43 rain shadow effect diagram
Rain shadow effect diagram What causes a rain shadow? When the wind blows up a mountain, the air moves into an area with lower air pressure, making the rising air expand and cool. When air cools, its capacity to hold moisture in the form of water vapor decreases. Water vapor is the gaseous form of water. 17. $4.00. PPTX. Microsoft OneDrive. This PowerPoint explains the rain shadow effect where moist air gets blocked by mountains. Includes photos and diagrams of how rain shadow affects the windward and leeward side of a mountain range, examples of rain shadow around the world, and a five question review quiz at the end.
rain shadow effect diagram how does topography affect climate. See more articles in category: FAQ. admin Send an email 4 seconds ago. 0 7 minutes read. admin. Website; what is the definition of bluff. Related Articles. what is the definition of bluff. 1 min ago. what would happen if there was no photosynthesis?
Rain shadow effect diagram
5 What is the shadow effect definition? 6 What are the 3 essential items needed to see a rain shadow effect? 7 What is a rain shadow and what creates it? 8 What is the dry side of the mountain called? 9 Which area will be the driest as result of the rain shadow effect? 10 What is meant by a rain shadow area give two examples? 11 What is the ... A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope ... Sep 08, 2021 · The dry side is referred to as a rain shadow. Learn the definition of the Rain Shadow Effect, and read an explanation for this effect, including how proximity to a large body of water, wind ...
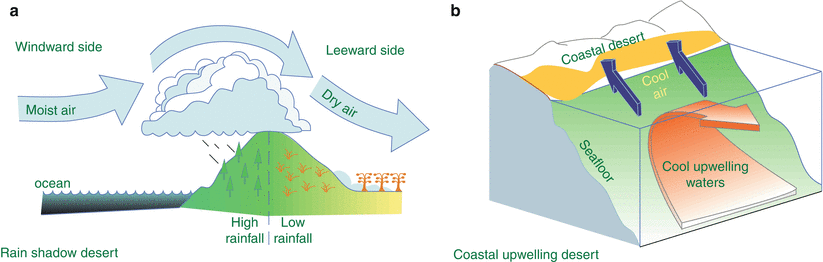
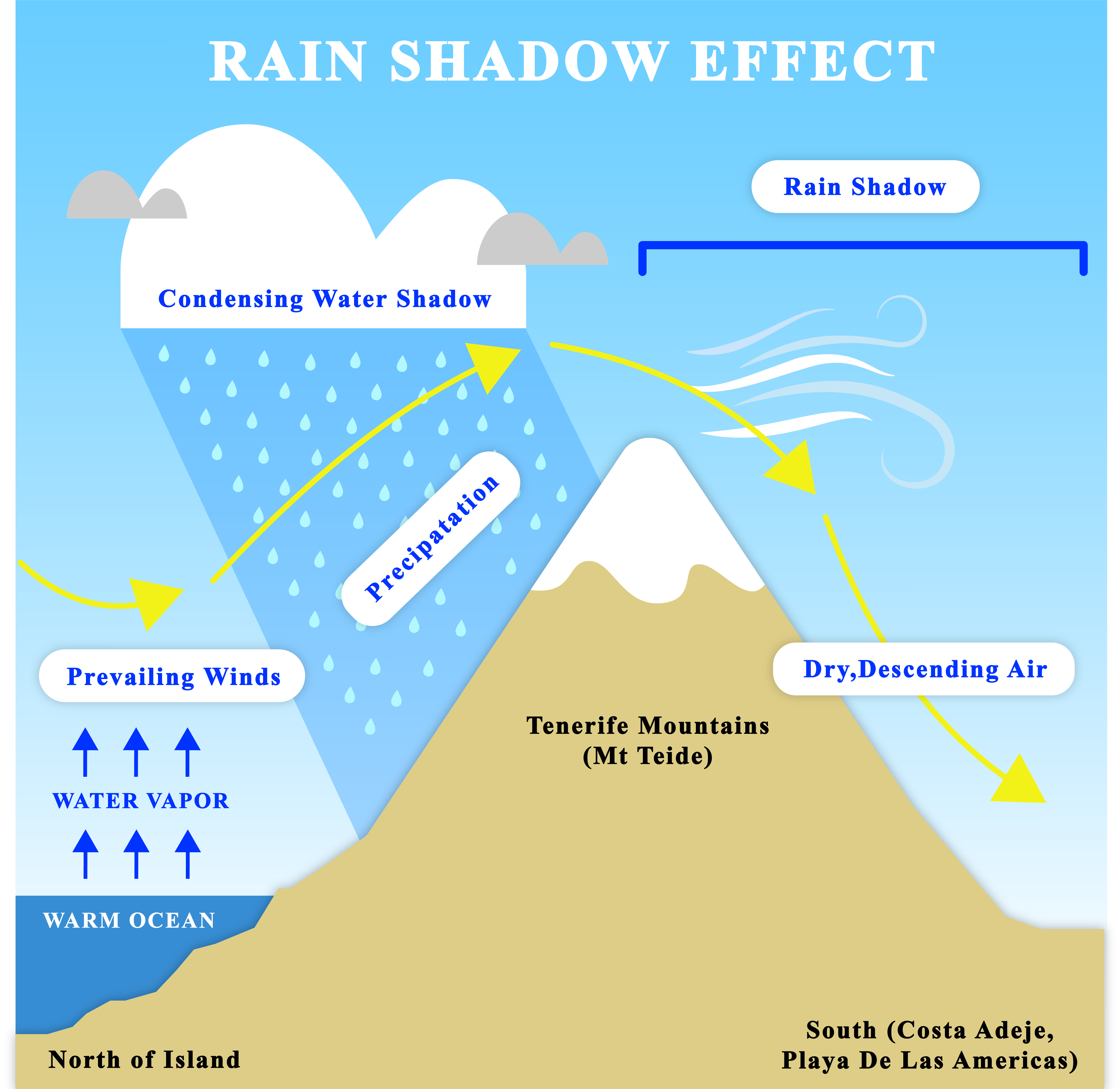
Rain shadow effect diagram. All of these prevailing winds help generate the rain shadow effect that is commonly found around the world. 3. Examples of Rain Shadow Areas . In Asia, the Himalaya mountain range acts as the catalyst for the rain shadow effect over the Tibetan Plateau, Central Asia, and the Gobi Desert. The Japanese Alps create that same phenomenon over the ... rain shadow effect. Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, ... the rain shadow effect of mountains, global wind and ocean current patterns, cloud cover, and ... be in a rain shadow, with drastically decreased precipitation. For more information, visit these links: ... Use the Venn diagram (slide 6) to compare and contrast the two. Ideally this should be 16 Jul 2021 — As shown by the diagram to the right, the incoming warm and moist air is drawn by the prevailing winds towards the top of the mountains. As it ...
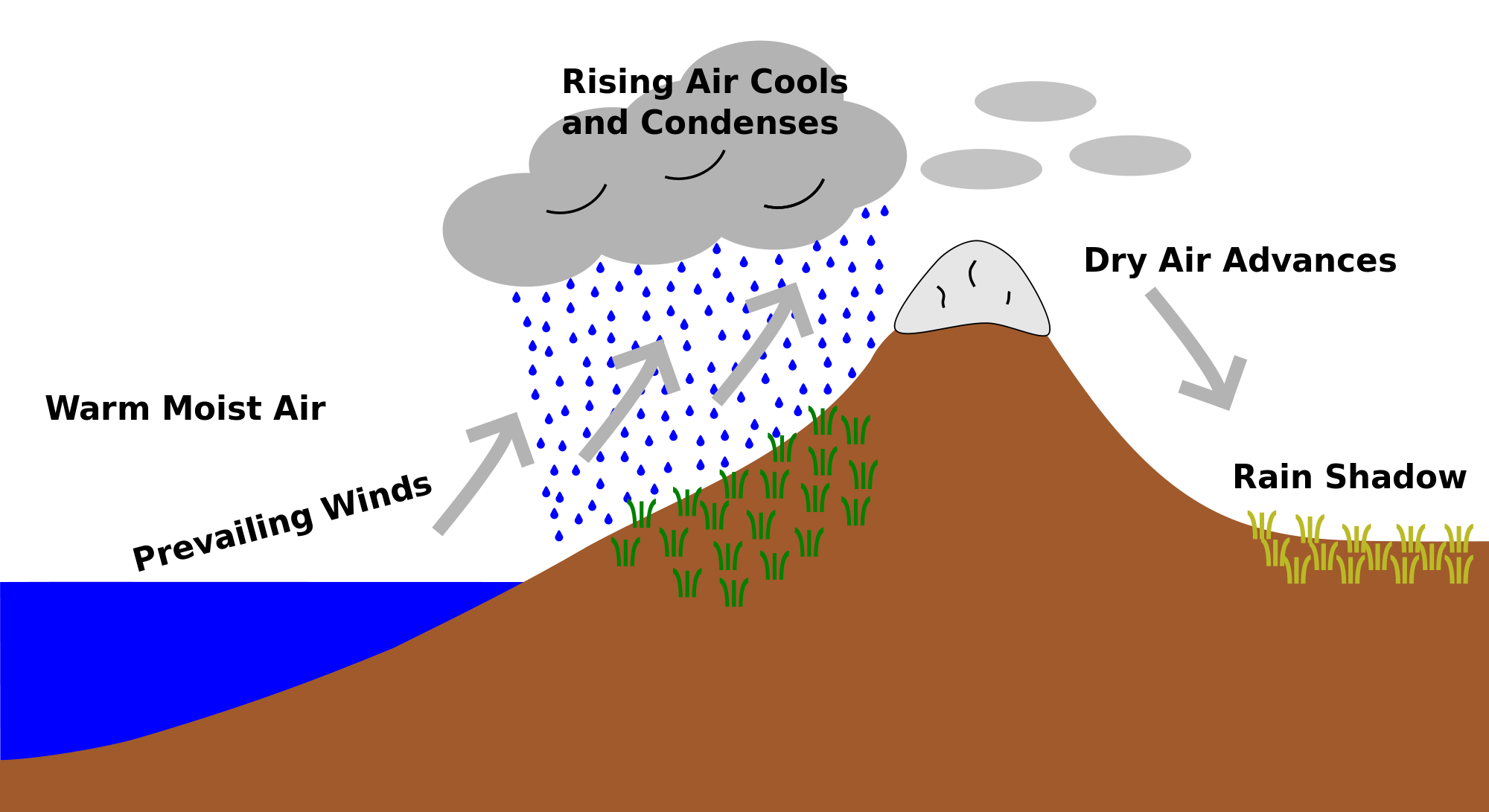
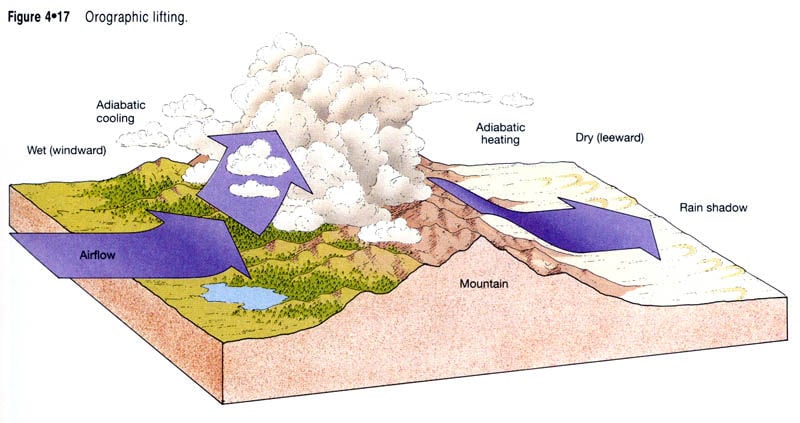
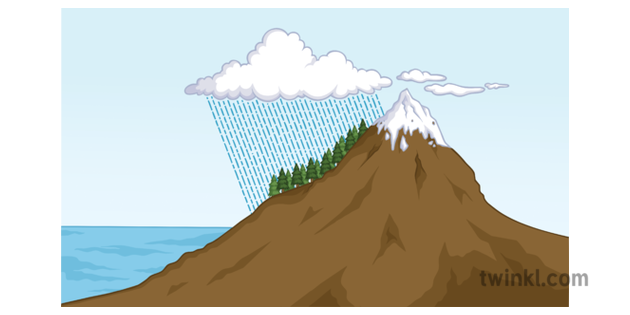
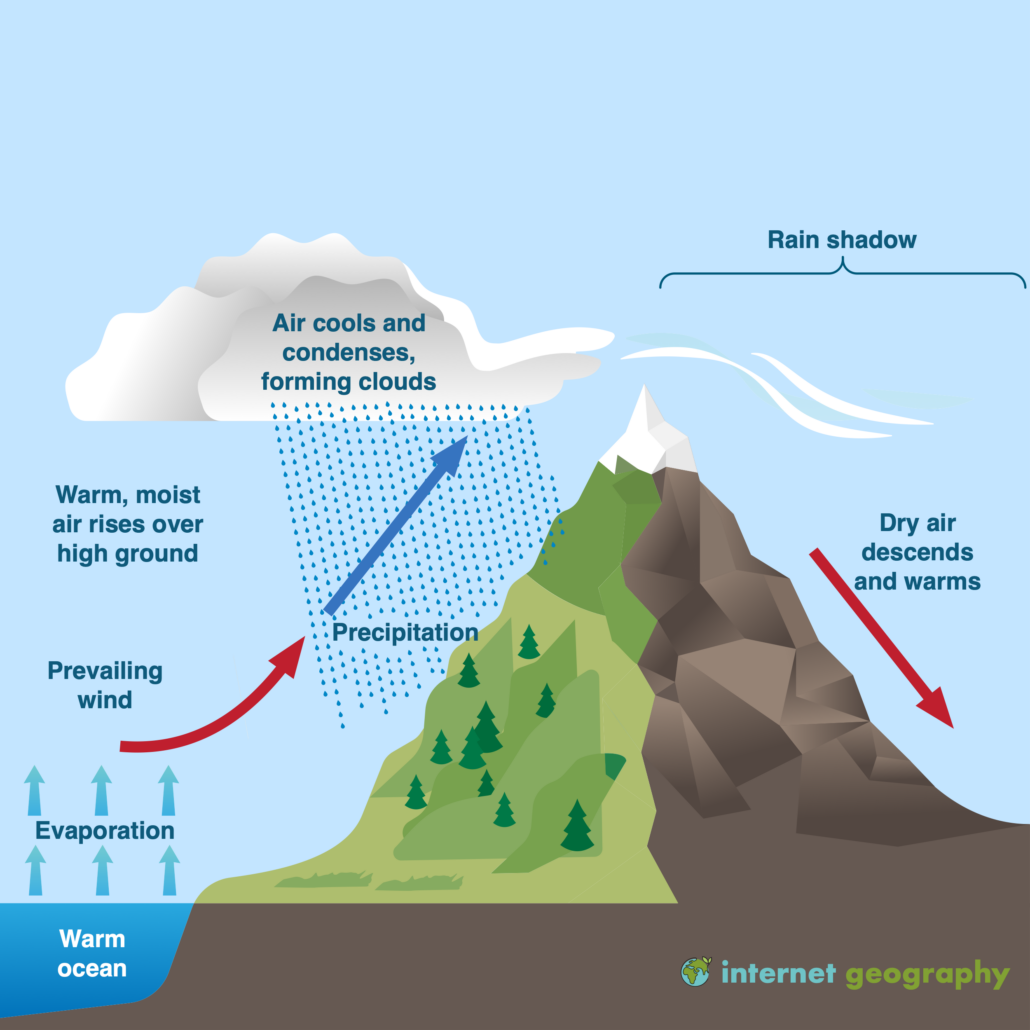
