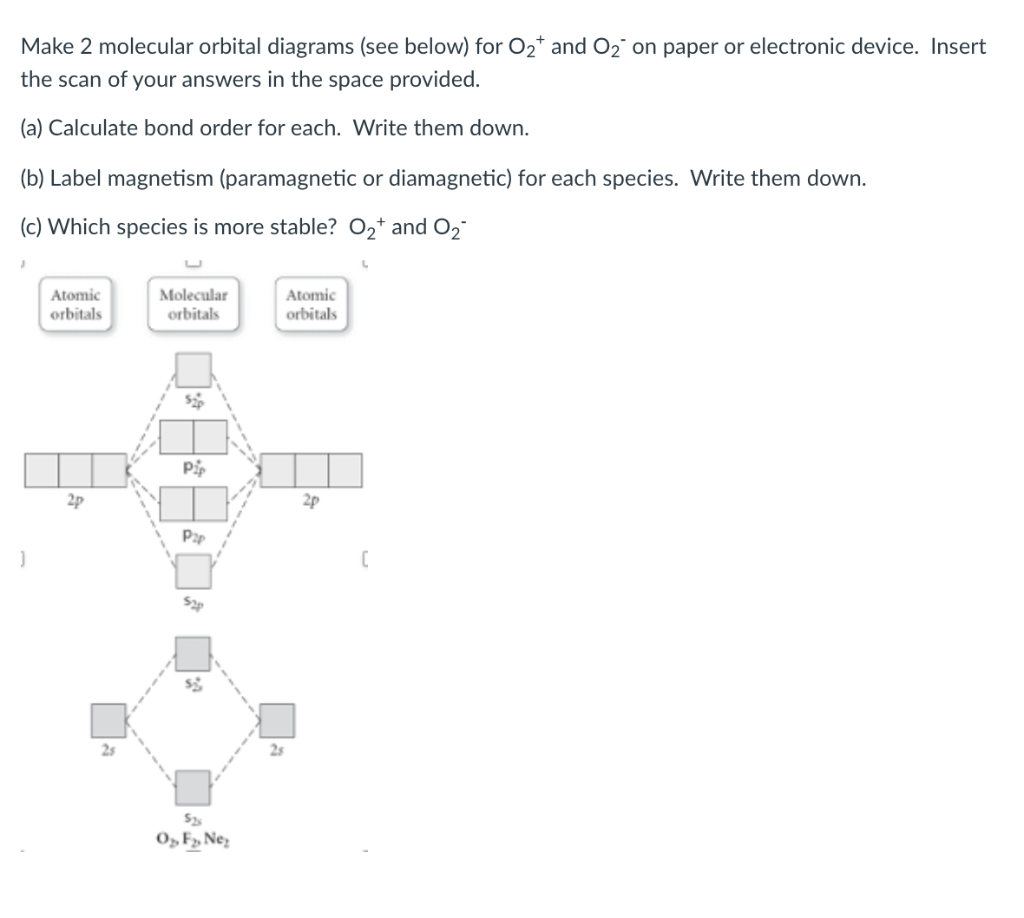
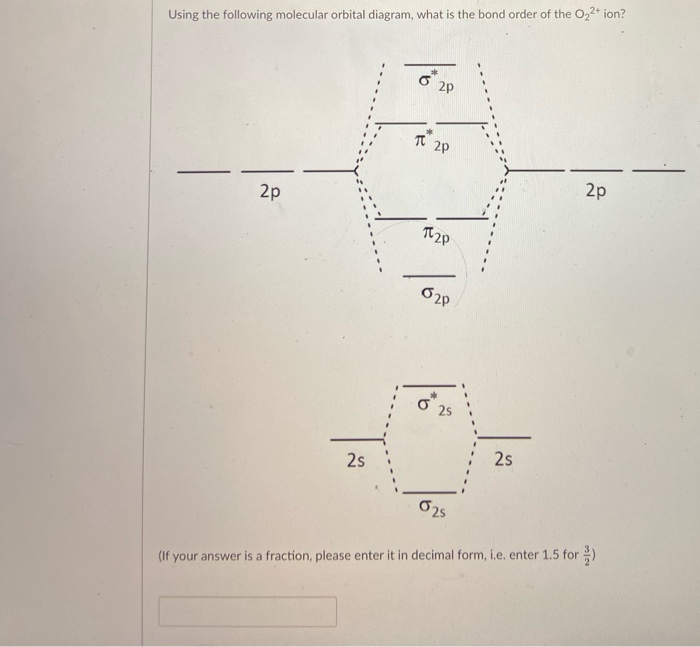
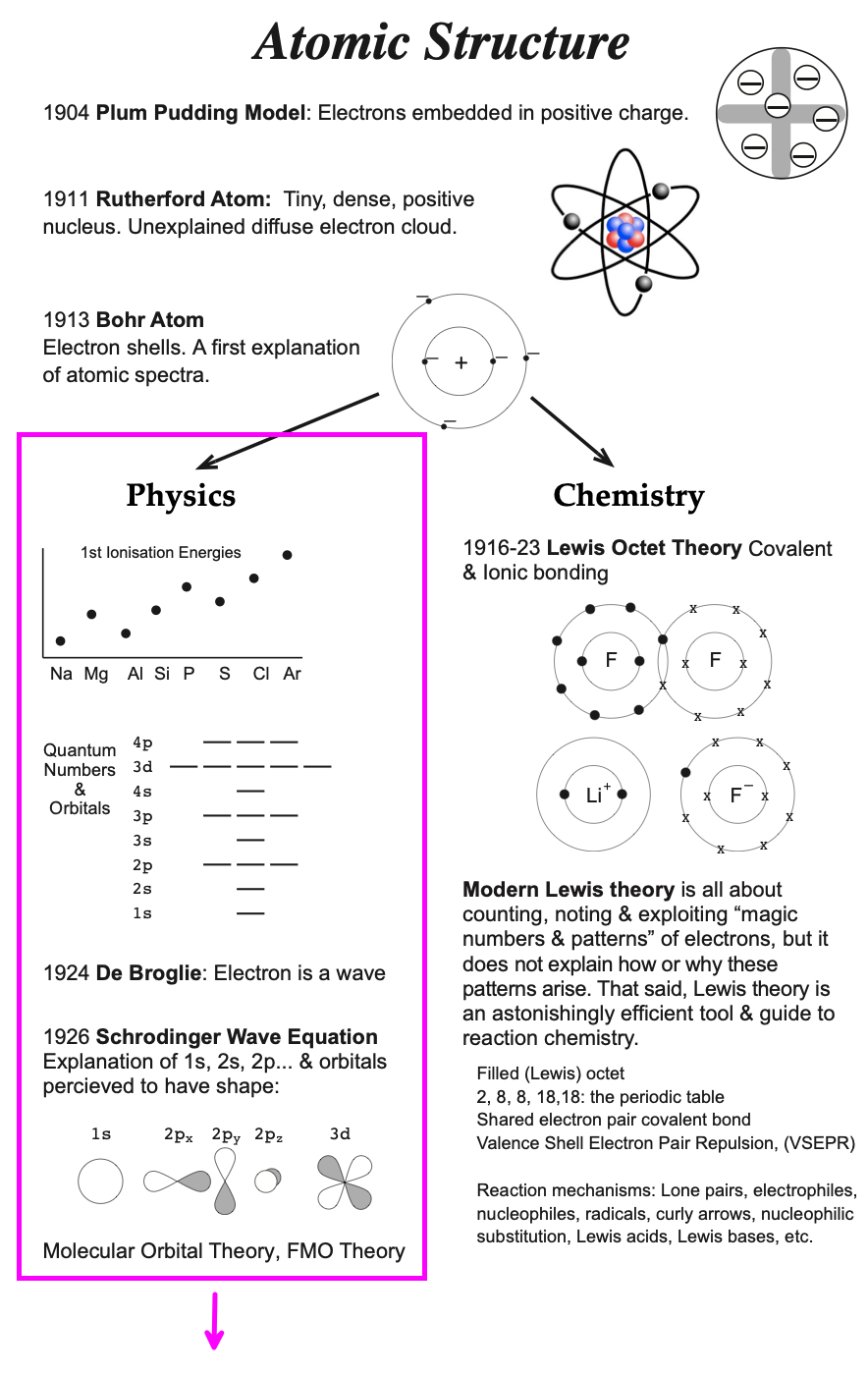
40 o2+ molecular orbital diagram
27 Mar 2017 — From that diagram, you can then easily fill out what the O2- and O2+ MO diagrams should be—and that is in the second photo I included. The O2- MO diagram will ...5 answers · 33 votes: Hello! I actually just covered this question in my gen chem class this week. I have attached ...What is the molecular orbital diagram for oxygen ...4 answers20 Aug 2015What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2 ...6 answers12 Mar 2017Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O₂ ...3 answers1 Aug 2019What's the MOT diagram of O2 +2 ion? - Quora3 answers25 Aug 2017More results from www.quora.com Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center. Atomic orbitals (AO) energy levels are shown for comparison. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
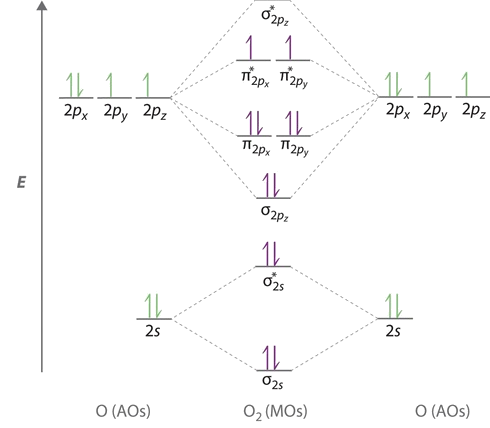
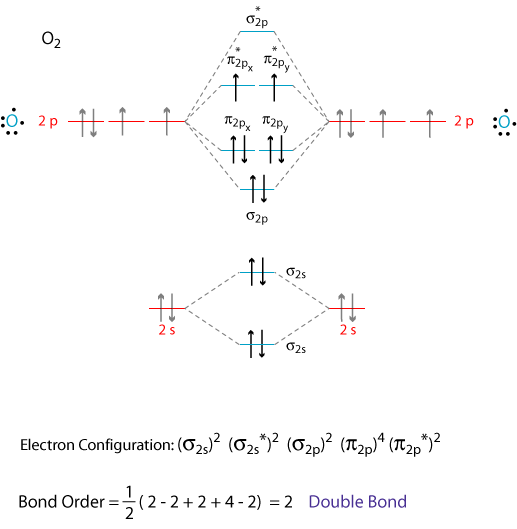
