42 cn- molecular orbital diagram
MO Diagram of CN-< - Hunt Research Group Molecular Orbital Mixing. More detail was added to this answer in response to input and questions from students in the class of 2008. If you have suggestions or contributions please e-mail me. First of all while the stage 1 (pre mixing diagram) of diatomics is very easy to produce, the mixing in diatomics is very difficult to evaluate because ... PDF Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
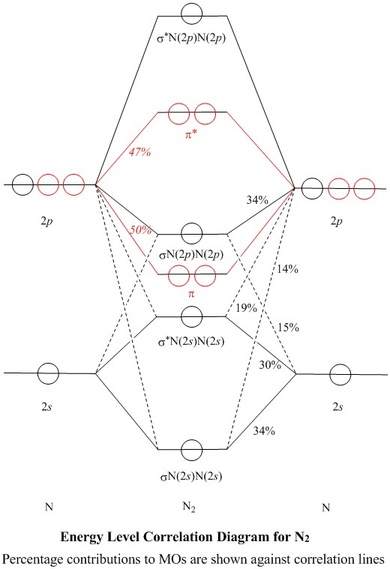
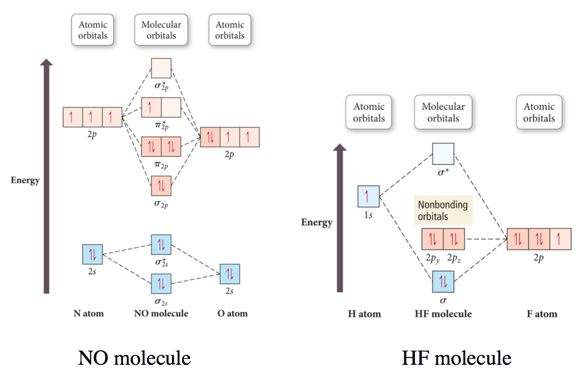
Draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for oxygen ... Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...

Cn- molecular orbital diagram
Answered: 1. Draw the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby Solution for 1. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the following molecules: (a) NH3 (b) CO (c) CN 2. Explain how the backbonding occur between metal and CO… Properties of water - Wikipedia Water is the chemical substance with chemical formula H 2 O; one molecule of water has two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom. Water is a tasteless, odorless liquid at ambient temperature and pressure.Liquid water has weak absorption bands at wavelengths of around 750 nm which cause it to appear to have a blue colour. This can easily be observed in … PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
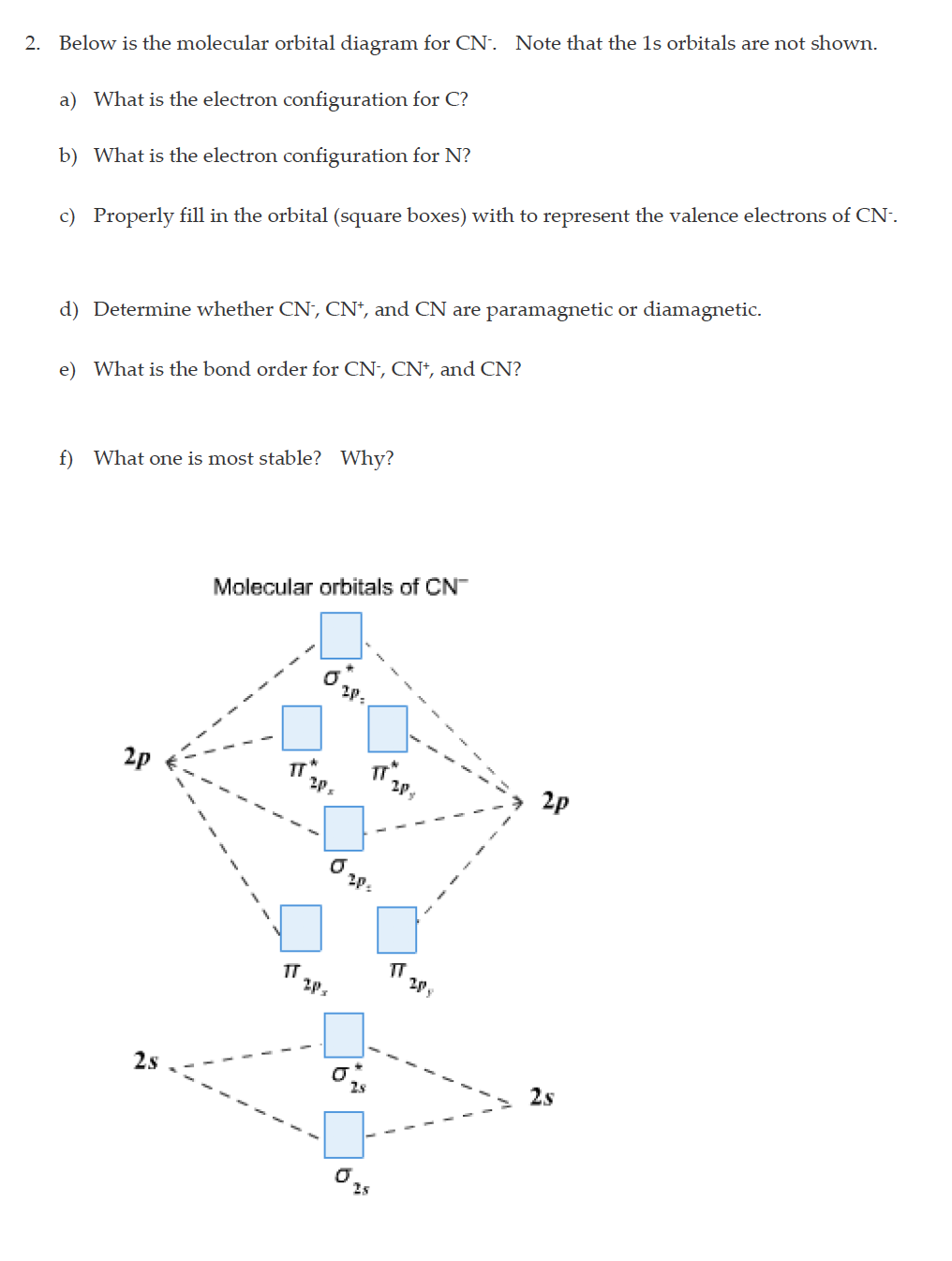
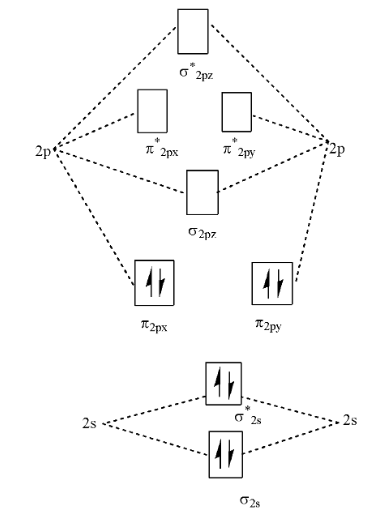
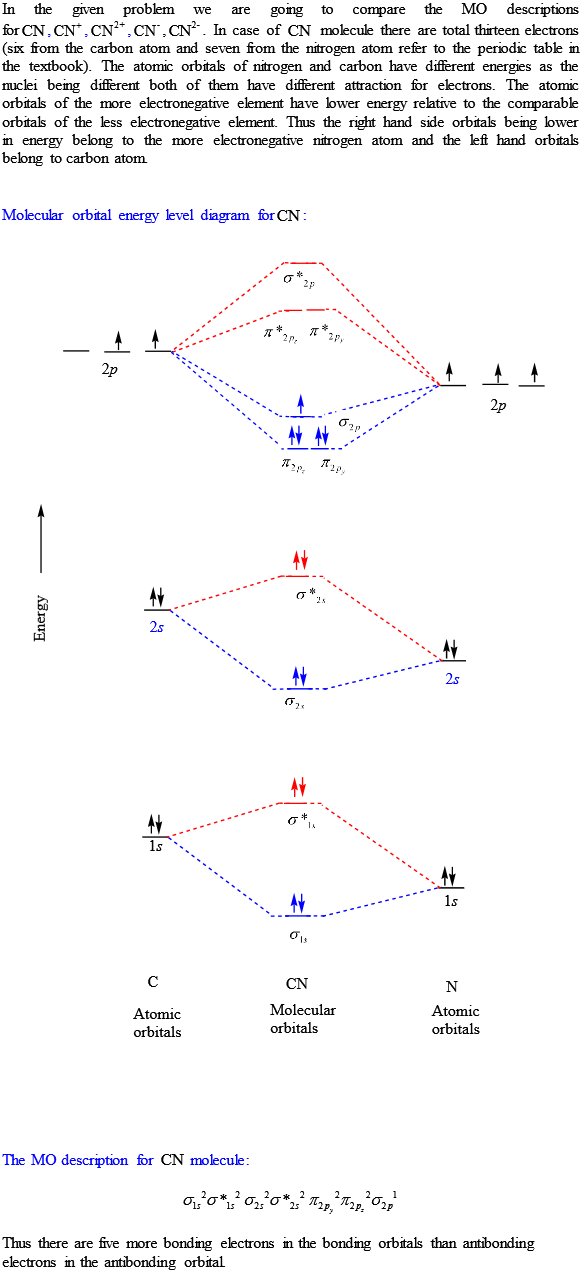
Cn- molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbital diagram of CN- - YouTube MO Diagram #3 - CN- - YouTube This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN- 42 complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn - Wiring ... Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3. orbital from the σ-bonding. topblogtenz.com › cyanide-cn-lewis-structureCN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond order Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
quizlet.com › 538030724 › module-two-chem-101Module Two Chem 101 Problems Flashcards - Quizlet Draw the orbital energy diagram for C to find where its valence electrons are. They are found in 2s,2pₓ,2py,2pz2s,2pₓ,2py,2pz. Which hybrid orbitals overlap in the C - N bond in CO(NH₂)₂? molecular orbital theory - How to know whether s-p mixing ... Mathematically, hybridization process is transformation of several orbitals using linear transform. Since molecular orbitals are described as linear combinations of atomic orbitals, there is no problem to use any imaginable set of atomic orbitals as long as their linear combinations can produce all 'original' atomic orbitals. O2 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. 0:00 Lewis Structure 1:51 Shape and angle 2:30 Dipoles 4:23 Formal A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of N2O including a description of the N2O bond angles. › articles › s41560/020/0667-9Molecular engineering of dispersed nickel ... - Nature Energy Aug 10, 2020 · Kohn–Sham molecular orbital analysis revealed that the ... Although NiPc–OMe-H 2 required the least energy to generate *COOH from the free energy diagram, NiPc–CN-H 2 was generated with the ...
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. 37 no+ molecular orbital diagram - Diagram For You Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital configuration of CN^+ is - Toppr Ask The molecular orbital configuration of C N + is K K σ (2 s) 2, σ ∗ (2 s) 2, π (2 p x ) 2, π (2 p y ) 2. Bond order is 2 . All the electrons are paired and ion is diamagnetic. Cyanide (CN−) - Structure, Molecular mass, Properties & Uses Cyanide (CN−) - Cyanide is the chemical name of CN− . Visit BYJU'S to understand the properties, structure and uses of CN− Cyanide) explained by India's best teachers.
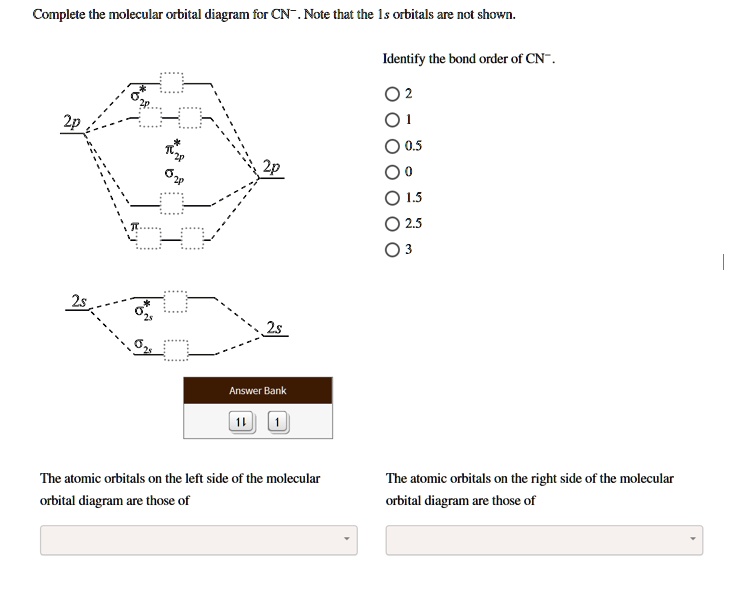
Answered: Complete the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN¯. О 1.5 2p ´2p 2p 2 1 0.5 2.5 3 2s 2s 2.s Answer Bank 11 1 The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of orbital diagram are those of 9.