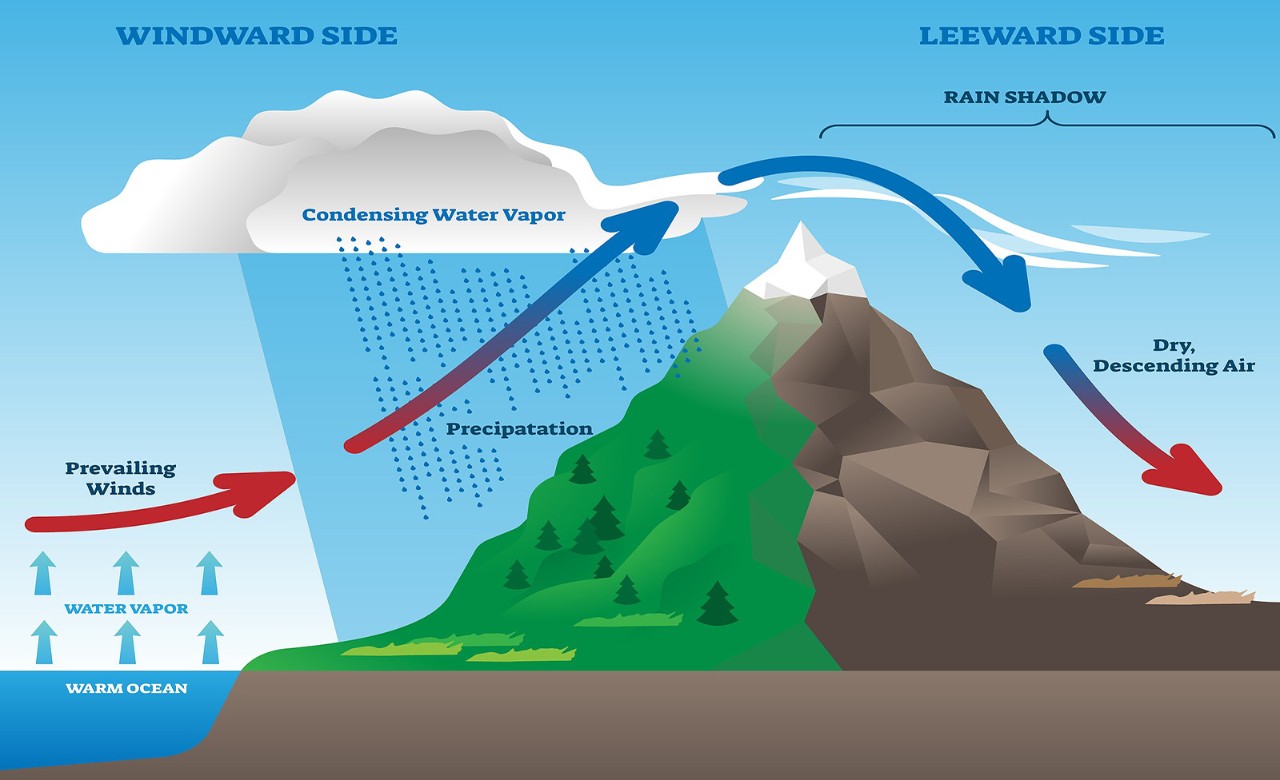
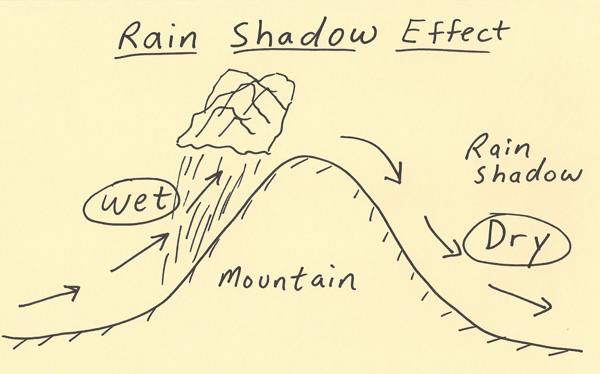
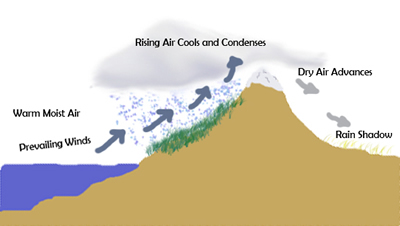
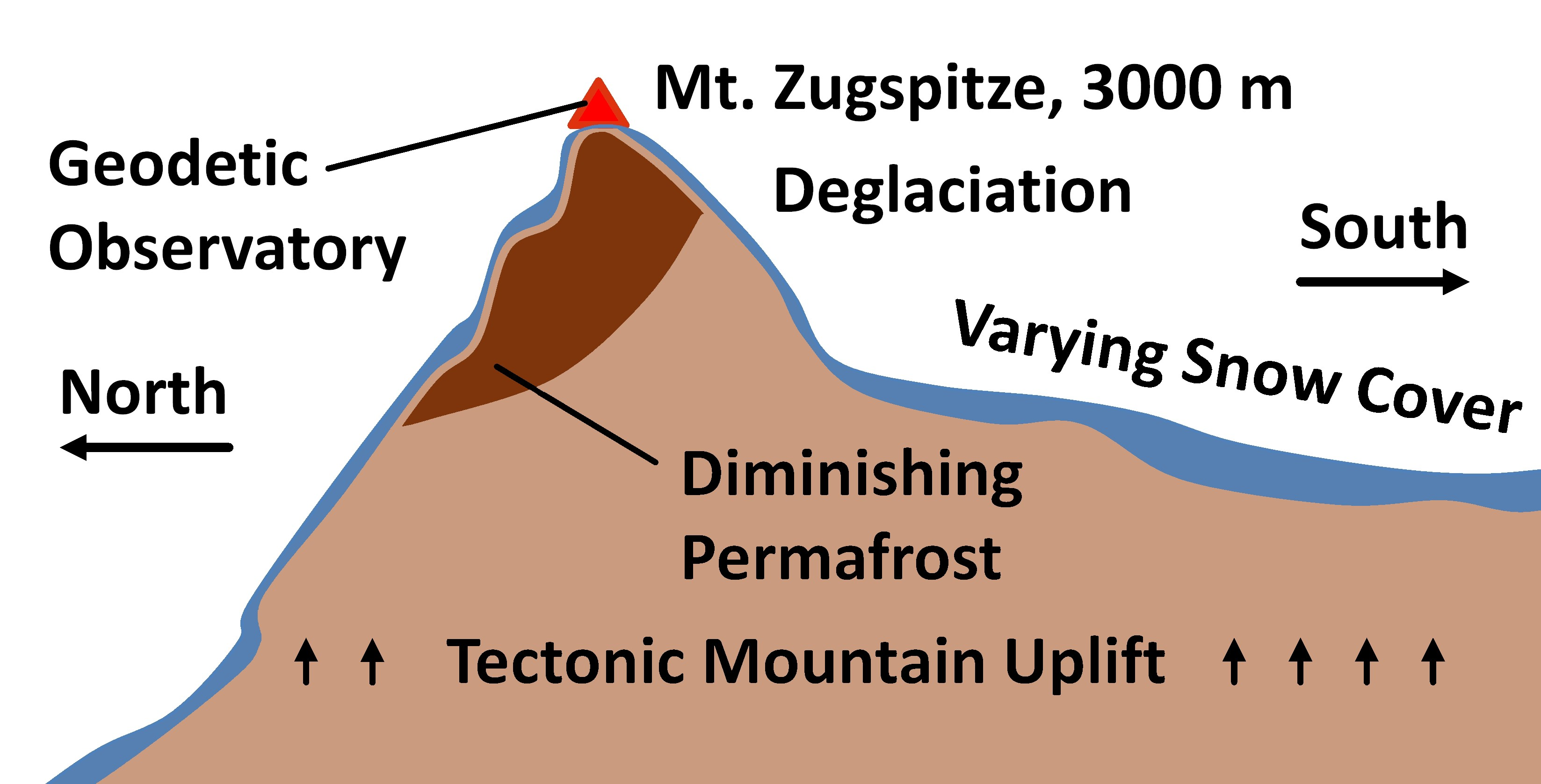
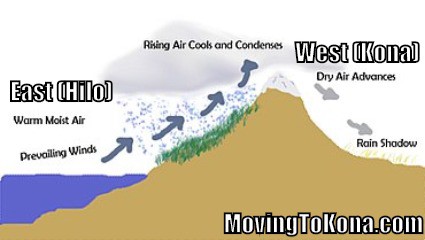
As shown by the diagram to the right, the incoming warm and moist air is drawn by the prevailing winds towards the top of the mountains. As it does so, it cools, condenses and rain falls before it crosses the top. The air, without much moisture left, goes on over the mountains creating a dry side called the "rain shadow". Categories: Weather stubs Rain Shadow Diagram. While this effect can occur near any mountain range, one of the more prominent areas where it can be observed is in the Sierra Nevadas. Many times, these mountains can be snowcapped while just to the east Death Valley can be hot and dry. Below is a look at snow in the mountains from satellite. Referring to the diagram you have created, write a paragraph explaining the rain shadow effect. Support your explanation with evidence from the videos, data, and other media resources you have observed. rain shadow effect diagram rain shadow effect definition how is a rain shadow formed what landforms must be present to have a rain shadow? what is the rain-shadow effect quizlet give an example and state the mountains which are responsible for the rain shadow area rain shadow in a sentence.
the rain shadow effect described in the introduction to this unit. 1. Enlarge the rain shadow diagram on the activity page on a piece of poster board. Cut it into pieces to create a puzzle. If you have a large group, you may want to make more than one puzzle. Laminating or covering the pieces with clear contact paper will extend their life. 2. Earth Science 4: The Rain Shadow Effect Please use the following to prepare for the next SfS lesson. Description: This lesson provides an introduction to the rain shadow phenomenon. Students read a story that describes a rain shadow and use key terms to build a model of the described environment. They next ask questions about the rain shadow Moist warm air blows on shore from ocean Rising air (step 2) Air forced up, cools and condenses causing precipitation to form Precipitation (step 3) Rain, snow, sleet, or hail Sinking air (step 4) Cool dry air descends, warms and promotes evaporation ( this side is known as the rainshadow side) Windward side (non rain shadow side) Rain Shadow Effect As a parcel of air rises up the windward side of a mountain range, it has its moisture squeezed out. Thus, when the air begins to descend the leeward side of the mountain, it is dry. As the cool air descends, it warms and expands, reducing its possibility of precipitation.
A rain shadow is an area of dry land that results when precipitation is intercepted from a nearby formation. Most commonly, rain shadows are created when water rising from a large body of water is ...
draw a rain shadow diagram answers a rain shadow is when clouds e up to a mountain and say hi but the mountains dont let them cross if they have rain in them rain shadow diagram wiring diagram fuse box rain shadow diagram furthermore pg244 to her with revised personal history further moreover works in addition fascia board also rear View r Image
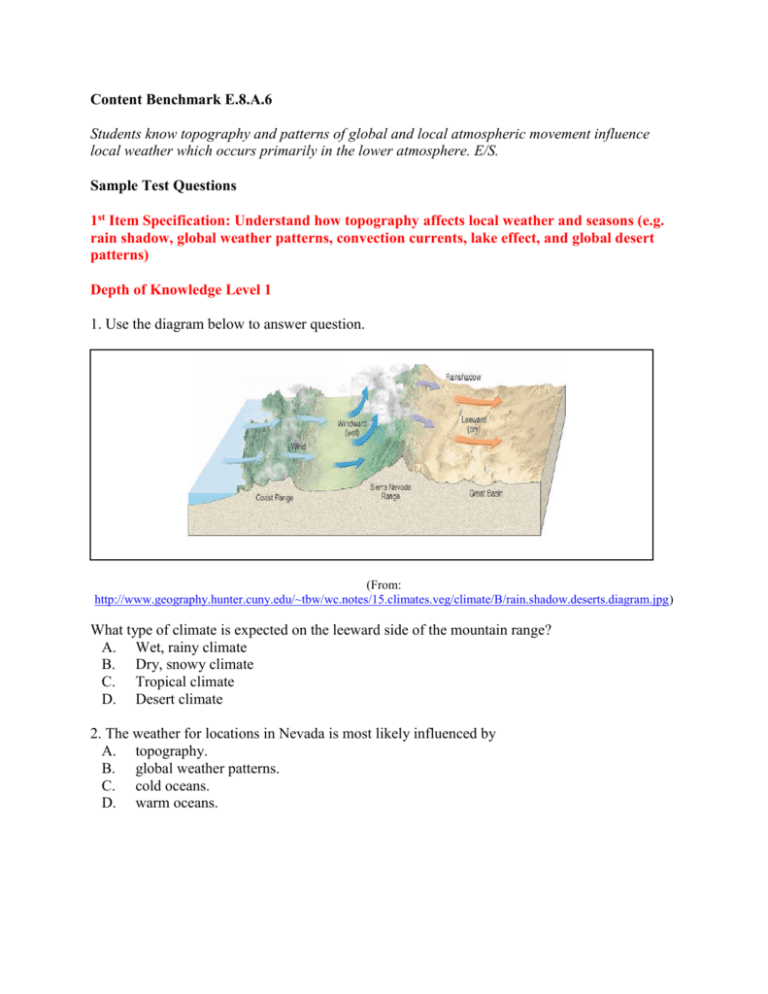
Rain Shadow Diagram In the diagram below, label the following: • Pacific Ocean • Spring Mountains/Mt. Charleston • Mojave Desert/Las Vegas Valley • Moist air • Dry air • Total Precipitation (from data analysis) for Mt. Charleston • Total Precipitation (from data analysis) for Las Vegas Region direction of wind
The effect itself • Orographic lifting or the rain shadow effect is a fascinating process that occurs naturally. • It keeps the windward side of mountain ranges lush with lots of vegetation and moisture, but the leeward sides are arid deserts.
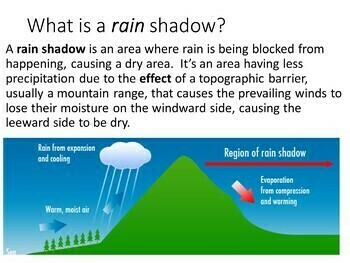
A rain shadow is a patch of land that has been forced to become a desert because mountain ranges blocked all plant-growing, rainy weather. On one side of the mountain, wet weather systems drop rain and snow. On the other side of the mountain—the rain shadow side—all that precipitation is blocked. In a rain shadow, it's warm and dry.
•The rain shadow effect occurs when tall structures, like mountain ranges, interrupt wind flow. The rain shadow effect creates a wet, tropical climate on the side facing the wind and a dry, desert climate on the leeward side of the mountain. •The air above cities is often warmer than the surrounding area, called an urban heat island effect.
The animation shows the "rain shadow" effect that results in desert regions behind large mountain ranges. An inset graph at bottom right illustrates combinations of temperature (x-axis) and moisture content (y-axis) in grams per cubic meter of the air mass as it passes over various topographic features on the land surface.
The rain shadow effect can also be seen outside the typical Southern California rainy season. Between July and early September the summer monsoon rages over the desert southwest. The monsoon is a seasonal reversal of the winds. Instead of the westerly flow we experiences most of the year, a southerly flow develops.
The "epicenter" of the rain shadow is a matter of debate, but it is likely somewhere to the north east of the town of Sequim, and only receives about 13" of rain per year, about the same as relatively dry cities like Los Angeles, or Salt Lake City. Our best estimate of the rain shadow area is depicted by the map below.
The rain shadow effect causes City B to be drier because the mountain blocks precipitation from reaching the city.
As air rises up the side of the mountain near City B, the temperature and the relative humidity increase, causing increased precipitation on the other side of the mountain over City A.
Rain Shadow – The region on the lee-side of a mountain.This is where the precipitation is far less than on the windward side. Typically a dry climate. Generic view of Oregon from the Pacific ...
Sep 08, 2021 · The dry side is referred to as a rain shadow. Learn the definition of the Rain Shadow Effect, and read an explanation for this effect, including how proximity to a large body of water, wind ...
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope ...
5 What is the shadow effect definition? 6 What are the 3 essential items needed to see a rain shadow effect? 7 What is a rain shadow and what creates it? 8 What is the dry side of the mountain called? 9 Which area will be the driest as result of the rain shadow effect? 10 What is meant by a rain shadow area give two examples? 11 What is the ...





















0 Response to "43 rain shadow effect diagram"
Post a Comment