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. Bond Order. Bonding in Diatomic Molecules. We would write the following Lewis structure for O2: This electronic structure adheres to all the rules governing Lewis theory. There is an O=O double bond, and each oxygen atom has eight electrons around it.

O2+ molecular orbital diagram
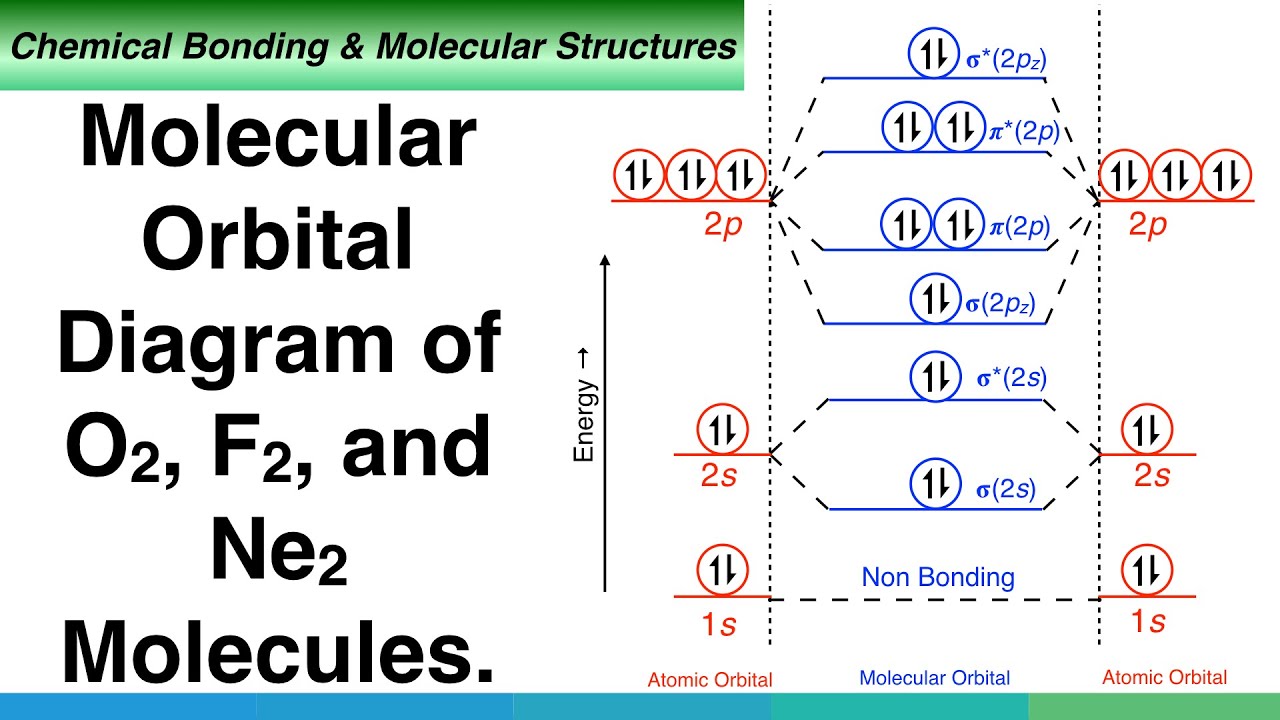
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Molecular orbital calculations indicate, however, that for O2, F2, and hypothetical Ne2 molecules, the 2p orbital is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation diagram) Feel free to ask clarification questions. I'll use your example of O2-. An orbital correlation attempts to show how the atomic orbitals belonging to...
O2+ molecular orbital diagram. Download scientific diagram | Schematic of the 'O2' molecular orbital diagram. The figure explains the nature of the oxygenated (O2)n− species that we are discussing within the text and to highlight the fact that we are dealing with holes (or electrons) having antibonding characters. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row Figure 8: Molecular orbital energy-level diagrams for (A) beryllium hydride, BeH2, with linear shape, and (B) water, H2O, with bent shape. The molecular orbitals are labeled to reflect the atomic orbitals from which they are composed as well as their symmetry properties.
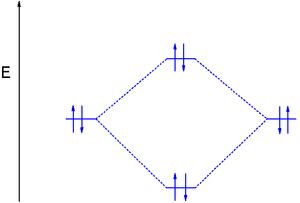
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and... There are two molecular orbitals for hydrogen, the lower energy orbital has its greater electron density between the two nuclei. If possible - the energy level diagram is included and clicking upon the relelvant level will generate the accompanying molecular orbital in the right-hand frame. molecular orbital diagram for O2. number of elections in the sigma*2p molecular orbital is. their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. which of the following statements about nitrogen oxide, NO, is FALSE.
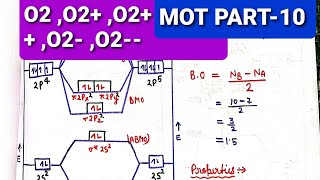
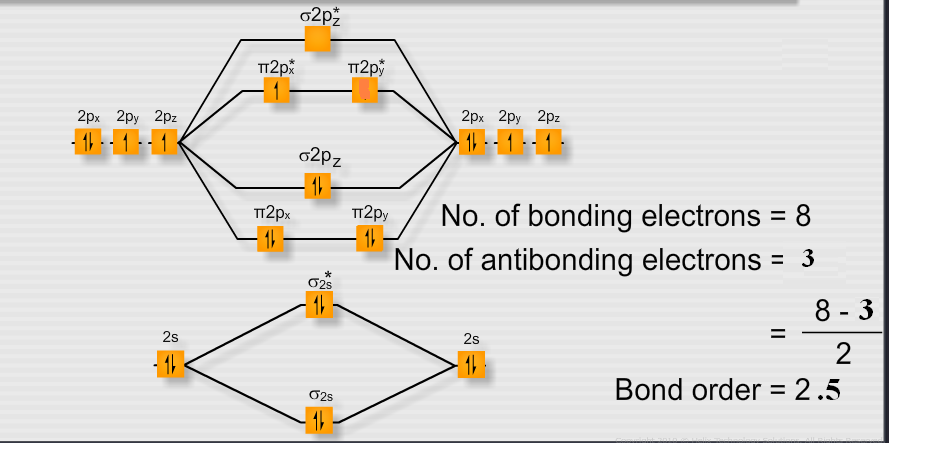
The molecular orbital energy level diagram of oxygen molecule is given as follows : Bond order 2Nb −Na =28−4 =2 Thus, oxygen molecule has two The energy of σ2pz molecular orbital is greater than and molecular orbitals in nitrogen molecule. Write the complete sequence of energy levels in... Answer to: Construct Molecular Orbital Diagram and determine unpaired electrons in O2- , O2+ , BN , NO- By signing up, you'll get thousands of...1 answer · Top answer: The MO diagram of O−2O2− is O−2O2− contains one unpaired electron The MO diagram of O+2O2+ is {eq}O_2^+ {/... Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams, Chemistry Viva, Chemistry Molecular Orbital diagram of O2- ion : This is superoxide ion. This would also have two molecular orbitals formed from the overlap of 1s orbitals on the atoms, giving a molecular orbital diagram of the same appearance It is now possible to obtain the ground state electronic configurations of the diatomic molecules of the second period from O2 to Ne2 by inserting...