Solved Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note ... Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
What is the bond order of CN+? - Quora Answer (1 of 8): I personally think the best way to determine the bond order is by drawing the Lewis structure however complex the molecule is. After that just follow the rules I've linked below from a reputable website. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indi...
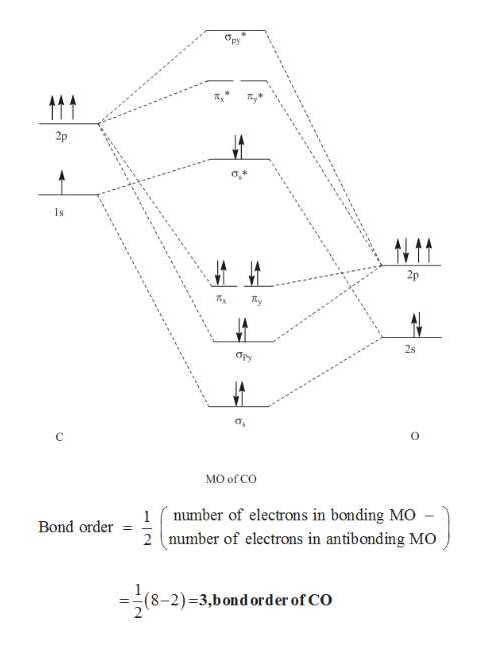
What is the bond order of CN-? - Quora Answer (1 of 6): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
Acetonitrile CH3CN: Molecular Geometry - Hybridization ... The hybrid orbitals are more prominent outward so that their ability to overlap is stronger than that of normal orbitals. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula is a brief way of expressing the number and type of atoms that make up a particular chemical compound.
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular Orbital Theory is slightly different from VBT and orbital hybridization. Here, AOs from different atoms inside the molecule can come together to form molecular orbitals or MOs. Therefore, valence electrons are shared inside the molecule. The electronic configuration of both C and N are as follows:
Chemistry Review: Exam 2 Flashcards - Quizlet b. Electrons in the 2s orbital are shielded by electrons in the 2p. c. The larger number of electrons found in the 2p orbital leads to greater repulsion. d. The shape of the orbital ultimately determines the energy of the electrons. e. Electrons in the 2s orbital can penetrate the 1s orbital and be closer to the nucleus .
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Crystal_field_theoryCrystal field theory - Wikipedia Overview of crystal field theory. According to crystal field theory, the interaction between a transition metal and ligands arises from the attraction between the positively charged metal cation and the negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand.
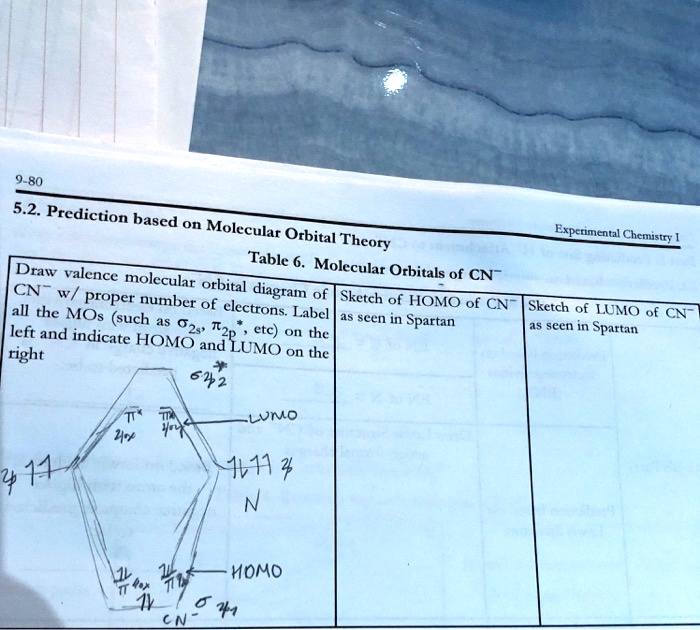
SOLVED:Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ... uh, molecular orbital represents. So they have, like, behavior off electron. They're formed into the linear combination for atomic orbital spawned in there at them. So fair manicure. Um, the the electronic configuration off carbon and nitrogen is carbon is one is to toe to toe pay two and a nitrogen is 12 tourist to and to be three. So the total electron in the Hadron ah, hit your own nuclear ...
faculty.uml.edu › ndeluca › 84d-Metal Complexes - University of Massachusetts Lowell A molecular orbital diagram which estimates the energies of the bonding (show above) antibonding and non-bonding orbitals is shown below. Since there is a large disparity in energy between the ligand orbitals and the metal orbitals, the lower lying molecular orbitals in the diagram are essentially ligand orbitals.
Describe The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co - 17 images ... [Describe The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co] - 17 images - solved 13 choose the orbital diagram that represents the, linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao, explain step by step how to draw molecular orbital diagram, choose the orbital diagram that represents the ground,
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram - wiringall.com The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion). Figure \ (\PageIndex {2}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for \ (\ PageIndex {12}\) to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). In the traditional Lewis picture there are two lone pairs on the cyanide ion.
› ncert-solutions-for-class-11NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 - LearnCBSE.in Answer: Bonding molecular orbital has lower energy and higher stability. Question 19. Define antibonding molecular orbital. Answer: The molecular orbital formed by the subtractive effect of the electron waves of the combining atomic orbitals, is called antibonding molecular orbital. Question 20.
What is the molecular orbital diagram for CN? - Book Vea A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. What is the bond length of CN+? The bond length in CN+ is 0.129 nm Does CN have no bond order?
5.4: Spectrochemical Series - Chemistry LibreTexts Jun 03, 2021 · Weak field I-< Br-< Cl-< NO 3-< F-< OH-< H 2 O < Pyridine < NH 3 < NO 2-< CN-< CO Strong field. Orbital overlap. Referring to the molecular orbital diagram above, we see that the splitting between d-electron levels reflects the antibonding interaction between the e g metal orbitals and the ligands. Thus, we expect ligand field strength to ...
› ~lawm › Ch 5 SolutionsMiessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM Ch 05 CM The S orbital energies are –22.7 eV (3s) and –11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of –13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
PDF MO Diagrams for More Complex Molecules d orbitals •l = 2, so there are 2l + 1 = 5 d-orbitals per shell, enough room for 10 electrons. •This is why there are 10 elements in each row of the d-block. σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes 1. Point group Oh 2. The six ligands can interact with the metal in a sigma or pi fashion.
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram - schematron.org CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in carbon is six. What do the molecular orbitals of cyanide look like, compared with those paired HOMO's and LUMO's in the molecular orbital energy diagram.
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Properties of water - Wikipedia Water is the chemical substance with chemical formula H 2 O; one molecule of water has two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom. Water is a tasteless, odorless liquid at ambient temperature and pressure.Liquid water has weak absorption bands at wavelengths of around 750 nm which cause it to appear to have a blue colour. This can easily be observed in …
Answered: 1. Draw the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby Solution for 1. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the following molecules: (a) NH3 (b) CO (c) CN 2. Explain how the backbonding occur between metal and CO…



![On the gold–ligand covalency in linear [AuX 2 ] − complexes ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2015/DT/c4dt04031g/c4dt04031g-f5_hi-res.gif)















0 Response to "42 cn- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment