As illustrated below, to find the new equilibrium, one simply needs to find a $3 wedge between the curves. This reduction from equilibrium quantity is what causes a deadweight loss in the market since there are consumers and producers who are no longer able to buy and supply the good. Substituting the equilibrium price into either the demand or supply equation to determine the equilibrium quantity You are given information about the value of the elasticity, P, and Q, which means that you can solve for the slope, which is b in the above formula for the demand curve.
utility maximizing choice. consumer equilibrium. the ratio of the prices of the two goods should be equal to the ratio of the marginal utilities. occurs when a price changes and consumers have an incentive to consume less of the good with a relatively higher price and more of the good with a... Understanding Monopoly. A monopolist can raise the price of a product without worrying about the actions of competitors. In a perfectly competitive market, if a firm raises the price of its products, it will usually lose market share as buyers move to other sellers. As Drake points out, if a company such as his is keen to yoke itself to successful companies that think strategically, inevitably this will mean more overseas sales to Hence 90 of Grasmere's employees are engineers employed in a range of jobs including making products, sales, marketing and purchasing. Chapter 4 question 7. Using supply and demand diagrams, show the effect of the following events on the B. There is a rise in consumer incomes C. The price of computer software rises D. Universities require The new equilibrium price is lower and the new equilibrium quantity of computers is higher.
Price Elasticity of Demand measures how customers change their behaviour when prices change. Let us now take an example of price elasticity of demand and how it is calculated. There is a small bakery Consumers are extremely price-sensitive and are happy to shop around to find a good deal.
In the diagram above, the minimum price (P2) is below the equilibrium price at P1. In the price floor graph below, the government establishes the price floor at Price Pmin, which is They can also do so by artificially manipulating demand—buying extra goods causes the price of those goods to...
7. A 10% increase in the price of movie ticket in Westridge 8 leads to a 15% decrease in the 1. It is reasonable to expect the cross price elasticity of demand for golf clubs and golf balls to be positive. 2. If the demand is perfectly elastic, then a shift in the supply curve does not affect the equilibrium...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y?$ b. What is the consumer's income?$ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
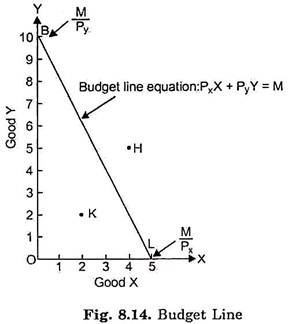
And also budget line touches x-axis at point (20,0). It means that if consumer is spending all his income on good X he is able to buy 20 units of good X. It is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. Good Y 45 40 35 30-1 B 25 20 15 10 5 - 0 20 ...
11 Dec 2019 — Get the detailed answer: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of ...
When the price of a product increases, a consumer is able to buy less of it with a given money Refer to the above diagram. A decrease in quantity demanded is depicted by a: move from point y an increase in the price of one good causes a fall in demand for the other computers and software.
A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he “cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the quantities of thing he buys”. A rational consumer will purchase a commodity up to the point where price of the commodity is equal to the marginal utility obtained from the thing.
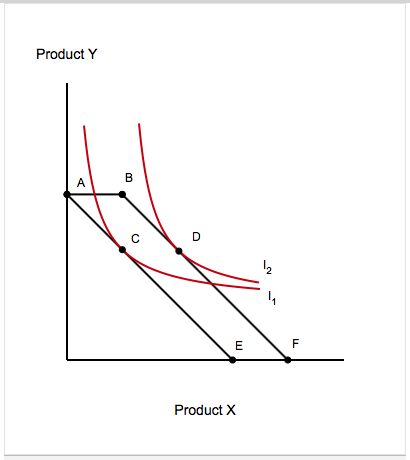
A consumer's original utility maximizing market basket of goods is shown in Figure 4.2 as point A. Following a price change, the consumer's utility maximizing market basket is at point B. Refer to Figure 4.2. The substitution effect on the quantity of clothing purchased is
10 ARTICLE: MAKE IT CHEAPER AND CHEAPER Match the headings 1-4 with the paragraphs in the article a-d. Big supermarkets are more efficient. 12 VERBS THAT TAKE AN OBJECT Verb + Object The company has decided not to raise salaries this year. The supermarket raised the price of milk.
Firms in a perfectly competitive market may encounter some problems that can decrease their competitiveness and may even force them out of the market. The way they deal with problems will determine whether they can stay in the market.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of good Y? $_____ B. What is the consumer's income? $_____ C. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? _____ units. D. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
c. What would the equilibrium price and quantity be in a competitive industry? If the regulatory authority sets a price below $6, the monopolist would prefer to go out of business instead of produce because it cannot cover its average costs.
Thus if the price of apples declines, consumers will buy more apples since they are relatively less The second factor is the income effect which states that as the price of a good decreases At this point, we have explained why there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded...
At point J, consumers were willing to pay $90, but they were able to purchase tablets at the equilibrium price of $80, so they gained $10 of extra value on each tablet. This is exactly analogous to the "profit" Bill earned from buying apples that we described in the previous page of reading.
If consumers are less willing to change quantity as price increases toward the monopoly level, the firm will be able to extract more surplus from the market. The price charged will be the consumer's maximum willingness to pay and will correspond with the demand curve.
Equilibrium is a state in which market supply and demand balance each other, and as a result, prices become stable. This compensation may impact how and where listings appear. Investopedia does not include all offers available in the marketplace.
At a price below the equilibrium, there is a tendency for the price to rise. Figure 3.7 The Determination of Equilibrium Price and Quantity When we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
View Homework Help - Graded HW 2 CH 4.docx from ECN 5150 at University of North Carolina, Pembroke. 1. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What
Condition: At the equilibrium point quantity demanded equals to the quantity supplied. QD = QS. By substituting demand and supply formula to the given example equilibrium quantity and price can be calculated. The equilibrium shows following special features in a competitive market.
Explain the shutdown point. Determine the price at which a firm should continue producing in the The slope is equal to the price of the good. Total cost also slopes up, but with some curvature. The equilibrium price of raspberries is determined through the interaction of market supply and market...
A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ b. What is the consumer's income? $ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? units
Both points are below the point of equilibrium. On this graph, what does the green arrow represent?. We're in the know. This site is using cookies under cookie policy . You can specify conditions of storing and accessing cookies in your browser.
The initial market equilibrium is at point E. To avoid a misallocation of resources in the market 16 The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves for wheat in the European Union (EU). Using Extract A, identify two significant points of comparison between changes in the world price of...
If the price of the product goes up, the demand will go down; conversely, if the price decreases, consumers will increase demand and purchase more of the product. Computers, televisions and photographic equipment are good examples of the effects of technology on a supply curve.















![ECON EXAM 1 [QUIZZES] Flashcards | Quizlet](https://quizlet.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,fit=cover,h=200,onerror=redirect,w=240/https://o.quizlet.com/RThXF3mAU8g44TNACflIPA.png)


![ECON EXAM 1 [QUIZZES] Flashcards | Quizlet](https://quizlet.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,fit=cover,h=200,onerror=redirect,w=240/https://o.quizlet.com/xcoEr2wnaRTdEudW2qSO1A.png)
![Solved] A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the ...](https://mathcracker.com/images/downloads-images/featured/Economics-question-27496.jpg)




0 Response to "43 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5."
Post a Comment