Transcribed image text : Complete this valence molecular-orbital diagram for oxygen, O2. Click the blue boxes to add electrons as needed.
Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure. Molecular Orbital theory starts by assuming that the three atomic p orbitals on the O atoms overlap to form three molecular π orbitals that extend over the whole How do you draw an atomic level diagram for 2S+3O2=2SO3 ?
3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. Bond order=2.5. The presence of unpaired electron makes the molecule paramagnetic. 16) O2- ion.
MOLECULAR ORBITAL and valence bond calculations of the w-electron energies of unsaturated molecules custom-arily start with models in which lecular orbital representations. . Knowledge of how to s e t up a n atomic orbital model for an organic molecule i s c r u c i a l to the LCAO...
Explanation: Bond order. for O2-. 6 electrons in bonding and 3 in anti bonding orbital. positive bond order means the molecule is stable.
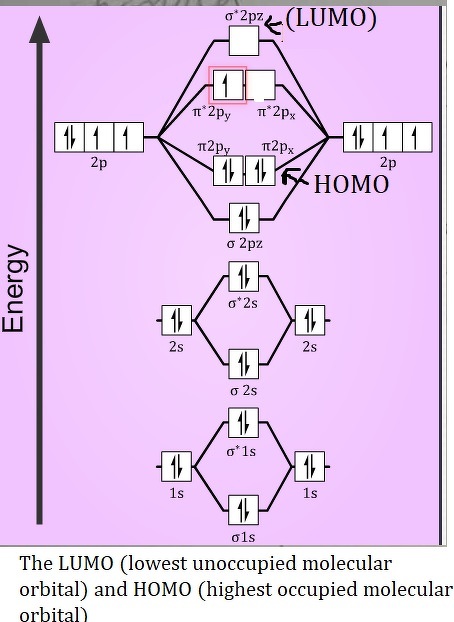
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
• Bonding - Review VSEPR and Hybridisation - Linear combination of molecular orbitals (LCAO), bonding / antibonding - Labelling of molecular orbitals (MOs) (σ, π and g, u) - Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams - mixing of different AO's - More complex molecules (CO, H2O ….)
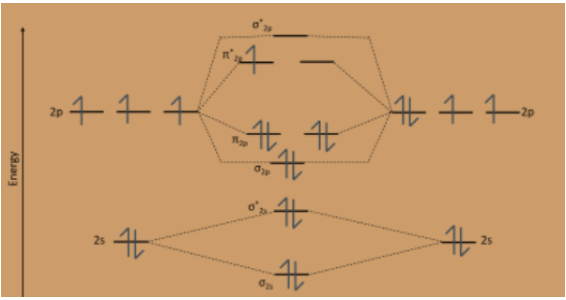
The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
Figure %: Orbital correlation diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules other than B2, C2, and N2. To draw the correlation diagrams for heteronuclear diatomic molecules, we face a new problem: where do we place the atomic orbitals on an atom relative to atomic orbitals on other atoms?
Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8.34).
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. This kind of mixing of orbitals or symmetry interaction is not applicable for O2 and F2 molecule formation because of larger energy gap between 2s and 2p orbitals for these atoms.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s...
Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation diagram) Feel free to ask clarification questions. I'll use your example of O2-. An orbital correlation attempts to show how the atomic orbitals belonging to...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Molecular orbital calculations indicate, however, that for O2, F2, and hypothetical Ne2 molecules, the 2p orbital is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals...


















0 Response to "40 o2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment