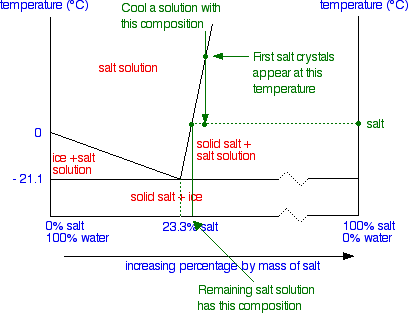
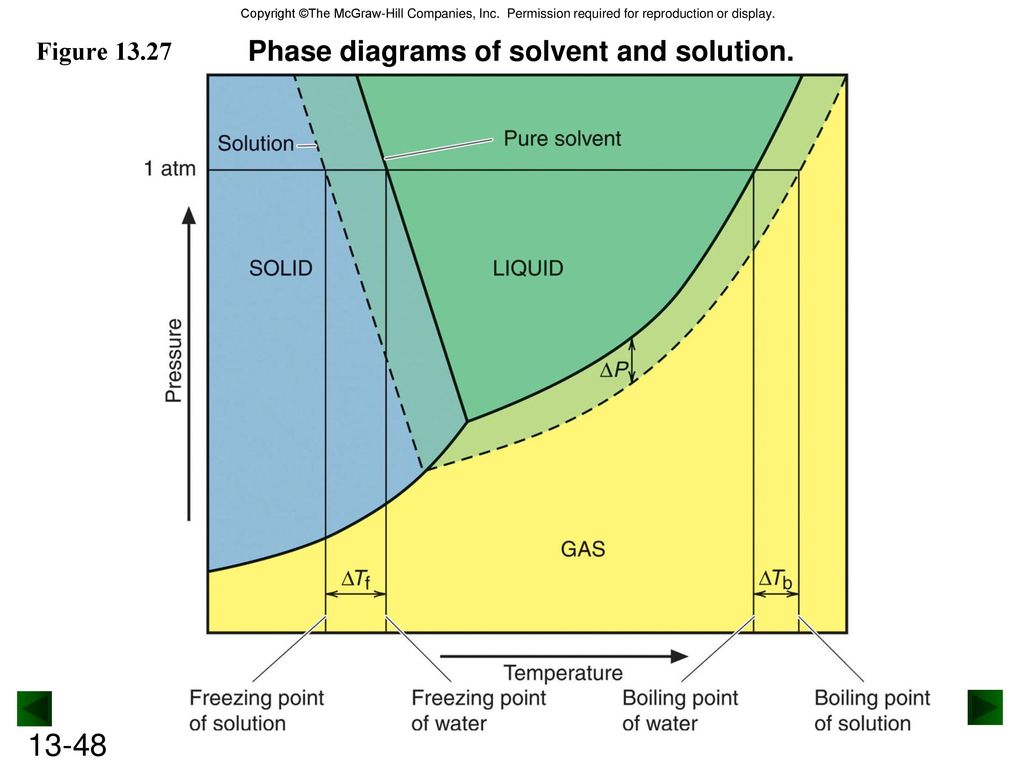
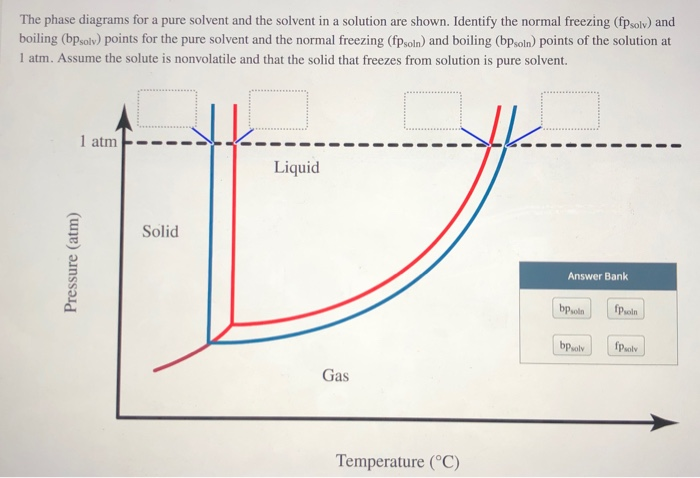
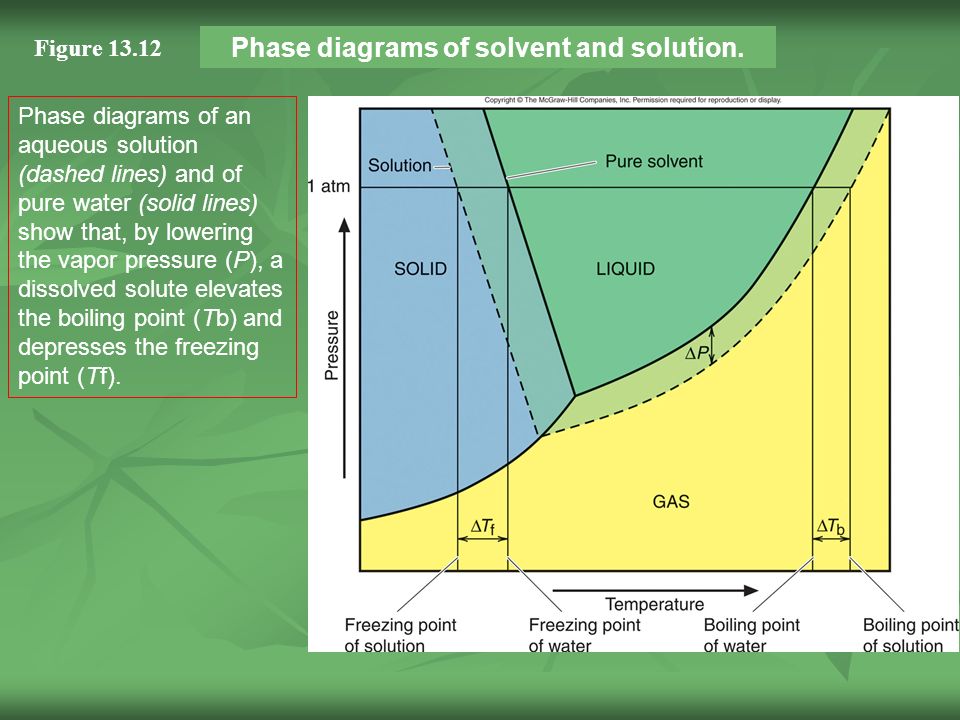
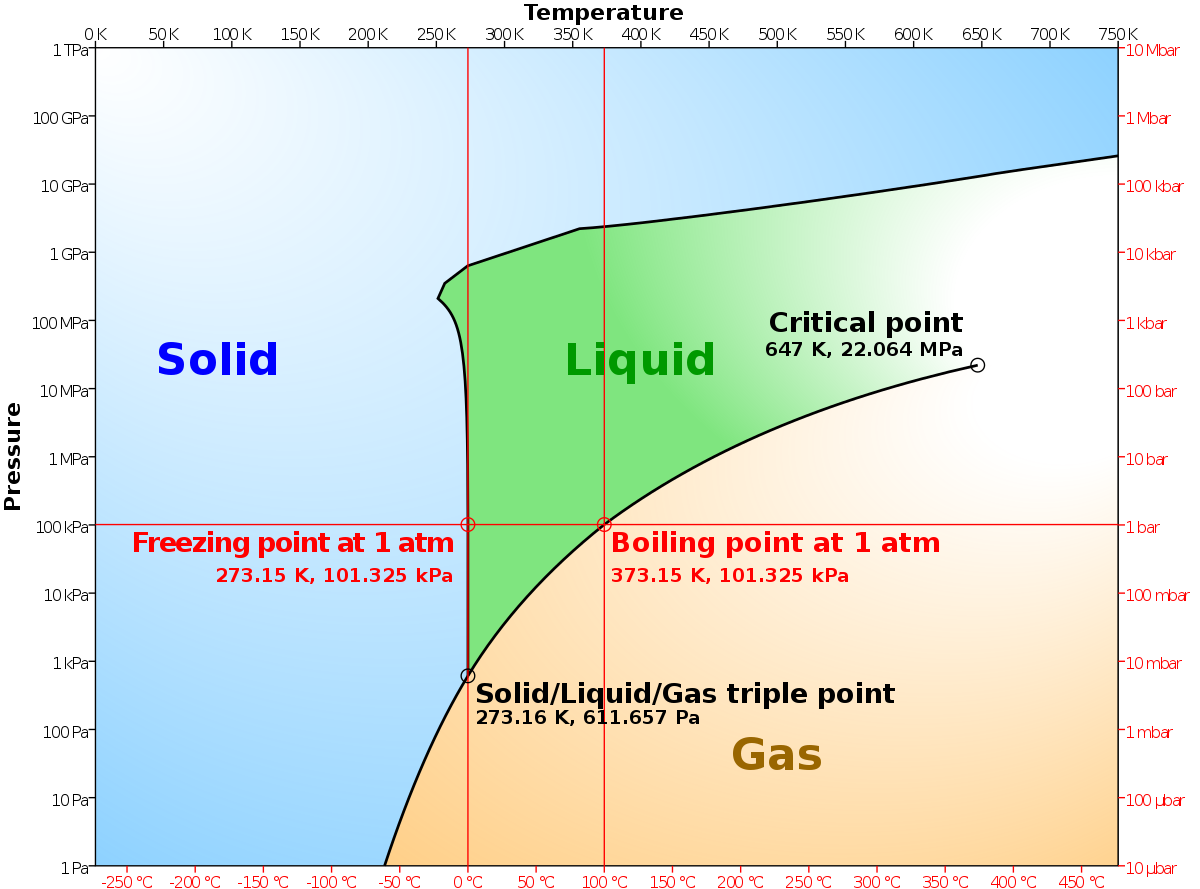
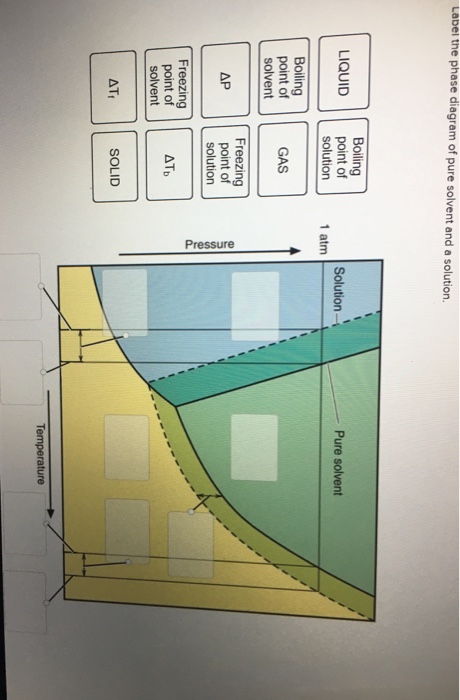
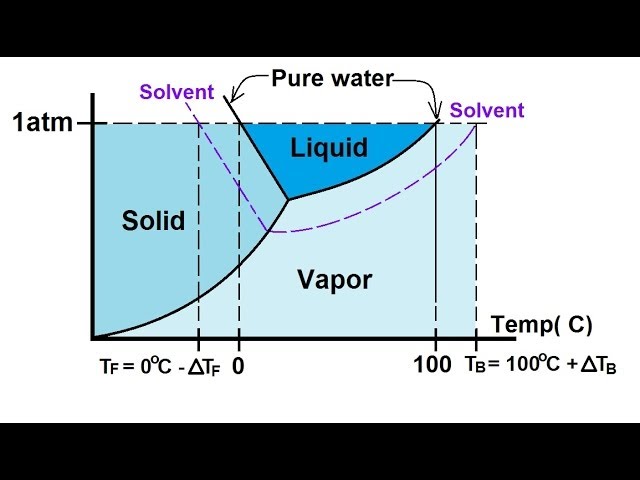
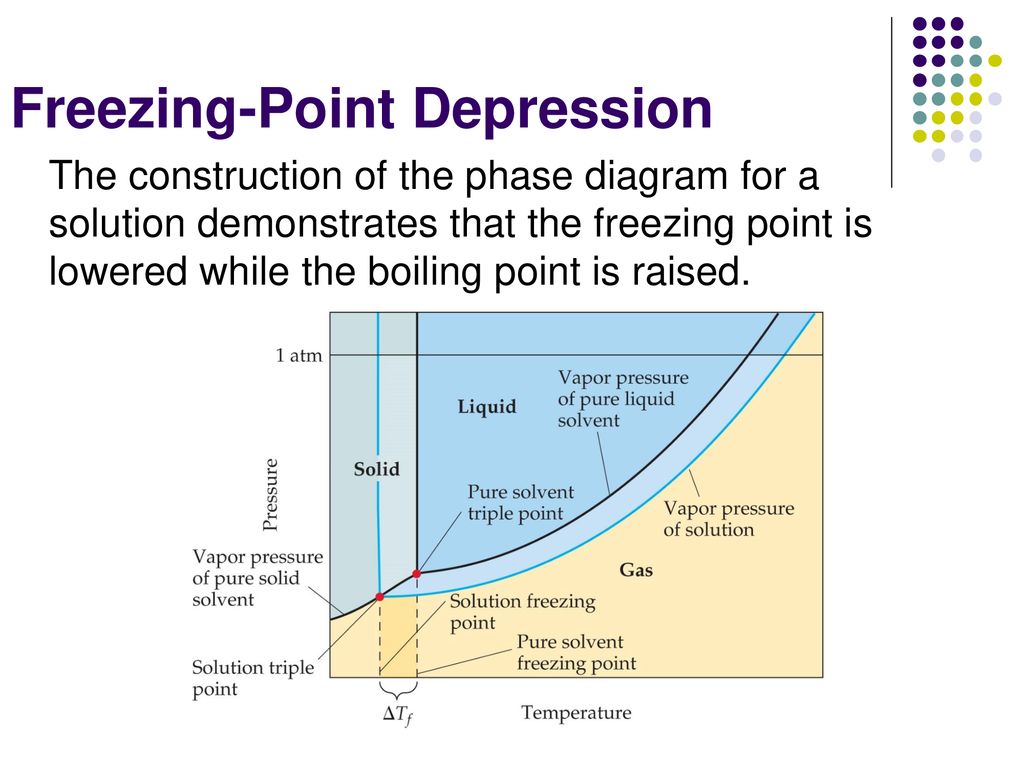
41 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution
1. Introduction. According to George Whitesides, one of the most important personalities in this field, microfluidics represents "the science and technology of systems that process or manipulate small (10 -9 to 10 -18 L) amounts of fluids, using channels with dimensions of tens to hundreds of micrometers" [1,2,3].Microfluidics evolved from the convergence of technologies and principles ... Process schematic for multistage liquid-liquid extraction. Determining number of stages N when (1) feed rate; (2) feed composition; (3) incoming solvent rate; (4) incoming solvent composition; and (5) outgoing raffinate composition have been specified/selected. Locate points F and S on the ternary phase diagram.
A counter-current extraction column is designed to remove 99% of solute C from a solution of solvent A and solute C using pure solvent B. the initial concentration of solute in the solution of A + C is 20 wt%, and the total flow of solution is 1000 kg/h.

Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution
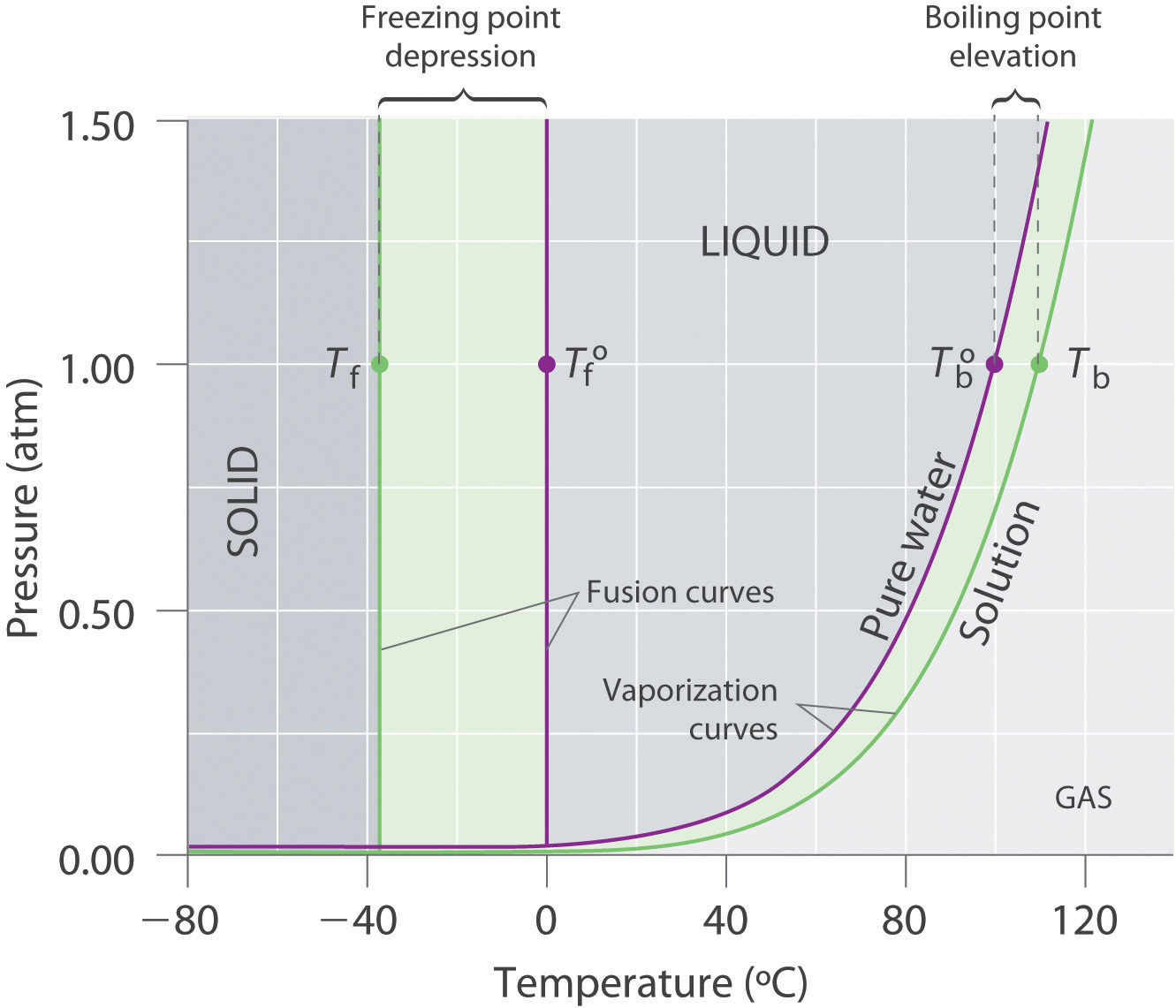
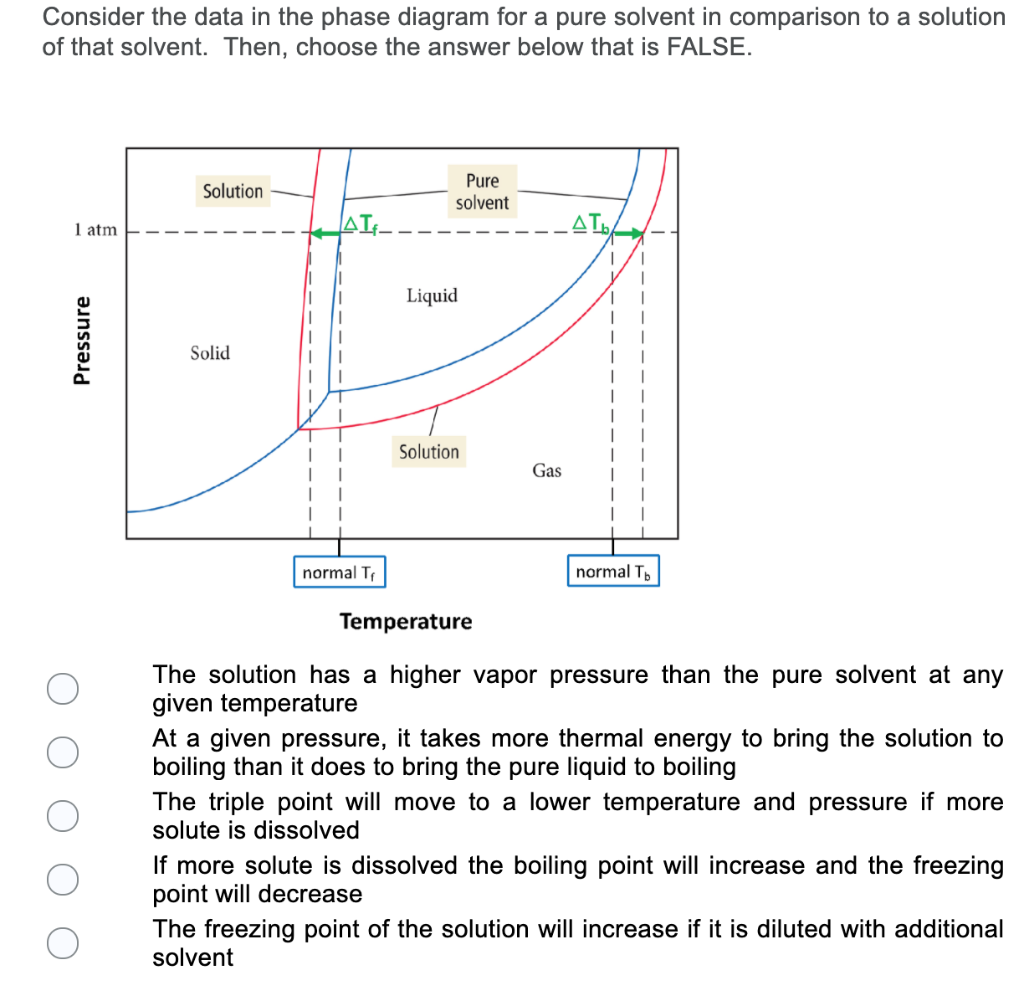
We can see why this must be true by comparing the phase diagram for an aqueous solution with the phase diagram for pure water (Figure (PageIndex{1})). The vapor pressure of the solution is less than that of pure water at all temperatures. Consequently, the liquid-vapor curve for the solution crosses the horizontal line corresponding to P = 1 ... Buffer solution is a mixture of salt and weak acid/weak base which can maintain the pH of the solution when small amount of strong acid or strong base is added to the solution. b) Explain how the pH of a buffer solution made from a weak acid and its conjugate base changes when; i. the acid dissociation constant, Ka, of the weak acid increases. Label the diagram. reflux. Draw a diagram to show how two methanol molecules interact with each other through hydrogen bonding in the liquid phase. ... Aldehydes can be oxidised by Tollens' reagent or by Fehling's solution. An unknown pure liquid A contains only a single alcohol. Outline a simple procedure to allow you to determine whether A is ...
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. 9. The process of phase change from a vapor to a liquid is known as _____. 10. The components of a mixture have different _____ points. Answer Key. 1. WATER 2. PHYSICAL 3. SEPARATION 4. HEAT 5 ... View bio. An isotonic solution is defined as two solutions of equal concentrations of solutes and water separated by a semipermeable membrane to allow water to move freely in and out of a cell ... Dec 11, 2019 — Label the phase diagram of a pure solvent and a solution. Answer. +20. Watch. 1. answer. 0. watching. 105. views.1 answer · Top answer: Explanation: A phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. ... The solvent is the substance that does the dissolving and is present in the largest amount, while the solute is the substance being dissolved. Solvents and solutes can be in any phase of matter ...
1 answerRecall that a phase diagram shows the transition of matter between solid, liquid, and gas phases as temperature and pressure changes. In a phase diagram, ... The full phase diagram of this BSA-PEG system is shown in Fig. 1b. With this system, we can vary the concentration of BSA in the droplets from about 350 to 500 mg/mL. Oct 21, 2016 — Chemistry 4 qs missed. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Skilled solution 100 25 rankings this downside has been solved. For the experiments, a clear single phase stock solution of (formaldehyde + water + trioxane) was prepared by mixing the aqueous formaldehyde solution with trioxane at 313 K; the composition of the stock mixture (cf. Table 1) was chosen based on preliminary process simulations. Samples of the stock mixture were filled in 100 or 200 ml glass ...
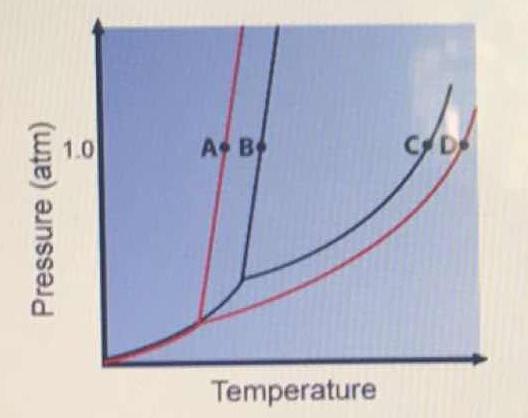
A pure compound will melt over a narrow range and an impure compound will melt over a broad range. As heat is applied to the apparatus of a pure sample, a high energy input is needed to break strong IMFs. An impure compound will have a wider range because it is not homogenous and different areas will start to melt before pure areas. Jun 10, 2017 — Now consider the solution made using the pure liquid substance as the solvent, with the phase diagram indicated by the red curves.1 answer · Consider the following general phase diagram: http://www.kentchemistry.com/ Now, consider the pure substance, whose phase diagram was represented by the ... The computational method to determine this phase diagram is illustrated in Figures S2 and S3. For good solvent conditions, the solution remains uniform over the whole range of solute concentrations corresponding to mole fractions Φ S S ≤ 1. In contrast, for poor solvent conditions, the solution undergoes phase separation into two coexisting ... 3. Liquid solvent used in gas absorption is below its boiling point. 3. Liquid in distillation operation is at its bubble point. 4. In gas absorption, a gas phase contacts a liquid phase and mass (solute) is transferred from the gas phase to liquid phase (i.e., mass transfer takes place in one direction).
Reverse phase chromatography utilizes a hydrophobic solvent (typically acetonitrile) and the binding of a ligand is a function of the phase partition between the hydrophobic nature of the solvent and column functional group. Proteins are typically denatured in such solvents and bind due to the hydrophobic nature of the entire polypeptide sequence.
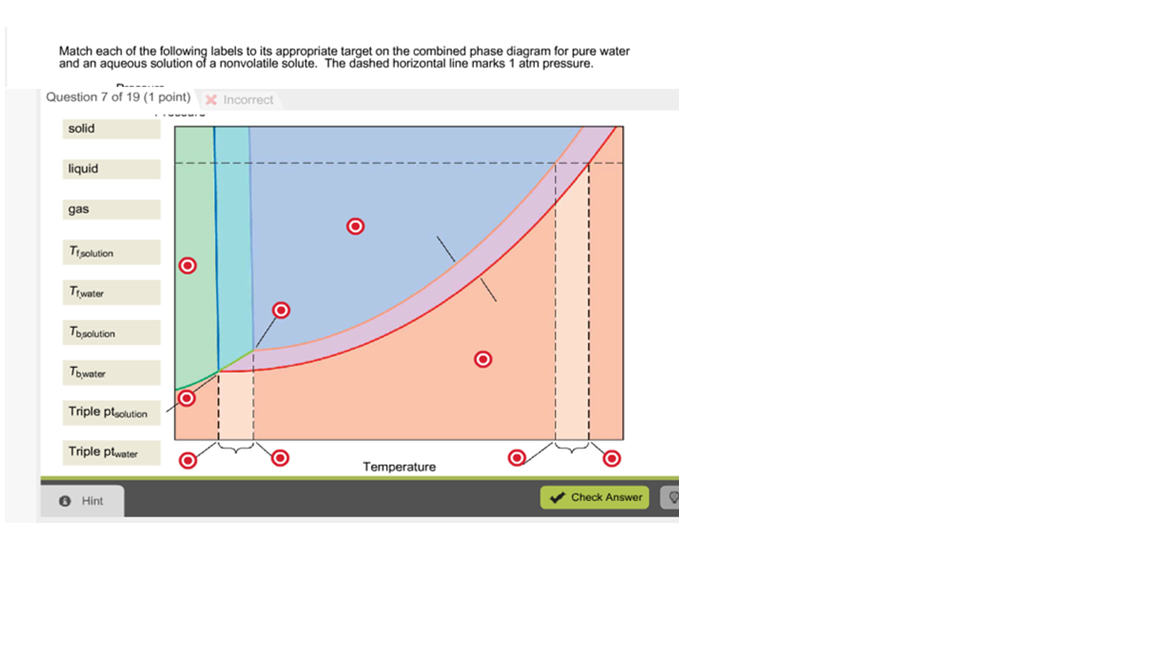
Thus the boiling point of a solution is always greater than that of the pure solvent. We can see why this must be true by comparing the phase diagram for an aqueous solution with the phase diagram for pure water (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). The vapor pressure of the solution is less than that of pure water at all temperatures.
For a pure DNA sample, the ratio of absorbance at 260 nm and absorbance at 280 nm (A260/A280) is 1.8. A ratio of 1.8 indicates the sample is contaminated with protein or an organic solvent such as phenol, often used during extraction processes.
The ink will be spotted onto strips of chromatography paper and put in a beaker containing a solution of alcohol and water. The paper (or more precisely the water that is adsorbed to the paper molecules) is the stationary phase and the alcohol and water solution is the solvent (mobile phase). The solvent will move by capillary action.
Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
The Role of Enthalpy in Solution Formation. Energy is required to overcome the intermolecular interactions in a solute, which can be supplied only by the new interactions that occur in the solution, when each solute particle is surrounded by particles of the solvent in a process called solvation (or hydration when the solvent is water). Thus all of the solute-solute interactions and many of ...
The maximum solid solubility of Gd in Mg is 23.5 wt.%. When added to Mg, Gd forms a Mg 5 Gd phase with a high melting point of 548 °C. Figure 2.1024 shows the as-cast microstructure (a) and the solution-treated micro-structure (b) of the Mg-14Gd binary alloy. Chapter 11, Reserve Question 92: Phase diagrams for precipitation hardening x Incorrect.
A multi-stage, counter-current liquid-liquid extractor is used to separate solute C from a binary mixture (F) of a and C using solvent B. Pure solvent b is recovered from the raffinate R by distillation, as shown in the schematic diagram below.
37 Label The Phase Diagram Of Pure Solvent And A Solution Written By Jon L Ruth Thursday, May 20, 2021 Add Comment Edit. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Phase Diagram Wikipedia. Lab 7 Determination Of The Molar Mass Of An Unknown Solid By Freezing Point Depression.
Learning Objectives. Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas: Sketch out a typical boiling point diagram for a binary liquid solution, and use this to show how a simple one-stage distillation works.; Explain the role of the lever rule in fractional distillation; Describe the purpose and function of a fractionating column; Sketch out boiling point diagrams for high ...
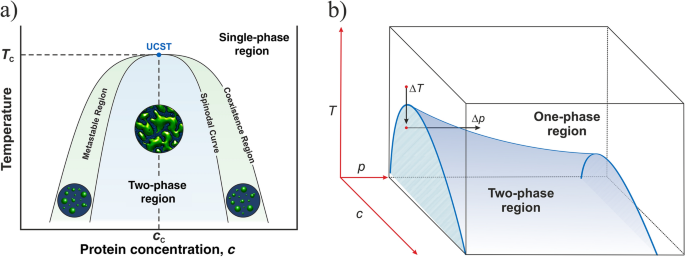
A typical phase diagram for such a mixture is shown in Figure 8.6. 2. Some combinations of substances show both an upper and lower critical temperature, forming two-phase liquid systems at temperatures between these two temperatures. An example of a combination of substances that demonstrate the behavior is nicotine and water.
Phase Diagram for an Aqueous Solution of a Nonelectrolyte. The colligative effects on vapor pressure, boiling point, and freezing point described in the previous section are conveniently summarized by comparing the phase diagrams for a pure liquid and a solution derived from that liquid.
The study had three phases: a 2.5 week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover phase in which each man received in-office injections of placebo or 2.5 mcg, 5 mcg, 7.5 mcg, or 10 mcg of CaverJect; a 2 week, open-label, in-office dose-titration phase to identify the optimum home-use dose (the latter dose was defined as a dose ...
synthesize a product of pure or of high load of VO 2(M1) nanoparticles opted for gas-phase or liquid-phase reactions[8] among which the hydrothermal path has been the most explored one because it permits a relatively good control of shape and crystallinity,[9-12] although it is not the most scalable, cheap and fast way of production.
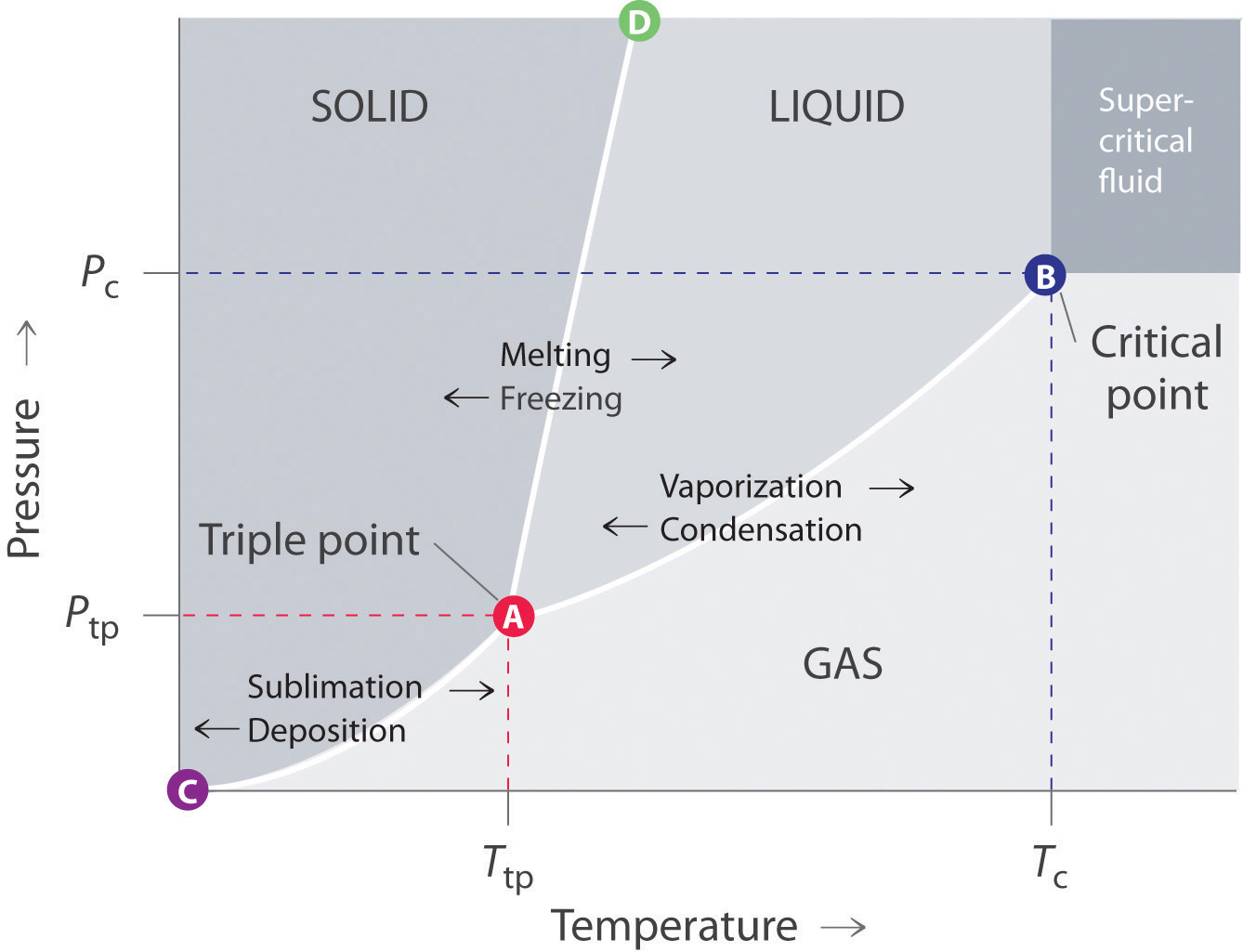
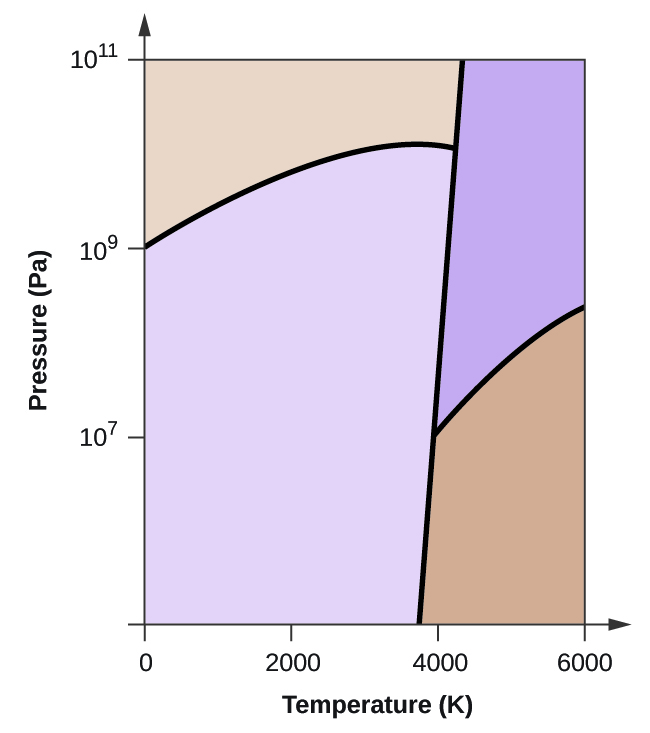
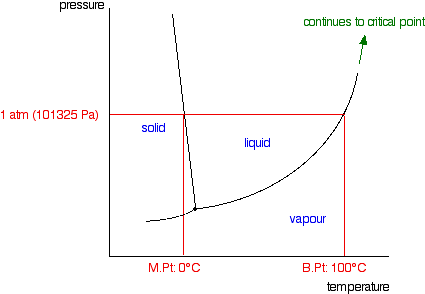
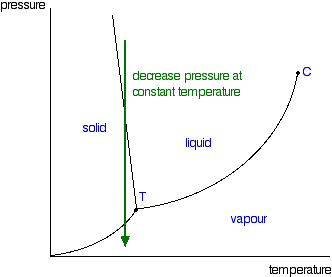
A typical phase diagram for a pure substance is shown in Figure 1. A graph is shown where the x-axis is labeled “Temperature” and the Figure 1.
A solution is a homogeneous type of mixture of two or more substances. A solution has two parts: a solute and a solvent. The solute is the substance that dissolves, and the solvent is the majority ...
An ideal single stage extraction process is used to treat 100 mol/s of an organic feed solution. The solute concentration in this solution is to be reduced from 0.5 mol% to 0.1 mol%. A pure solvent S is used. To reduce the solvent requirement by half for the same separation, (A) Add one more ideal co-current stage
Label the diagram. reflux. Draw a diagram to show how two methanol molecules interact with each other through hydrogen bonding in the liquid phase. ... Aldehydes can be oxidised by Tollens' reagent or by Fehling's solution. An unknown pure liquid A contains only a single alcohol. Outline a simple procedure to allow you to determine whether A is ...
Buffer solution is a mixture of salt and weak acid/weak base which can maintain the pH of the solution when small amount of strong acid or strong base is added to the solution. b) Explain how the pH of a buffer solution made from a weak acid and its conjugate base changes when; i. the acid dissociation constant, Ka, of the weak acid increases.
We can see why this must be true by comparing the phase diagram for an aqueous solution with the phase diagram for pure water (Figure (PageIndex{1})). The vapor pressure of the solution is less than that of pure water at all temperatures. Consequently, the liquid-vapor curve for the solution crosses the horizontal line corresponding to P = 1 ...














0 Response to "41 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution"
Post a Comment